DR 2313PARP inhibitor CAS# 284028-90-6 |
- MK-4827
Catalog No.:BCC1761
CAS No.:1038915-60-4
- BMN-673 8R,9S
Catalog No.:BCC1422
CAS No.:1207456-00-5
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 284028-90-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10219702 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H10N2OS | M.Wt | 182.24 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 40 mM in water | ||
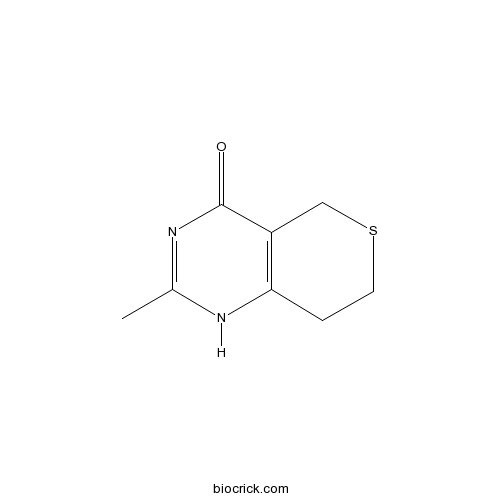
| Chemical Name | 2-methyl-1,5,7,8-tetrahydrothiopyrano[4,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1=NC(=O)C2=C(N1)CCSC2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HRYKZAKEAVZGJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H10N2OS/c1-5-9-7-2-3-12-4-6(7)8(11)10-5/h2-4H2,1H3,(H,9,10,11) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Competitive inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) (IC50 values are 0.20 and 0.24 μM for PARP-1 and PARP-2 respectively). Neuroprotective; reduces neuronal cell death in models of cerebral ischemia in vivo and in vitro. Brain penetrant. |

DR 2313 Dilution Calculator

DR 2313 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.4873 mL | 27.4363 mL | 54.8727 mL | 109.7454 mL | 137.1817 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0975 mL | 5.4873 mL | 10.9745 mL | 21.9491 mL | 27.4363 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5487 mL | 2.7436 mL | 5.4873 mL | 10.9745 mL | 13.7182 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1097 mL | 0.5487 mL | 1.0975 mL | 2.1949 mL | 2.7436 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0549 mL | 0.2744 mL | 0.5487 mL | 1.0975 mL | 1.3718 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Competitive inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) (IC50 values are 0.20 and 0.24 μM for PARP-1 and PARP-2 respectively). Neuroprotective; reduces neuronal cell death in models of cerebral ischemia in vivo and in vitro. Brain penetrant.
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- FR 236924
Catalog No.:BCC7564
CAS No.:28399-31-7
- 1(10)-Aristolen-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN7634
CAS No.:28398-06-3
- Bumetanide
Catalog No.:BCC1119
CAS No.:28395-03-1
- 7-Neohesperidosides
Catalog No.:BCN8200
CAS No.:28383-41-7
- Aloin B
Catalog No.:BCN2576
CAS No.:28371-16-6
- Chrysin 6-C-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN3324
CAS No.:28368-57-2
- Mahanine
Catalog No.:BCN3176
CAS No.:28360-49-8
- Canolol
Catalog No.:BCC8371
CAS No.:28343-22-8
- Oxychelerythrine
Catalog No.:BCN4864
CAS No.:28342-33-8
- 6-Ethoxydihydrosanguinarine
Catalog No.:BCN7589
CAS No.:28342-31-6
- IVHD-valtrate
Catalog No.:BCN7125
CAS No.:28325-56-6
- NPS-2143
Catalog No.:BCC4409
CAS No.:284035-33-2
- Ac9-25
Catalog No.:BCC5997
CAS No.:284040-76-2
- 6-Hydroxy-2,6-dimethyl-2,7-octadienoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1463
CAS No.:28420-25-9
- Sorafenib
Catalog No.:BCN2174
CAS No.:284461-73-0
- 4-(4-Aminophenoxy)-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide
Catalog No.:BCC8649
CAS No.:284462-37-9
- Bavachalcone
Catalog No.:BCN3193
CAS No.:28448-85-3
- Tomentin
Catalog No.:BCN5180
CAS No.:28449-62-9
- 20-Deacetyltaxuspine X
Catalog No.:BCN7374
CAS No.:284672-76-0
- 9-Deacetyltaxinine E
Catalog No.:BCN7227
CAS No.:284672-78-2
- Delphinidin-3-O-galactoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3019
CAS No.:28500-00-7
- Petunidin-3-O-galactoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3024
CAS No.:28500-02-9
- Petunidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3026
CAS No.:28500-03-0
Insights into the binding of PARP inhibitors to the catalytic domain of human tankyrase-2.[Pubmed:25286857]
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Oct;70(Pt 10):2740-53.
The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) family represents a new class of therapeutic targets with diverse potential disease indications. PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitors have been developed for breast and ovarian tumors manifesting double-stranded DNA-repair defects, whereas tankyrase 1 and 2 (TNKS1 and TNKS2, also known as PARP5a and PARP5b, respectively) inhibitors have been developed for tumors with elevated beta-catenin activity. As the clinical relevance of PARP inhibitors continues to be actively explored, there is heightened interest in the design of selective inhibitors based on the detailed structural features of how small-molecule inhibitors bind to each of the PARP family members. Here, the high-resolution crystal structures of the human TNKS2 PARP domain in complex with 16 various PARP inhibitors are reported, including the compounds BSI-201, AZD-2281 and ABT-888, which are currently in Phase 2 or 3 clinical trials. These structures provide insight into the inhibitor-binding modes for the tankyrase PARP domain and valuable information to guide the rational design of future tankyrase-specific inhibitors.
A newly synthesized poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, DR2313 [2-methyl-3,5,7,8-tetrahydrothiopyrano[4,3-d]-pyrimidine-4-one]: pharmacological profiles, neuroprotective effects, and therapeutic time window in cerebral ischemia in rats.[Pubmed:15466246]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Feb;312(2):472-81.
We investigated the pharmacological profiles of DR2313 [2-methyl-3,5,7,8-tetrahydrothiopyrano[4,3-d]pyrimidine-4-one], a newly synthesized poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, and its neuroprotective effects on ischemic injuries in vitro and in vivo. DR2313 competitively inhibited poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in nuclear extracts of rat brain in vitro (K(i) = 0.23 microM). Among several NAD(+)-utilizing enzymes, DR2313 was specific for PARP but not selective between PARP-1 and PARP-2. DR2313 also showed excellent profiles in water solubility and rat brain penetrability. In in vitro models of cerebral ischemia, exposure to hydrogen peroxide or glutamate induced cell death with overactivation of PARP, and treatment with DR2313 reduced excessive formation of poly(ADP-ribose) and cell death. In both permanent and transient focal ischemia models in rats, pretreatment with DR2313 (10 mg/kg i.v. bolus and 10 mg/kg/h i.v. infusion for 6 h) significantly reduced the cortical infarct volume. To determine the therapeutic time window of neuroprotection by DR2313, the effect of post-treatment was examined in transient focal ischemia model and compared with that of a free radical scavenger, MCI-186 (3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolone-5-one). Pretreatment with MCI-186 (3 mg/kg i.v. bolus and 3 mg/kg/h i.v. infusion for 6 h) significantly reduced the infarct volume, whereas the post-treatment failed to show any effects. In contrast, post-treatment with DR2313 (same regimen) delaying for 2 h after ischemia still prevented the progression of infarction. These results indicate that DR2313 exerts neuroprotective effects via its potent PARP inhibition, even when the treatment is initiated after ischemia. Thus, a PARP inhibitor like DR2313 may be more useful in treating acute stroke than a free radical scavenger.
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and the therapeutic effects of its inhibitors.[Pubmed:15864271]
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005 May;4(5):421-40.
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) are involved in the regulation of many cellular functions. Three consequences of the activation of PARP1, which is the main isoform of the PARP family, are particularly important for drug development: first, its role in DNA repair; second, its capacity to deplete cellular energetic pools, which culminates in cell dysfunction and necrosis; and third, its capacity to promote the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes. Consequently, pharmacological inhibitors of PARP have the potential to enhance the cytotoxicity of certain DNA-damaging anticancer drugs, reduce parenchymal cell necrosis (for example, in stroke or myocardial infarction) and downregulate multiple simultaneous pathways of inflammation and tissue injury (for example, in circulatory shock, colitis or diabetic complications). The first ultrapotent novel PARP inhibitors have now entered human clinical trials. This article presents an overview of the principal pathophysiological pathways and mechanisms that are governed by PARP, followed by the main structures and therapeutic actions of various classes of novel PARP inhibitors.


