Angelol ACAS# 19625-17-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 19625-17-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 21669994 | Appearance | Powder |
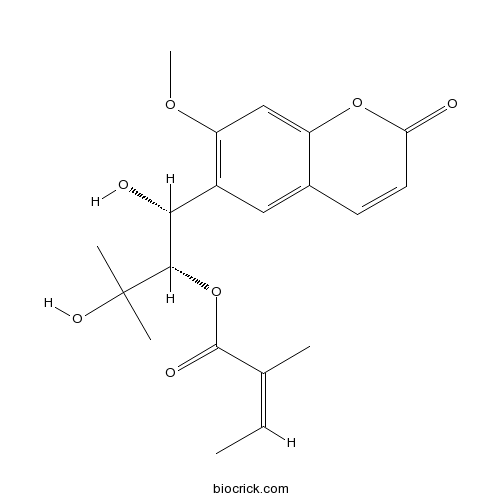
| Formula | C20H24O7 | M.Wt | 376.4 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(1R,2S)-1,3-dihydroxy-1-(7-methoxy-2-oxochromen-6-yl)-3-methylbutan-2-yl] (Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CC=C(C)C(=O)OC(C(C1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C=CC(=O)O2)OC)O)C(C)(C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GFMYIOGFYYHKLA-PWZGUCPHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H24O7/c1-6-11(2)19(23)27-18(20(3,4)24)17(22)13-9-12-7-8-16(21)26-14(12)10-15(13)25-5/h6-10,17-18,22,24H,1-5H3/b11-6-/t17-,18+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Angelol A and angelol B are passive diffusion as the dominating process in Caco-2 cell monolayer model. |
| In vitro | Absorption and transport of 6 coumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata in human Caco-2 cell monolayer model.[Pubmed: 18405608]Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008 Apr;6(4):392-8.To study the absorption and transepithelial transport of six coumarins (umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, columbianetin acetate, Angelol A and angelol B, isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata) in the human Caco-2 cell monolayer model.
|
| Structure Identification | Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2014, 45(13):1820-1828.New natural product from lipophilic parts in roots of Angelica dahurica.[Reference: WebLink]
To study the chemical constituents of lipophilic parts from the roots of Angelica dahurica. |

Angelol A Dilution Calculator

Angelol A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6567 mL | 13.2837 mL | 26.5675 mL | 53.135 mL | 66.4187 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5313 mL | 2.6567 mL | 5.3135 mL | 10.627 mL | 13.2837 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2657 mL | 1.3284 mL | 2.6567 mL | 5.3135 mL | 6.6419 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0531 mL | 0.2657 mL | 0.5313 mL | 1.0627 mL | 1.3284 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0266 mL | 0.1328 mL | 0.2657 mL | 0.5313 mL | 0.6642 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 17 alpha-propionate
Catalog No.:BCC1296
CAS No.:19608-29-8
- 25S-Inokosterone
Catalog No.:BCN3873
CAS No.:19595-18-7
- (R)-Nepicastat HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4315
CAS No.:195881-94-8
- HTMT dimaleate
Catalog No.:BCC6736
CAS No.:195867-54-0
- 2,6,16-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1509
CAS No.:195735-16-1
- Atrasentan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1380
CAS No.:195733-43-8
- (+-)-Byakangelicin
Catalog No.:BCN5000
CAS No.:19573-01-4
- 2,16,19-Kauranetriol 2-O-beta-D-allopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1510
CAS No.:195723-38-7
- Methyl 4-O-feruloylquinate
Catalog No.:BCC9041
CAS No.:195723-10-5
- Piromidic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC3840
CAS No.:19562-30-2
- AP1903
Catalog No.:BCC5361
CAS No.:195514-63-7
- Chiirirhamnin
Catalog No.:BCN3179
CAS No.:195450-50-1
- Indole-3-acrylic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN1190
CAS No.:19626-92-7
- 4-Methoxycinnamaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN2700
CAS No.:1963-36-6
- Bay 11-7085
Catalog No.:BCC5105
CAS No.:196309-76-9
- Axillarine
Catalog No.:BCN2059
CAS No.:19637-66-2
- Prosaptide TX14(A)
Catalog No.:BCC8020
CAS No.:196391-82-9
- Siegesmethyethericacid
Catalog No.:BCC9248
CAS No.:196399-16-3
- (4S,5R)-3-tert-butoxycarbony-2-(4-anisy)-4-phenyl-5-oxazolidinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8365
CAS No.:196404-55-4
- (RS)-3,5-DHPG
Catalog No.:BCC6613
CAS No.:19641-83-9
- 2S-Amino-3R-octadecanol
Catalog No.:BCN1775
CAS No.:196497-48-0
- 4-Acetyl Ramelteon
Catalog No.:BCC1107
CAS No.:1346598-94-4
- BIBX 1382
Catalog No.:BCC1418
CAS No.:196612-93-8
- Oseltamivir
Catalog No.:BCC1825
CAS No.:196618-13-0
[Absorption and transport of 6 coumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata in human Caco-2 cell monolayer model].[Pubmed:18405608]
Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008 Apr;6(4):392-8.
OBJECTIVE: To study the absorption and transepithelial transport of six coumarins (umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, columbianetin acetate, angelol-A and angelol-B, isolated from the roots of Angelica pubescens f. biserrata) in the human Caco-2 cell monolayer model. METHODS: The in vitro cultured human colon carcinoma cell line, Caco-2 cell monolayer model, was applied to study the absorption and transport of the six coumarins from apical (AP) to basolateral (BL) side and from BL to AP side. The six coumarins were measured by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with ultraviolet absorption detector. Transport parameters and apparent permeability coefficients (P(app)) were calculated and compared with those of propranolol as a control substance of high permeability and atenolol as a control substance of poor permeability. The transport mechanism of angelol-B was assayed by using iodoacetamide as a reference standard to inhibit ATP-dependent transport and MK571 as a well-known inhibitor of MRP2. RESULTS: The absorption and transport of six coumarins were passive diffusion as the dominating process. The P(app) values of umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, columbianetin acetate, angelol-A and angelol-B from AP to BL side were (2.679+/-0.263) x 10(-5), (1.306+/-0.324) x 10(-5), (0.595+/-0.086) x 10(-6), (2.930+/-0.410) x 10(-6), (1.532+/-0.444) x 10(-5) and (1.413+/-0.243) x 10(-5) cm/s, and from BL to AP side were (3.381+/-0.410) x 10(-5), (0.898+/-0.134) x 10(-5), (0.510+/-0.183) x 10(-6), (0.222+/-0.025) x 10(-6), (1.203+/-0.280) x 10(-5) and (0.754+/-0.092) x 10(-5) cm/s, respectively. In this assay, the P(app) value of propranolol was 2.18 x 10(-5) cm/s and the P(app) value of atenolol was 2.77 x 10(-7) cm/s. Among the 6 coumarins, the P(app) values of umbelliferone, osthole, angelol-A and angelol-B from AP to BL side were identical with that of propranolol, and columbianadin and columbianetin acetate lied between propranolol and atenolol. When replaced the HBSS with EBSS, and iodoacetamide or MK-591 were used in the experiment, the P(app) of angelol-B had no statistical difference as compared with the control group. In the mean total recoveries, umbelliferone was (83.31+/-3.52)%, angelol-A was (77.39+/-7.38)%, osthole, columbianadin and angelol-B were between 50% to 65%, and columbianetin acetate was lower than 10%. The accumulation rates of osthole and columbianadin in the Caco-2 cells were (36.15+/-5.87)% and (53.90+/-4.39)%, respectively. CONCLUSION: The absorption and transport of umbelliferone, osthole, columbianadin, columbianetin acetate, angelol-A and angelol-B are passive diffusion as the dominating process in Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Umbelliferone, osthole, angelol-A and angelol-B are estimated to be highly absorbed compounds, and columbianadin and columbianetin acetate are estimated to be moderately absorbed compounds. In the Caco-2 cells, osthol and columbianadin appear to accumulate, and columbianetin acetate may be metabolized. The absorption and transport of angelol-B are not influenced by the change of pH and the presence of iodoacetamide or MK571.


