DexmedetomidineCAS# 113775-47-6 |
- Vinblastine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2292
CAS No.:143-67-9
- Doxorubicin
Catalog No.:BCC2082
CAS No.:23214-92-8
- Pepstatin A
Catalog No.:BCC1218
CAS No.:26305-03-3
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
- E 64d
Catalog No.:BCC1127
CAS No.:88321-09-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 113775-47-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311068 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H16N2 | M.Wt | 200.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
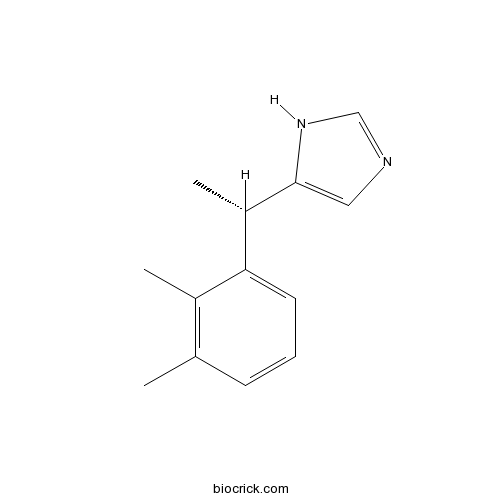
| Chemical Name | 5-[(1S)-1-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)ethyl]-1H-imidazole | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=CC=C1)C(C)C2=CN=CN2)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CUHVIMMYOGQXCV-NSHDSACASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H16N2/c1-9-5-4-6-12(10(9)2)11(3)13-7-14-8-15-13/h4-8,11H,1-3H3,(H,14,15)/t11-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Dexmedetomidine Dilution Calculator

Dexmedetomidine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.993 mL | 24.965 mL | 49.9301 mL | 99.8602 mL | 124.8252 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9986 mL | 4.993 mL | 9.986 mL | 19.972 mL | 24.965 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4993 mL | 2.4965 mL | 4.993 mL | 9.986 mL | 12.4825 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0999 mL | 0.4993 mL | 0.9986 mL | 1.9972 mL | 2.4965 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0499 mL | 0.2497 mL | 0.4993 mL | 0.9986 mL | 1.2483 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Dexmedetomidine is a sedative medication used by intensive care units and anesthetists.
- Eudesm-4(15)-ene-3alpha,11-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4060
CAS No.:113773-90-3
- Ilexhainanoside D
Catalog No.:BCN7863
CAS No.:1137648-52-2
- LX1606
Catalog No.:BCC1713
CAS No.:1137608-69-5
- BRD 7552
Catalog No.:BCC8035
CAS No.:1137359-47-7
- cis-Ned 19
Catalog No.:BCC6089
CAS No.:1137264-00-6
- Tenatoprazole
Catalog No.:BCC4732
CAS No.:113712-98-4
- BOC-D-ARG-OH.HCL.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3069
CAS No.:113712-06-4
- 4-Aminobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8684
CAS No.:1137-41-3
- Shizukanolide H
Catalog No.:BCN6016
CAS No.:1136932-34-7
- 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanone
Catalog No.:BCN6015
CAS No.:113681-11-1
- Neuropeptide Y 13-36 (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC6959
CAS No.:113662-54-7
- Ustusolate A
Catalog No.:BCN6756
CAS No.:1136611-58-9
- MDL 72832 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6637
CAS No.:113777-40-5
- TAK960
Catalog No.:BCC6411
CAS No.:1137868-52-0
- (Z)-FeCP-oxindole
Catalog No.:BCC6079
CAS No.:1137967-28-2
- Z-Gly-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2770
CAS No.:1138-80-3
- Picrasidine T
Catalog No.:BCN6017
CAS No.:113808-03-0
- N1,N12-Diethylspermine tetrahydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6669
CAS No.:113812-15-0
- N-p-coumaroyl-N'-caffeoylputrescine
Catalog No.:BCN6018
CAS No.:1138156-77-0
- Cidofovir
Catalog No.:BCC2546
CAS No.:113852-37-2
- CX-5461
Catalog No.:BCC3700
CAS No.:1138549-36-6
- Cinnamyl 3-aminobut-2-enoate
Catalog No.:BCC8914
CAS No.:113898-97-8
- Caryophyllene oxide
Catalog No.:BCN6019
CAS No.:1139-30-6
- Koumine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN4807
CAS No.:113900-75-7
The sedative effects of the intranasal administration of dexmedetomidine in children undergoing surgeries compared to other sedation methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis.[Pubmed:28372674]
J Clin Anesth. 2017 May;38:33-39.
STUDY OBJECTIVE: Administration of intranasal Dexmedetomidine for sedation is comfortable and effective in children who are afraid of needles, and it offers efficient sedation similar to that of intravenous administration. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the clinical effects of the pre-procedural administration of intranasal Dexmedetomidine. DESIGN: We identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared intranasal Dexmedetomidine administration to other administration methods of various sedatives or placebo from MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane, KoreaMed and hand searches of trial registries. SETTING: Pediatrics who underwent interventional procedures and surgeries. PATIENTS: Children under the age of 18. INTERVENTIONS: Studies were included if they were compatible with the criteria that Dexmedetomidine was administered intranasally. MEASUREMENTS: We pooled data on the sedation status as the primary outcome and considered the behavioral score, blood pressure, heart rate and side effects to be secondary outcomes. Risk ratio (RR) and the standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for dichotomous and continuous outcomes, respectively. MAIN RESULTS: This meta-analysis included 11 RCTs. The SMD for the sedative effects of intranasal Dexmedetomidine was -2.45 (random, 95% CI; -3.33, -1.58) for continuous outcomes and RR of unsatisfactory patient outcome was 0.42 (M-H, random 95% CI; 0.26, 0.68 I(2)=45%) for dichotomous outcomes compared to that of intranasal saline. The SMD for the sedative effects of intranasal Dexmedetomidine was -0.41 (random, 95% CI; -1.09, 0.27 I(2)=69%) for continuous outcomes and RR was 0.43 (M-H, random 95% CI; 0.32, 0.58 I(2)=0%) for dichotomous outcomes compared to that of per os benzodiazepines. CONCLUSIONS: This review suggests that intranasal Dexmedetomidine is associated with better sedative effects than oral benzodiazepines without producing respiratory depression, but it had a significantly delayed onset of effects.
Effect of Adding Dexmedetomidine to Ropivacaine on Ultrasound-Guided Dual Transversus Abdominis Plane Block after Gastrectomy.[Pubmed:28374183]
J Gastrointest Surg. 2017 Jun;21(6):936-946.
OBJECTIVES: Transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block is an analgesic technique. Adding Dexmedetomidine can enhance regional anesthesia. This study's aim was to evaluate whether Dexmedetomidine prolonged analgesic time of TAP block after gastrectomy. METHODS: Patients scheduled for gastrectomy were randomly assigned to receive a TAP block with saline (group S), ropivacaine (group R), or ropivacaine and Dexmedetomidine (group RD). Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) scores, sedation scores, tramadol consumption, ropivacaine concentration, and Quality of Recovery Questionnaire 40 (QoR-40) were recorded. RESULTS: Patients in group R and group RD had lower VAS scores 2, 4, 12, and 24 h after surgery compared with group S (P < 0.05). PONV scores were lower in group R and group RD compared with group S after 2, 12, 24, and 36 h (P < 0.05). Patients in group R and group RD required less tramadol and had better QoR-40 scores than those in group S (P < 0.05). The aforementioned variables and ropivacaine concentrations did not differ between group R and group RD (P > 0.05). Sedation scores were similar between three groups (P > 0.05). CONCLUSIONS: TAP block can provide analgesia and improve the quality of recovery. Adding Dexmedetomidine does not significantly improve the quality or duration of TAP block.
The Cardioprotective Effect of Dexmedetomidine in Rats Is Dose-Dependent and Mediated by BKCa Channels.[Pubmed:28375904]
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;69(4):228-235.
The alpha-2 receptor agonist Dexmedetomidine (Dex) protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury. We investigated the signaling cascade underlying Dex-induced acute cardioprotection, with special emphasis on large-conductance Ca2+-sensitive potassium (BKCa) channels. Rats were anesthetized with pentobarbital. Hearts were isolated, mounted on a Langendorff system and perfused with Krebs-Henseleit buffer. Hearts underwent 33 minutes of ischemia followed by 60 minutes of reperfusion. Before the beginning of ischemia, Dex was administered at different doses (0.1-30 nM) for characterization of a dose-effect relationship. In another set of experiments, Dex (3 nM) was administered together with the BKCa channel inhibitor paxilline and the connexin-43 inhibitor peptide Gap27. Also, the BKCa channel opener NS1619 was administered. In control animals, infarct size was 49% +/- 5%. Dex at 3-30 nM reduced infarct size to approximately 22%, whereas lower (0.1-1 nM) doses reduced infarct size to approximately 38%. Paxilline (1 muM) and GAP27 (6 muM) blocked the Dex-induced cardioprotection. NS1619 (10 muM) reduced infarct size to about the same magnitude as did the higher doses of Dex. Functional heart parameters and coronary flow were not different between the study groups. In male rats, the Dex-induced protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury involves connexin-43 and activation of BKCa channels.


