cis-Ned 19CAS# 1137264-00-6 |
- CFM 1571 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5924
CAS No.:1215548-30-3
- A 350619 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5939
CAS No.:1217201-17-6
- BAY 41-2272
Catalog No.:BCC7932
CAS No.:256376-24-6
- Riociguat
Catalog No.:BCC1899
CAS No.:625115-55-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1137264-00-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1427626 | Appearance | Powder |
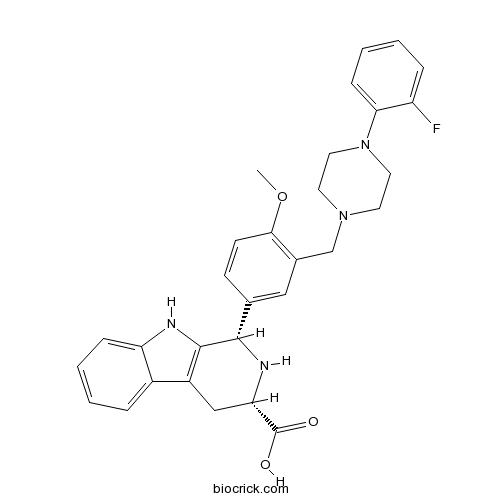
| Formula | C30H31FN4O3 | M.Wt | 514.59 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | (1S,3S)-1-[3-[[4-(2-fluorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]methyl]-4-methoxyphenyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2C3=C(CC(N2)C(=O)O)C4=CC=CC=C4N3)CN5CCN(CC5)C6=CC=CC=C6F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FUHCEERDBRGPQZ-LSYYVWMOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H31FN4O3/c1-38-27-11-10-19(16-20(27)18-34-12-14-35(15-13-34)26-9-5-3-7-23(26)31)28-29-22(17-25(33-28)30(36)37)21-6-2-4-8-24(21)32-29/h2-11,16,25,28,32-33H,12-15,17-18H2,1H3,(H,36,37)/t25-,28-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Irreversible nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) antagonist; inhibits Ca2+ release (IC50 = 800 nM) and [32P]NAADP binding (IC50 = 15 μM). Stereoisomer of trans-Ned 19. Fluorescently labels NAADP receptors in intact cells (excitation 351 and 365 nm using an ultraviolet Argon laser). |

cis-Ned 19 Dilution Calculator

cis-Ned 19 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9433 mL | 9.7165 mL | 19.4329 mL | 38.8659 mL | 48.5824 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3887 mL | 1.9433 mL | 3.8866 mL | 7.7732 mL | 9.7165 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1943 mL | 0.9716 mL | 1.9433 mL | 3.8866 mL | 4.8582 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0389 mL | 0.1943 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.7773 mL | 0.9716 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0194 mL | 0.0972 mL | 0.1943 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.4858 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tenatoprazole
Catalog No.:BCC4732
CAS No.:113712-98-4
- BOC-D-ARG-OH.HCL.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3069
CAS No.:113712-06-4
- 4-Aminobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8684
CAS No.:1137-41-3
- Shizukanolide H
Catalog No.:BCN6016
CAS No.:1136932-34-7
- 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanone
Catalog No.:BCN6015
CAS No.:113681-11-1
- Neuropeptide Y 13-36 (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC6959
CAS No.:113662-54-7
- Ustusolate A
Catalog No.:BCN6756
CAS No.:1136611-58-9
- IDE 2
Catalog No.:BCC6099
CAS No.:1136466-93-7
- Stigmast-4-ene-3,6-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6014
CAS No.:113626-76-9
- Metasequoic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6652
CAS No.:113626-22-5
- 6beta-(Hexa-2,4-dienoyloxy)-9alpha,12-dihydroxydrimenol
Catalog No.:BCN7277
CAS No.:1136245-81-2
- Orbifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4689
CAS No.:113617-63-3
- BRD 7552
Catalog No.:BCC8035
CAS No.:1137359-47-7
- LX1606
Catalog No.:BCC1713
CAS No.:1137608-69-5
- Ilexhainanoside D
Catalog No.:BCN7863
CAS No.:1137648-52-2
- Eudesm-4(15)-ene-3alpha,11-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4060
CAS No.:113773-90-3
- Dexmedetomidine
Catalog No.:BCC4326
CAS No.:113775-47-6
- MDL 72832 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6637
CAS No.:113777-40-5
- TAK960
Catalog No.:BCC6411
CAS No.:1137868-52-0
- (Z)-FeCP-oxindole
Catalog No.:BCC6079
CAS No.:1137967-28-2
- Z-Gly-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2770
CAS No.:1138-80-3
- Picrasidine T
Catalog No.:BCN6017
CAS No.:113808-03-0
- N1,N12-Diethylspermine tetrahydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6669
CAS No.:113812-15-0
- N-p-coumaroyl-N'-caffeoylputrescine
Catalog No.:BCN6018
CAS No.:1138156-77-0
Characteristics of minerals in vesicles produced by human osteoblasts hFOB 1.19 and osteosarcoma Saos-2 cells stimulated for mineralization.[Pubmed:28380345]
J Inorg Biochem. 2017 Jun;171:100-107.
Bone cells control initial steps of mineralization by producing extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins and releasing vesicles that trigger apatite nucleation. Using transmission electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (TEM-EDX) we compared the quality of minerals in vesicles produced by two distinct human cell lines: fetal osteoblastic hFOB 1.19 and osteosarcoma Saos-2. Both cell lines, subjected to osteogenic medium with ascorbic acid (AA) and beta-glycerophosphate (beta-GP), undergo the entire osteoblastic differentiation program from proliferation to mineralization, produce the ECM and spontaneously release vesicles. We observed that Saos-2 cells mineralized better than hFOB 1.19, as probed by Alizarin Red-S (AR-S) staining, tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) activity and by analyzing the composition of minerals in vesicles. Vesicles released from Saos-2 cells contained and were surrounded by more minerals than vesicles released from hFOB 1.19. In addition, there were more F and Cl substituted apatites in vesicles from hFOB 1.19 than in those from Saos-2 cells as determined by ion ratios. Saos-2 and h-FOB 1.19 cells revealed distinct mineralization profiles, indicating that the process of mineralization may proceed differently in various types of cells. Our findings suggest that TNAP activity is correlated with the relative proportions of mineral-filled vesicles and mineral-surrounded vesicles. The origin of vesicles and their properties predetermine the onset of mineralization at the cellular level.
Is MPP a good prognostic factor in stage III lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR exon 19 mutation?[Pubmed:28380449]
Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 20;8(25):40594-40605.
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a transmembrane glycoprotein encoded by a gene located in the short arm of chromosome 7. This study aimed to investigate the clinicopathologic characteristics of classic EGFR exon mutation in Chinese patients with TMN stage III lung adenocarcinoma who received radical surgery. A total of 1,801 lung adenocarcinomas were analyzed for mutations in EGFR; 35% exhibited mutation of classic EGFR exons. Clinical and pathologic characteristics of patients with EGFR exon 19 mutation were compared with those who harbored EGFR exon 21 mutation. Patients with EGFR exon 19 mutation had a higher overall survival (OS, p=0.023) than those harboring EGFR exon 21 mutation. Our results demonstrated that patients with a micropapillary pattern (MPP) pathologic type in EGFR exon 19 mutation had a higher OS (p=0.022), and patients with exon 19 mutation were more sensitive to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (p=0.032). The results of the current study can be used in decision-making regarding the treatment of patients with classic EGFR exon mutations.
Chenodeoxycholic acid stimulated fibroblast growth factor 19 response - a potential biochemical test for bile acid diarrhoea.[Pubmed:28378364]
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jun;45(11):1433-1442.
BACKGROUND: Bile acid diarrhoea is underdiagnosed and better diagnostic tests are needed. Fasting serum fibroblast growth factor-19 (FGF19) has insufficient diagnostic value, but this may be improved by stimulation. AIM: To explore if an impaired FGF19 response identifies primary bile acid diarrhoea. METHODS: Eight patients with primary bile acid diarrhoea and eight healthy volunteers ingested (i) a meal plus 1250 mg chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), (ii) 1250 mg CDCA or (iii) the meal. Blood was sampled at fasting and repeatedly after stimulation. We analysed FGF19 by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and bile acids including 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. RESULTS: Stimulation with the meal plus CDCA increased median FGF19 in healthy volunteers from fasting 62 pg/mL [interquartile range (IQR): 41-138] to 99 pg/mL (IQR: 67-147; P = 0.012) after 90 min and peaked after 150 min at 313 pg/mL (IQR: 54-512). This response was impaired in primary bile acid diarrhoea patients [fasting 56 pg/mL (IQR: 42-79); 90 min: 48 pg/mL [IQR: 37-63); 150 min: 57 pg/mL (48-198)]. Receiver operating characteristics (ROCAUC ) for fasting FGF19 was 0.55 (P = 0.75) and at 90 min 0.84 (P = 0.02). The difference in FGF19 from fasting to 90 min after the meal plus CDCA separated the groups (ROCAUC 1.0; P = 0.001). 7alpha-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one was elevated in primary bile acid diarrhoea (P = 0.038) and not significantly affected by stimulation. CONCLUSIONS: The FGF19 response following chenodeoxycholic acid plus meal is impaired in primary bile acid diarrhoea. This may provide a biochemical diagnostic test.
Identification of a chemical probe for NAADP by virtual screening.[Pubmed:19234453]
Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Apr;5(4):220-6.
Research into the biological role of the Ca(2+)-releasing second messenger NAADP (nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate) has been hampered by a lack of chemical probes. To find new chemical probes for exploring NAADP signaling, we turned to virtual screening, which can evaluate millions of molecules rapidly and inexpensively. We used NAADP as the query ligand to screen the chemical library ZINC for compounds with similar three-dimensional shape and electrostatic properties. We tested the top-ranking hits in a sea urchin egg bioassay and found that one hit, Ned-19, blocks NAADP signaling at nanomolar concentrations. In intact cells, Ned-19 blocked NAADP signaling and fluorescently labeled NAADP receptors. Moreover, we show the utility of Ned-19 as a chemical probe by using it to demonstrate that NAADP is a key causal link between glucose sensing and Ca(2+) increases in mouse pancreatic beta cells.


