IDE 1Induces definitive endoderm formation in mouse and human ESCs CAS# 1160927-48-9 |
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- Dexrazoxane HCl (ICRF-187, ADR-529)
Catalog No.:BCC1087
CAS No.:149003-01-0
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1117
CAS No.:25316-40-9
- Etoposide
Catalog No.:BCC1151
CAS No.:33419-42-0
- Genistein
Catalog No.:BCN5499
CAS No.:446-72-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1160927-48-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 66974738 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H18N2O5 | M.Wt | 306.31 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL (97.94 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
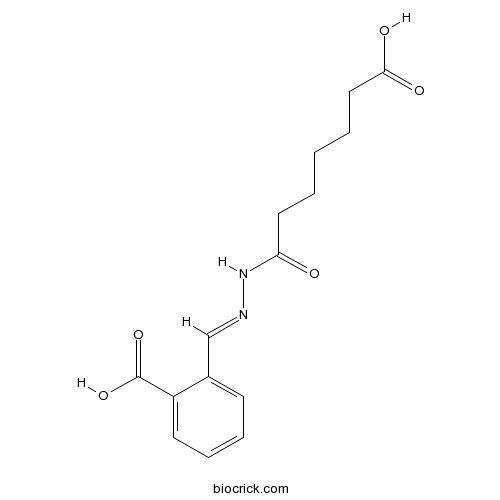
| Chemical Name | 2-[(6-carboxyhexanoylhydrazinylidene)methyl]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)C=NNC(=O)CCCCCC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ABKJCDILEUEJSH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H18N2O5/c18-13(8-2-1-3-9-14(19)20)17-16-10-11-6-4-5-7-12(11)15(21)22/h4-7,10H,1-3,8-9H2,(H,17,18)(H,19,20)(H,21,22) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Induces definitive endoderm formation in mouse and human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) (EC50 = 125 nM). Thought to activate the TGF-β signaling pathway; induces Smad2 phosphorylation and increases levels of Nodal expression. |

IDE 1 Dilution Calculator

IDE 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2647 mL | 16.3233 mL | 32.6467 mL | 65.2933 mL | 81.6167 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6529 mL | 3.2647 mL | 6.5293 mL | 13.0587 mL | 16.3233 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3265 mL | 1.6323 mL | 3.2647 mL | 6.5293 mL | 8.1617 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0653 mL | 0.3265 mL | 0.6529 mL | 1.3059 mL | 1.6323 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0326 mL | 0.1632 mL | 0.3265 mL | 0.6529 mL | 0.8162 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IDE1 is an inducer of definitive endoderm 1 (IDE1).
In Vitro:IDE1 enhances the definitive endoderm (DE) differentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) with Activin A/Wnt3a being significantly more potent in both 2D and 3D cultures compared to IDE1. IDE1 could efficiently induces DE differentiation through various protocols in vitro. Treatment of the hiPSCs-derived EBs with IDE-1 shows minor increase (p<0.01) of DE-markers cells compared to Activin A/Wnt3a treatment. IDE1 possess several advantages over other inducing factors including high permeability, influence, diversity, low cost, and easy to use and for the first time, Melton’s team showed that Activin A can be substituted by two cell-permeable small molecules, IDE1 and IDE2. IDE1 could induce phosphorylation of Smad2 after incubation for 24 h or more at levels comparable to those induced by Activin A treatment. Treatment of hiPSCs with IDE1 (2 mM) also leads to endodermal differentiation but with a significantly lower efficiency than Activin A/Wnt3a[1].
References:
[1]. Hoveizi E, et al. Definitive endoderm differentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells using signaling molecules and IDE1 in three-dimensional polymer scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014 Nov;102(11):4027-36.
- Dehydromiltirone
Catalog No.:BCN5357
CAS No.:116064-77-8
- Piperolactam C
Catalog No.:BCN4818
CAS No.:116064-76-7
- Pyr3
Catalog No.:BCC7771
CAS No.:1160514-60-2
- MLN4924 HCl salt
Catalog No.:BCC1773
CAS No.:1160295-21-5
- VU 0238429
Catalog No.:BCC7729
CAS No.:1160247-92-6
- 1-Amino-4-hydroxyanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8452
CAS No.:116-85-8
- 4-Amino-3-hydroxy-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8680
CAS No.:116-63-2
- Aldicarb
Catalog No.:BCC5475
CAS No.:116-06-3
- TC-I 2000
Catalog No.:BCC6244
CAS No.:1159996-20-9
- Caulophine
Catalog No.:BCN7990
CAS No.:1159989-19-1
- Abiesadine N
Catalog No.:BCN6041
CAS No.:1159913-80-0
- CZC24832
Catalog No.:BCC1507
CAS No.:1159824-67-5
- RETF-4NA
Catalog No.:BCC6073
CAS No.:1160928-63-1
- Z-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2756
CAS No.:1161-13-3
- Phenamil
Catalog No.:BCC7673
CAS No.:1161-94-0
- G-15
Catalog No.:BCC6058
CAS No.:1161002-05-6
- VU 0361737
Catalog No.:BCC4596
CAS No.:1161205-04-4
- Brevicolline
Catalog No.:BCN2459
CAS No.:20069-02-7
- Alexine
Catalog No.:BCN2054
CAS No.:116174-63-1
- Complanatoside
Catalog No.:BCN8213
CAS No.:116183-66-5
- Aflatoxin B1
Catalog No.:BCC9212
CAS No.:1162-65-8
- Levobetaxolol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4671
CAS No.:116209-55-3
- MCB-613
Catalog No.:BCC3982
CAS No.:1162656-22-5
- Pyrroside B
Catalog No.:BCN4042
CAS No.:116271-35-3
2-(Pyridinium-1-yl)-1,1-bis(perfluoroalkylsulfonyl)ethan-1-ide: A Practical Reagent for Synthesis of Strongly Acidic 1,1-Bis(perfluoroalkylsulfonyl)alkanes.[Pubmed:28266793]
Chemistry. 2017 Jun 16;23(34):8203-8211.
On mixing (Rf SO2 )2 CH2 (Rf =perfluoroalkyl), paraformaldehyde, and substituted pyridines, a three-component reaction proceeded smoothly to give unusual zwitterions bearing both pyridinium and stabilized carbanion moieties in good to excellent yields. Of these, 2-fluoropyridinium derivatives rapidly dissociated in acetonitrile to give equilibrium mixtures of the zwitterions and (Rf SO2 )2 C=CH2 /2-fluoropyridine, as confirmed by detailed variable-temperature NMR studies. The dynamic behavior of such 2-fluoropyridinium compounds allows them to be used as shelf-stable, easy-to-handle sources of (Rf SO2 )2 C=CH2 . With these reagents, strongly acidic carbon acids (Rf SO2 )2 CHR were synthesized, which served as a new type of acid catalysts. Moreover, C-C bond-forming reactions with a ketene silyl acetal proceeded efficiently with Tf2 C=CH2 generated in situ.
Efficacy and safety of once-daily ritonavir-boosted atazanavir or darunavir in combination with a dual nucleos(t)ide analogue backbone in HIV-1-infected combined ART (cART)-naive patients with severe immunosuppression: a 48 week, non-comparative, randomized, multicentre trial (IMEA 040 DATA trial).[Pubmed:27068399]
J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Aug;71(8):2252-61.
OBJECTIVES: Boosted PIs are commonly prescribed in patients presenting with advanced HIV infection. We assessed the efficacy and tolerability of once-daily ritonavir-boosted atazanavir or darunavir plus two NRTIs in HIV-1-infected ART-naive patients with severe immunosuppression, targeting at least an 85% success rate at week 48. METHODS: This 48 week, open-label, non-comparative, randomized, multicentre trial included ART-naive patients with CD4 cell counts <200 cells/mm(3), with plasma HIV-1 RNA >1000 copies/mL and without genotypic mutations conferring resistance to the study drugs. Patients were randomized (1:1) to receive once-daily atazanavir/ritonavir (300/100 mg) or darunavir/ritonavir (800/100 mg) plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine or abacavir/lamivudine. The primary endpoint was treatment success, defined as plasma HIV-1 RNA
Identification and functional characterization of a putative IDE, C28F5.4 (ceIDE-1), in Caenorhabditis elegans: Implications for Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:27443962]
Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Nov;1860(11 Pt A):2454-2462.
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) is a zinc metalloprotease, known to degrade insulin peptide and amyloid-beta (Abeta); the key protein involved in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Considering the important role played by IDE in disease progression of AD and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), we endeavored to identify the Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) IDE orthologous genes and test them for their role in AD related outcomes. We employed bioinformatics, reverse genetics and molecular biology approaches towards identification and functional characterization of putative IDE candidates in C. elegans. Using in-silico analysis we have identified seven C. elegans genes that possess HXXEH motif, an identifying marker of IDE. We further carried out functional analysis of the identified genes in Abeta expressing C. elegans strain CL4176 [myo-3/Abeta1-42 long 3'-UTR] via studying effect on Abeta induced toxicity, cholinergic neuroanatomy, content of acetylcholine/acetylcholine-esterase, extent of reactive oxygen species and expression of FOXO transcription factor DAF-16. Our findings reveal that amongst the identified putative IDE orthologs, a functionally uncharacterized gene C28F5.4 had a profound effect on the tested endpoints. Knocking down C28F5.4 modulated the AD associated conditions by decreasing Abeta induced toxicity, severely compromising cholinergic neuroanatomy, reducing expression of acetylcholine-transporter, decreasing acetylcholine content, elevating ROS, with no effect on DAF-16 stress-response protein. These studies provide crucial insight into the structural/functional orthology of IDEs across human and nematode species and further our understanding of the involvement of these proteins and insulin pathway in AD. Further studies could aid in identifying novel drug-targets and in understanding the common modulating factors between AD and T2DM.
Small molecules efficiently direct endodermal differentiation of mouse and human embryonic stem cells.[Pubmed:19341624]
Cell Stem Cell. 2009 Apr 3;4(4):348-58.
An essential step for therapeutic and research applications of stem cells is the ability to differentiate them into specific cell types. Endodermal cell derivatives, including lung, liver, and pancreas, are of interest for regenerative medicine, but efforts to produce these cells have been met with only modest success. In a screen of 4000 compounds, two cell-permeable small molecules were indentified that direct differentiation of ESCs into the endodermal lineage. These compounds induce nearly 80% of ESCs to form definitive endoderm, a higher efficiency than that achieved by Activin A or Nodal, commonly used protein inducers of endoderm. The chemically induced endoderm expresses multiple endodermal markers, can participate in normal development when injected into developing embryos, and can form pancreatic progenitors. The application of small molecules to differentiate mouse and human ESCs into endoderm represents a step toward achieving a reproducible and efficient production of desired ESC derivatives.
Using small molecules to great effect in stem cell differentiation.[Pubmed:19427285]
Cell Stem Cell. 2009 May 8;4(5):373-4.
Several recent reports, including two Cell Stem Cell papers (Zhu et al., 2009 [this issue]; Borowiak et al., 2009), screened small molecule libraries for compounds that promote embryonic stem cell differentiation. Their combined success helps bypass challenges associated with using natural protein factors and has revealed insights into controlling stem cell differentiation.


