DehydromiltironeCAS# 116064-77-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 116064-77-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3082765 | Appearance | Red powder |
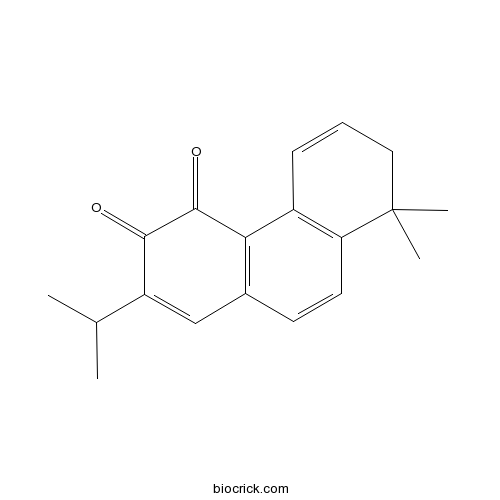
| Formula | C19H20O2 | M.Wt | 280.4 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 8,8-dimethyl-2-propan-2-yl-7H-phenanthrene-3,4-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C1=CC2=C(C3=C(C=C2)C(CC=C3)(C)C)C(=O)C1=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FQRLDPKLRMEKLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H20O2/c1-11(2)14-10-12-7-8-15-13(6-5-9-19(15,3)4)16(12)18(21)17(14)20/h5-8,10-11H,9H2,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dehydromiltirone has antioxidant activity, it shows significant anti-neuroinflammatory effects through inhibiting PI3K/Akt phosphorylation and then inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. |
| Targets | NOS | COX | NF-kB | PI3K | Akt | NO | TNF-α | IL Receptor | IkB | IKK |
| In vivo | Salvia miltiorrhiza compounds protect the liver from acute injury by regulation of p38 and NFκB signaling in Kupffer cells.[Pubmed: 25026357]Pharm Biol. 2014 Oct;52(10):1278-85.Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge is a traditional Asian medicine used to treat cerebral and cardiac ischemia. However, the effects of the active compounds of S. miltiorrhiza on liver damage are unclear.
In this study, we tested the effects on acute liver injury of crude S. miltiorrhiza extracts from roots as well as neotanshinone B, Dehydromiltirone, tanshinol A, tanshinone I, dihydrotanshinono I, neotanshinone A, cryptanshinono, tanshinone II A, and salvianolie acid B from purified S. miltiorrhiza extracts.
|
| Kinase Assay | The anti-neuroinflammatory effects of dehydromiltirone and related mechanisms.[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2016(2):177-83.To investigate the anti-neuroinflammatory activities of Dehydromiltirone and the underlying mechanisms in LPS-stimulated microglial cell line BV2 cells. |
| Structure Identification | Journal of Yantai University, 2000, 13(3):176-80.Structural Features and Antioxidative Activities on Miltirones.[Reference: WebLink]
|

Dehydromiltirone Dilution Calculator

Dehydromiltirone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5663 mL | 17.8317 mL | 35.6633 mL | 71.3267 mL | 89.1583 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7133 mL | 3.5663 mL | 7.1327 mL | 14.2653 mL | 17.8317 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3566 mL | 1.7832 mL | 3.5663 mL | 7.1327 mL | 8.9158 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0713 mL | 0.3566 mL | 0.7133 mL | 1.4265 mL | 1.7832 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0357 mL | 0.1783 mL | 0.3566 mL | 0.7133 mL | 0.8916 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Piperolactam C
Catalog No.:BCN4818
CAS No.:116064-76-7
- Pyr3
Catalog No.:BCC7771
CAS No.:1160514-60-2
- MLN4924 HCl salt
Catalog No.:BCC1773
CAS No.:1160295-21-5
- VU 0238429
Catalog No.:BCC7729
CAS No.:1160247-92-6
- 1-Amino-4-hydroxyanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8452
CAS No.:116-85-8
- 4-Amino-3-hydroxy-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8680
CAS No.:116-63-2
- Aldicarb
Catalog No.:BCC5475
CAS No.:116-06-3
- TC-I 2000
Catalog No.:BCC6244
CAS No.:1159996-20-9
- Caulophine
Catalog No.:BCN7990
CAS No.:1159989-19-1
- Abiesadine N
Catalog No.:BCN6041
CAS No.:1159913-80-0
- CZC24832
Catalog No.:BCC1507
CAS No.:1159824-67-5
- Poricoic acid AE
Catalog No.:BCN7282
CAS No.:1159753-88-4
- IDE 1
Catalog No.:BCC7841
CAS No.:1160927-48-9
- RETF-4NA
Catalog No.:BCC6073
CAS No.:1160928-63-1
- Z-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2756
CAS No.:1161-13-3
- Phenamil
Catalog No.:BCC7673
CAS No.:1161-94-0
- G-15
Catalog No.:BCC6058
CAS No.:1161002-05-6
- VU 0361737
Catalog No.:BCC4596
CAS No.:1161205-04-4
- Brevicolline
Catalog No.:BCN2459
CAS No.:20069-02-7
- Alexine
Catalog No.:BCN2054
CAS No.:116174-63-1
- Complanatoside
Catalog No.:BCN8213
CAS No.:116183-66-5
- Aflatoxin B1
Catalog No.:BCC9212
CAS No.:1162-65-8
- Levobetaxolol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4671
CAS No.:116209-55-3
- MCB-613
Catalog No.:BCC3982
CAS No.:1162656-22-5
Salvia miltiorrhiza compounds protect the liver from acute injury by regulation of p38 and NFkappaB signaling in Kupffer cells.[Pubmed:25026357]
Pharm Biol. 2014 Oct;52(10):1278-85.
CONTEXT: Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge is a traditional Asian medicine used to treat cerebral and cardiac ischemia. However, the effects of the active compounds of S. miltiorrhiza on liver damage are unclear. OBJECTIVE: In this study, we tested the effects on acute liver injury of crude S. miltiorrhiza extracts from roots as well as neotanshinone B, Dehydromiltirone, tanshinol A, tanshinone I, dihydrotanshinono I, neotanshinone A, cryptanshinono, tanshinone II A, and salvianolie acid B from purified S. miltiorrhiza extracts. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Various compounds or ethanol extract of S. miltiorrhiza (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) were administered to rats for five consecutive days. After acute carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury by treatment of rats with a single dose of CCl4 (0.75 mL/kg, p.o), rat liver function was tested by measuring serum biochemical parameters. Serum cytokine concentrations were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Expression of p38 and NFkappaB was evaluated by western blot. RESULTS: All S. miltiorrhiza components showed their effects on liver function from the dose from 50 to 200 mg/kg. At the dose of 200 mg/kg, they reduced serum levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) by 34-77%, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) by 30-57%, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) by 43-72%, creatine total bilirubin (BIL-T) by 33-81%, albumin (ALB) by 37-67%, indicating that S. miltiorrhiza extracts protected liver from CCl4-induced damage. Moreover, S. miltiorrhiza extracts at 200 mg/kg reduced the increase in the proinflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) by 25-82%, interleukin-1 (IL-1) by 42-74% and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by 67-83%, indicating an effect on alleviating liver inflammation. Furthermore, in vitro, S. miltiorrhiza extracts inhibited p38 and NFkappaB signaling in Kupffer cells. This effect could be a main mechanism by which S. miltiorrhiza protects against acute liver toxicity. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: Active compounds of S. miltiorrhiza protected the liver from CCl4-induced injury. Protection might have been due to inhibition of p38 and NFkappaB signaling in Kupffer cells, which subsequently reduced inflammation in the liver.


