DiclazurilCAS# 101831-37-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 101831-37-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 456389 | Appearance | Powder |
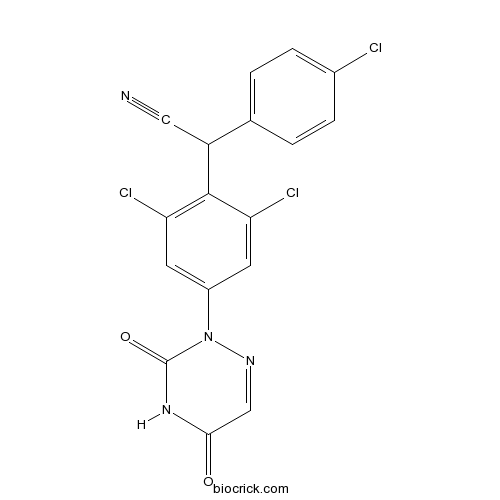
| Formula | C17H9Cl3N4O2 | M.Wt | 407.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 25 mg/mL (61.33 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-[2,6-dichloro-4-(3,5-dioxo-1,2,4-triazin-2-yl)phenyl]acetonitrile | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C(C#N)C2=C(C=C(C=C2Cl)N3C(=O)NC(=O)C=N3)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZSZFUDFOPOMEET-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H9Cl3N4O2/c18-10-3-1-9(2-4-10)12(7-21)16-13(19)5-11(6-14(16)20)24-17(26)23-15(25)8-22-24/h1-6,8,12H,(H,23,25,26) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Diclazuril Dilution Calculator

Diclazuril Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4534 mL | 12.2669 mL | 24.5339 mL | 49.0677 mL | 61.3346 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4907 mL | 2.4534 mL | 4.9068 mL | 9.8135 mL | 12.2669 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2453 mL | 1.2267 mL | 2.4534 mL | 4.9068 mL | 6.1335 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0491 mL | 0.2453 mL | 0.4907 mL | 0.9814 mL | 1.2267 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0245 mL | 0.1227 mL | 0.2453 mL | 0.4907 mL | 0.6133 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Butenafine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4768
CAS No.:101827-46-7
- TG 100801 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1997
CAS No.:1018069-81-2
- Desacetylmatricarin
Catalog No.:BCN7258
CAS No.:10180-88-8
- 7-O-Demethyl-3-isomangostin hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN7882
CAS No.:
- Elliotinol
Catalog No.:BCN5833
CAS No.:10178-31-1
- Boc-N-Me-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2613
CAS No.:101772-29-6
- PK 44 phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC2366
CAS No.:1017682-65-3
- LPA2 antagonist 1
Catalog No.:BCC5438
CAS No.:1017606-66-4
- Ladanein
Catalog No.:BCN6670
CAS No.:10176-71-3
- Nevadensin
Catalog No.:BCN6806
CAS No.:10176-66-6
- Jaceidin
Catalog No.:BCN5832
CAS No.:10173-01-0
- Sanggenofuran B
Catalog No.:BCN7194
CAS No.:1017277-40-5
- 7-Z-Trifostigmanoside I
Catalog No.:BCN7869
CAS No.:1018898-17-3
- LX-4211
Catalog No.:BCC1714
CAS No.:1018899-04-1
- sodium 4-pentynoate
Catalog No.:BCC1958
CAS No.:101917-30-0
- Dabigatran etexilate benzenesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC8925
CAS No.:1019206-65-5
- Regorafenib monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1884
CAS No.:1019206-88-2
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- S0859
Catalog No.:BCC1914
CAS No.:1019331-10-2
- Octacosyl (E)-ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN5834
CAS No.:101959-37-9
- Zardaverine
Catalog No.:BCC2069
CAS No.:101975-10-4
- GW791343 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1613
CAS No.:1019779-04-4
- Acetoacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8803
CAS No.:102-01-2
- 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8281
CAS No.:102-32-9
Diclazuril nonlinear mixed-effects pharmacokinetic modelling of plasma concentrations after oral administration to adult horses every 3-4 days.[Pubmed:30503548]
Vet J. 2018 Dec;242:74-76.
The purpose of this study was to determine if a low dose of Diclazuril (0.5mg/kg of 1.56% Diclazuril pellets) given to six healthy adult horses every 3-4 days for a total of five administrations would achieve steady-state plasma concentrations known to be inhibitory to Sarcocystis neurona and Neospora caninum. Blood was collected via venipuncture immediately before (trough concentrations) and 10h after (peak concentrations) each Diclazuril administration and analysed by high-pressure liquid chromatography. The mean population-derived peak concentration was 0.284mug/mL and the mean terminal half-life was 1.6 days, but with a large variation. Thus, low dose Diclazuril pellets produce steady-state plasma drug concentrations known to inhibit S. neurona (0.001mug/mL) and N. caninum (0.1mug/mL).
Efficacy of Sulphachloropyrazine, Amprolium Hydrochloride, Trimethoprim-Sulphamethoxazole, and Diclazuril against Experimental and Natural Rabbit Coccidiosis.[Pubmed:30426022]
J Vet Med. 2018 Oct 23;2018:5402469.
There are no anticoccidial drugs labelled for rabbits in Kenya and those available are used as extra labels from poultry. The drugs are used in rabbits with limited knowledge of their efficacy and safety. The aim of this study was to determine the efficacy of sulphachloropyrazine, amprolium hydrochloride, and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole relative to Diclazuril when used curatively against experimental and natural rabbit coccidiosis. In a controlled laboratory trial, sixty (60) rabbits were randomly allocated to six treatment groups, namely, 1A, 2B, 3C, 4D, 5E, and 6F, each with 10 rabbits. Groups 2B, 3C, 4D, 5E, and 6F were experimentally infected with mixed Eimeria species while group 1A served as uninfected-untreated (negative) control group. Four of the infected groups were treated with sulphachloropyrazine (5E), amprolium hydrochloride (2B), trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole (6F), and Diclazuril (4D) using dosages recommended by manufacturers. Group 3C served as infected-untreated (positive) control. A field efficacy trial in naturally infected rabbits was then undertaken. The results revealed that sulphachloropyrazine and Diclazuril were effective against rabbit clinical coccidiosis by significantly reducing oocyst counts from 149.00+/-110.39 x 10(4) to 3.31+/-0.86 x 10(4) Eimeria spp. oocysts per gram of feces (opg) and 59.70+/-12.35 x 10(4) to 0.0+/-0.0 x 10(4) opg, respectively, in the laboratory trial. Similarly, sulphachloropyrazine and Diclazuril recorded reduced oocyst counts in the field trial from 280.33+/-44.67 x 10(3) to 0.44+/-0.14 x 10(3) opg and 473.44+/-176.01 x 10(3) to 0.0+/-0.0 x 10(3) opg, respectively. Still, sulphachloropyrazine and Diclazuril showed superior efficacy by registering lesion scores and fecal scores close to those of uninfected untreated control group. Trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole recorded a satisfactory efficacy in the field trial by recording reduced oocyst counts from 266.78+/-37.03 x 10(3) to 0.75+/-0.11 x 10(3) opg but was not efficacious in the laboratory trial. Amprolium hydrochloride was not efficacious against clinical coccidiosis in both the experimental and field trials.
Revision of a European Union Official Method to Enforce Legal Provisions: The Case of Diclazuril.[Pubmed:30381090]
J AOAC Int. 2019 Mar 1;102(2):646-652.
Background: Diclazuril is a coccidiostat currently authorized as feed additive in the European Union (EU), with a legal limit set at 1 mg/kg. For official control, an official EU method based on reversed-phase HPLC coupled with UV detection at 280 nm needs to be applied. Recently, the EU Reference Laboratory for feed additives was informed that the recovery rate for Diclazuril was very low when implementing this method and performed experiments demonstrating that the indicated sorbent mass of the solid-phase extraction (SPE) was too low. Objective: Therefore, the paper presents a modified method protocol and the results of an interlaboratory study, performed on two compound feedingstuffs containing Diclazuril around the legal limit. Methods: The official method was modified by using a higher SPE sorbent mass and was further subjected to validation. Results: The obtained values for the relative standard deviation for repeatability were 4.5 and 11.2%, and the corresponding values for the relative standard deviation for reproducibility were 14.3 and 18.1%; the calculated HorRat values were 0.95 and 1.14. Furthermore, acceptable mean recovery values of 98 and 111% were obtained for the two test materials, respectively. Conclusions: Based on the obtained performance profile, it was concluded that the modified official method was fit for purpose. In consequence, the official EU method will be corrected accordingly. Highlights: The highlights of this work are reflected by the following terms, namely Diclazuril, correction of EU official method, and interlaboratory study.
In vitro activity of natural and chemical products on sporulation of Eimeria species oocysts of chickens.[Pubmed:29426468]
Vet Parasitol. 2018 Feb 15;251:12-16.
This study was designed to investigate the ability of two herbal extracts and different chemical substances to inhibit or disrupt sporulation of Eimeria species oocysts of the chickens. The two herbal extracts were Allium sativum (garlic) and Moringa olifiera while the chemical substances included commercial disinfectants and Diclazuril. Field isolates of Eimeria oocysts were propagated in chickens to obtain a continuous source of oocysts. The collected unsporulated oocysts (10(5)oocysts/5ml) were dispensed into 5cm Petri dish. Three replicates were used for each treatment. The treated oocysts were incubated for 48h at 25-29 degrees C and 80% relative humidity. The results showed that herbal extracts, the commercial recommended dose of Dettol, TH4, Phenol, Virkon((R))S, and Diclazuril 20% have no effect on the sporulation. While Sodium hypochlorite showed a significant degree of sporulation inhibition reached to 49.67%. Moreover, 70% ethanol, and 10% formalin showed 100% sporulation inhibition. It was concluded that 70% ethanol and 10% formalin are the most effective methods to inhibit Eimeria species sporulation.


