EperezolidOxazolidinone antibacterial agent CAS# 165800-04-4 |
- Ro 31-8220
Catalog No.:BCC4295
CAS No.:125314-64-9
- Go 6983
Catalog No.:BCC3705
CAS No.:133053-19-7
- Go 6976
Catalog No.:BCC3703
CAS No.:136194-77-9
- Chelerythrine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN8322
CAS No.:3895-92-9
- Dequalinium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4998
CAS No.:522-51-0
- Staurosporine
Catalog No.:BCC3612
CAS No.:62996-74-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 165800-04-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73214 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H23FN4O5 | M.Wt | 394.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | PNU-100592 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 44 mg/mL (111.56 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
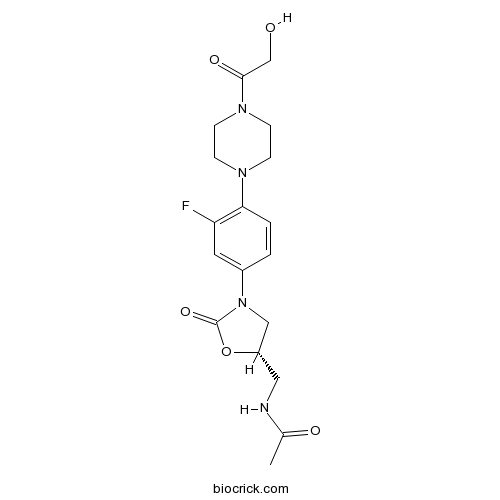
| Chemical Name | N-[[(5S)-3-[3-fluoro-4-[4-(2-hydroxyacetyl)piperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl]methyl]acetamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)NCC1CN(C(=O)O1)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)N3CCN(CC3)C(=O)CO)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SIMWTRCFFSTNMG-AWEZNQCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H23FN4O5/c1-12(25)20-9-14-10-23(18(27)28-14)13-2-3-16(15(19)8-13)21-4-6-22(7-5-21)17(26)11-24/h2-3,8,14,24H,4-7,9-11H2,1H3,(H,20,25)/t14-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Eperezolid(PNU-100592) is a oxazolidinone antibacterial agent, Eperezolid demonstrated good in vitro inhibitory activity, regardless of methicillin susceptibility for staphylococci(MIC90= 1-4 mg/ml).
IC50 value: 1-4 mg/ml (MIC90, staphylococci) [1]
Target: Antibiotic
Eperezolid binds specifically to the 50S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. The specific binding of eperezolid is dose dependent and is proportional to the ribosome concentrations. Scatchard analysis of the binding data reveals that the dissociation constant (Kd) is about 20 microM. The binding of eperezolid to the ribosome is competitively inhibited by chloramphenicol and lincomycin. However, unlike chloramphenicol and lincomycin, eperezolid does not inhibit the puromycin reaction, indicating that the oxazolidinones have no effect on peptidyl transferase [2]. eperezolid was found to bind only to the 50S subunit, with similar affinity as to the 70S ribosome, and to have no affinity for the 30S subunit [3]. References: | |||||

Eperezolid Dilution Calculator

Eperezolid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5355 mL | 12.6775 mL | 25.355 mL | 50.7099 mL | 63.3874 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5071 mL | 2.5355 mL | 5.071 mL | 10.142 mL | 12.6775 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2535 mL | 1.2677 mL | 2.5355 mL | 5.071 mL | 6.3387 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0507 mL | 0.2535 mL | 0.5071 mL | 1.0142 mL | 1.2677 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0254 mL | 0.1268 mL | 0.2535 mL | 0.5071 mL | 0.6339 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
MIC50: 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 1.0, 16.0 and 2.0 mg/L for Pcptostreptococcus, Propionibacterium acnes, Ciostridium pefringens, Clostridium dijiicile, Bactrroidesjagilis, and Fusobacterium, respectivley
Anaerobic bacteria are a common cause of serious infections. Anaerobic species which predominate in clinical infections include the Bacteroides fragilis group, Clostridium spp. and Peptostreptococcus spp. The oxazolidinones are a novel class of synthetic antimicrobials inhibiting the initiation of protein synthesis. Two compounds of this class, eperezolid and linezolid have been shown to inhibit Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium.
In vitro: Ninety per cent of all tested Propionibacterium acnes (30 strains), PeptostreptococccuJ spp. (50 strains), C. perjringens (50 strains) and C. dficile (50 strains) were inhibited by <2 mg>
In vivo: The in vivo effectiveness of eperezolid and linezolid against one strain each of Enterococcus faecalis and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium was examined in a rat intraabdominal abscess model. Eperezolid was ineffective at doses of 25 mg/kg of body weight twice daily for the reductions in abscess bacterial density for E. faecalis. Against E. faecium infections, intravenous eperezolid was effective, reducing densities approximately 2 log10 CFU/g [2].
Clinical trials: Oral administration of eperezolid (1 000 mg PO) to healthy volunteers has earlier been reported to yield peak serum concentration of 6.28 mg/L, respectively, while the trough concentration was estimated to be 1.62 mg/L, respectively [3].
References:
[1] Edlund C, Oh H, Nord CE. In vitro activity of linezolid and eperezolid against anaerobic bacteria. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1999;5(1):51-53.
[2] Schülin T, Thauvin-Eliopoulos C, Moellering RC Jr, Eliopoulos GM. Activities of the oxazolidinones linezolid and eperezolid in experimental intra-abdominal abscess due to Enterococcus faecalis or vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43(12):2873-6.
[3] Schaadt RD, Batts DH, Daley-Yates PT, Pawsey SD, Stalker DJ, Zurenko GE. Serum inhibitory titers and serum bactericidal titers for human subjects receiving multiple doses of the antibacterial oxazolidinones eperezolid and linezolid. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997;28(4):201-4.
- Linezolid
Catalog No.:BCC2496
CAS No.:165800-03-3
- Torososide A
Catalog No.:BCN4694
CAS No.:165689-32-7
- Methyl 6-acetoxyangolensate
Catalog No.:BCN1732
CAS No.:16566-88-4
- L-Stepholidine
Catalog No.:BCN2599
CAS No.:16562-13-3
- 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2511
CAS No.:16561-29-8
- DEPBT
Catalog No.:BCC2811
CAS No.:165534-43-0
- Di-Dnp-L-Lysine
Catalog No.:BCC8939
CAS No.:1655-49-8
- 16-Hydroxy-2-oxocleroda-3,13-dien-15,16-olide
Catalog No.:BCN1536
CAS No.:165459-53-0
- bis[6-(5,6-dihydrochelerythrinyl)]amine
Catalog No.:BCN8232
CAS No.:165393-48-6
- SA 4503 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6339
CAS No.:165377-44-6
- Hemiphroside B
Catalog No.:BCN1731
CAS No.:165338-28-3
- Hemiphroside A
Catalog No.:BCN1730
CAS No.:165338-27-2
- 1-Hydroxy-N-methylacridone
Catalog No.:BCN7551
CAS No.:16584-54-6
- Naltrexone
Catalog No.:BCC1783
CAS No.:16590-41-3
- Calystegine A5
Catalog No.:BCN1887
CAS No.:165905-26-0
- (-)-Tetramisole
Catalog No.:BCC4670
CAS No.:16595-80-5
- Z-Thr-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC2737
CAS No.:16597-50-5
- Cyclogrifolin
Catalog No.:BCN7547
CAS No.:1660156-04-6
- 3,4-O-dimethylcedrusin
Catalog No.:BCN8211
CAS No.:166021-14-3
- Ginkgolic acid C15:0
Catalog No.:BCN2483
CAS No.:16611-84-0
- CCT251545
Catalog No.:BCC6487
CAS No.:1661839-45-7
- Bathophenanthroline
Catalog No.:BCC8840
CAS No.:1662-01-7
- Argentinine
Catalog No.:BCN3987
CAS No.:16625-57-3
- Taberdivarine H
Catalog No.:BCN6958
CAS No.:1662688-34-7
Simple method for the assay of eperezolid in brain heart infusion broth by high-performance liquid chromatography.[Pubmed:15193729]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2004 Jun 29;35(4):847-51.
A sensitive high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method was developed and validated for quantification of Eperezolid in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) broth. Linezolid was employed as internal standard and sample deproteinization with methanol was used. Calibration standards ranged from 0.10 to 20 mg/l. Recovery was approximately 100% at the concentrations examined. Eperezolid was stable in the autosampler vial for at least 72 h at ambient temperature and in BHI broth for 72 h at 37 degrees C. The intra- and inter-day accuracy and reproducibility (relative standard deviation, R.S.D.) were less than 12.3%. This assay is rapid and ideal for analysis of a large number of samples.
Synthesis of eperezolid-like molecules and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities.[Pubmed:23342495]
Bioorg Khim. 2012 Sep-Oct;38(5):610-20.
3-Fluoro-4-(4-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)aniline (II) prepared from 3,4-difluoro nitrobenzene was converted to the corresponding Schiff bases (III) and (IV) by treatment with 4-methoxybenzaldehyde and indol-3-carbaldehyde, respectively. Treatment of amine (II) with 4-fluorophenyl isothiocyanate affordedthe corresponding thiourea derivative (V). Compound (V) was converted to thiazolidinone and thiazoline derivatives (VI) and (VII) by cyclocondensation with ethylbromoacetate or 4-chlorophenacylbromide, respectively. The synthesis of carbothioamide derivative (X) was performed starting from compound (II) by three steps. Treatment of compound (X) with sodium hydroxide, sulfuric acid, or chlorophenacyl bromide generated the corresponding 1,2,4-triazole (XI), 1,3,4-thiadiazole (XII), and 1,3-thiazolidinone (XIII) derivatives, respectively. The structural assignments of new compounds were based on their elemental analysis and spectral (IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, and LC-MS) data. In the antimicrobial activity study all the compounds revealed high anti-Mycobacterium smegmatis activity.
In vitro activity of linezolid and eperezolid, two novel oxazolidinone antimicrobial agents, against anaerobic bacteria.[Pubmed:16887605]
Anaerobe. 1997 Oct;3(5):301-6.
Linezolid (formerly U-100766) and Eperezolid (formerly U-100592) are novel oxazolidinone antimicrobial agents that are active against multi-drug-resistant staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, corynebacteria, and mycobacteria. Preliminary studies also demonstrated that the compounds inhibited some test strains of anaerobic bacteria. Therefore, we extended the in vitro evaluation of these agents to include a total of 54 different anaerobic species. Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values were determined using a standard agar dilution method for 143 anaerobic bacterial isolates. Eperezolid and linezolid demonstrated potent activity against the anaerobic Gram-positive organisms with most MIC values in the range of 0.25-4 microg/mL. Viridans streptococci demonstrated MICs of 1-2 microg/mL; Peptostreptococcus species and Propionibacterium species were inhibited by Eperezolid, especially for Bacteroides species. Linezolid inhibited most bacteroides in the range of 2-8 microg/mL, while Eperezolid was generally two- to eight-fold less active. Linezolid and Eperezolid both demonstrated potent activity against Fusobacterium species,Mobiluncus species,Prevotella intermedia, and Porphyromonas asaccharolytica (MICs of Eperezolid due to its greater activity against Bacteroides species.
Synthesis and antibacterial activities of eperezolid analogs with glycinyl substitutions.[Pubmed:19544480]
Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2009 Jul;342(7):377-85.
A series of Eperezolid analogs with glycinyl substitutions were prepared and their antibacterial activities were studied against a panel of susceptible and resistant Gram-positive bacteria. The compounds with N-arylacyl or N-heteroarylacyl glycinyl structural units showed good antibacterial activities. The compounds 11b, 11c, and 11e were twofold more active than linezolid against Staphylococcus epidermidis and Enterococcus faecalis. Several pyridine analogs were also prepared and found to have poor antibacterial activity against most of the tested Gram-positive bacteria, however, one of the compounds 12e showed very high activity against Enterococcus faecalis.


