EpibrassinolidePotential apoptosis inducer;steroidal plant growth stimulant CAS# 78821-43-9 |
- Flutamide
Catalog No.:BCC4364
CAS No.:13311-84-7
- Cyproterone Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC3758
CAS No.:427-51-0
- Spironolactone
Catalog No.:BCC4366
CAS No.:52-01-7
- TOK-001
Catalog No.:BCC3910
CAS No.:851983-85-2
- MDV3100 (Enzalutamide)
Catalog No.:BCC1268
CAS No.:915087-33-1
- Estradiol valerate
Catalog No.:BCC4482
CAS No.:979-32-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 78821-43-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 443055 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C28H48O6 | M.Wt | 480.68 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 24-Epibrassinolide; B1105; BP55 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 5 mg/mL (10.40 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
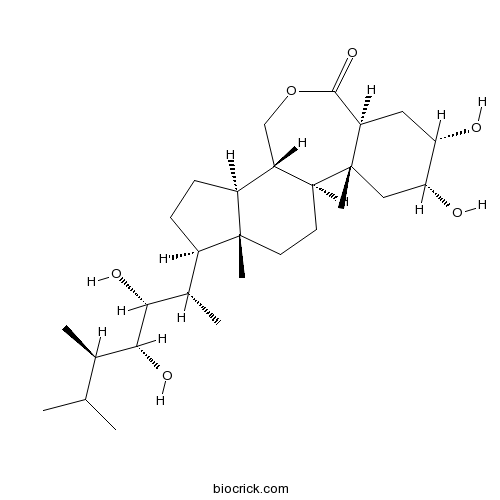
| Chemical Name | (1S,2R,4R,5S,7S,11S,12S,15R,16S)-15-[(2S,3R,4R,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5,6-dimethylheptan-2-yl]-4,5-dihydroxy-2,16-dimethyl-9-oxatetracyclo[9.7.0.02,7.012,16]octadecan-8-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C)C(C(C(C)C1CCC2C1(CCC3C2COC(=O)C4C3(CC(C(C4)O)O)C)C)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IXVMHGVQKLDRKH-QHBHMFGVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H48O6/c1-14(2)15(3)24(31)25(32)16(4)18-7-8-19-17-13-34-26(33)21-11-22(29)23(30)12-28(21,6)20(17)9-10-27(18,19)5/h14-25,29-32H,7-13H2,1-6H3/t15-,16+,17+,18-,19+,20+,21-,22+,23-,24-,25-,27-,28-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Epibrassinolide is a natural brassinosteroid (BR) derivative, is a plant regulator with a similar structure to mammalian steroids. Epibrassinolide is a potential apoptotic inducer in various cancer cells without affecting the non-tumor cell growth.In Vitro:Epibrassinolide (EBR) is a biologically active compound of the brassinosteroids, steroid-derived plant growth regulator family. Cells are incubated with various doses (0-100 μM) of Epibrassinolide for 24 or 48 h and cell viability is determined by MTT assay. Epibrassinolide induced cell viability loss in dose- and time-dependent manner compared to untreated samples in LNCaP and DU145 prostate cancer cells. Increasing concentrations of Epibrassinolide is more effective on LNCaP cell viability loss than DU145 cells suggesting that androgen-dependent cells are more sensitive to Epibrassinolide than androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. In further experiments, 25 μM Epibrassinolide is selected due to its moderate cytotoxic effect on both cell lines. The effect of Epibrassinolide treatment is examined on cell proliferation by counting the cell number within 96 h. A higher and earlier inhibition of cell proliferation is observed in LNCaP than DU145 cells[1]. References: | |||||

Epibrassinolide Dilution Calculator

Epibrassinolide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0804 mL | 10.4019 mL | 20.8039 mL | 41.6077 mL | 52.0097 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4161 mL | 2.0804 mL | 4.1608 mL | 8.3215 mL | 10.4019 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.208 mL | 1.0402 mL | 2.0804 mL | 4.1608 mL | 5.201 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0416 mL | 0.208 mL | 0.4161 mL | 0.8322 mL | 1.0402 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0208 mL | 0.104 mL | 0.208 mL | 0.4161 mL | 0.5201 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Epibrassinolide (EBR; B1105; 24-Epibrassinolide) is a biologically active compound of the brassinosteroids, steroid-derived plant growth regulator family; was shown as a potential apoptotic inducer in various cancer cells without affecting the non-tumor cell growth.
- 4-Benzyloxycarbonyl-2-piperazinone
Catalog No.:BCC8699
CAS No.:78818-15-2
- Zeylenol
Catalog No.:BCC8267
CAS No.:78804-17-8
- Calcitriol D6
Catalog No.:BCC1447
CAS No.:78782-99-7
- Calcifediol-D6
Catalog No.:BCC4075
CAS No.:78782-98-6
- Deapi-platycodin D
Catalog No.:BCN2614
CAS No.:78763-58-3
- TC 1698 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7394
CAS No.:787587-06-8
- Flumazenil
Catalog No.:BCC1259
CAS No.:78755-81-4
- Shizukanolide C
Catalog No.:BCN6570
CAS No.:78749-47-0
- D-AP4
Catalog No.:BCC6549
CAS No.:78739-01-2
- Ozagrel HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4926
CAS No.:78712-43-3
- Plantagoside
Catalog No.:BCN8077
CAS No.:78708-33-5
- 4,4'-Biphenyldicarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8655
CAS No.:787-70-2
- Garcinol
Catalog No.:BCC5623
CAS No.:78824-30-3
- Demethylasterriquinone B1
Catalog No.:BCC7189
CAS No.:78860-34-1
- 1-chloro-6-(5-(prop-1-ynyl)thiophen-2-yl)hexa-3,5-diyn-2-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1352
CAS No.:78876-52-5
- 1-chloro-6-(5-ethynylthiophen-2-yl)hexa-3,5-diyn-2-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1351
CAS No.:78876-53-6
- 6-Thio-dG
Catalog No.:BCC6507
CAS No.:789-61-7
- Orobanone
Catalog No.:BCN3562
CAS No.:78916-35-5
- Deacetylnimbinene
Catalog No.:BCN4578
CAS No.:912545-53-0
- Iloprost
Catalog No.:BCC7247
CAS No.:78919-13-8
- Chicanine
Catalog No.:BCN7818
CAS No.:78919-28-5
- L-AP6
Catalog No.:BCC6612
CAS No.:78944-89-5
- DL-AP7
Catalog No.:BCC6551
CAS No.:78966-69-5
- Guan-fu base G
Catalog No.:BCN8493
CAS No.:78969-72-9
Arsenic-induced genotoxic responses and their amelioration by diphenylene iodonium, 24-epibrassinolide and proline in Glycine max L.[Pubmed:28049059]
Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017 Mar;112:74-86.
Presence of the toxic metalloid, "arsenic (As)" is ubiquitous in the environment especially in the soil and water. Its excess availability in the soil retards growth and metabolism of plants via (a) slowing down the cell division/elongation, (b) overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), (c) modulation of antioxidant enzymes, and (d) alteration of DNA profile/genomic template stability (GTS). In the current study, diphenylene iodonium (DPI), 24-Epibrassinolide (EBL) and proline (Pro) were used to analyze their roles in eliminating the adverse effects of As. Glycine max L. (variety JS 335) seeds were subjected to As (75 muM, Sodium arsenite was used as source of As), and in combination with DPI (10 muM), EBL (0.5 muM) or Pro (10 mM), for five consecutive days, and effects of these treatment combinations were analyzed on germination percentage, biomass, membrane stability, GTS and expressions of defensive genes. In addition, the levels of As, ROS, malondialdehyde, DNA content, oxidation, fragmentation, polymorphism, DNase activity, endogenous Pro and pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase activity were evaluated. The results indicated that the treatments of DPI, EBL or Pro are capable to alleviate detrimental effects of As, gauged from above variables, but with different magnitudes. Apropos As-stress mitigation, Pro was found to be the most effective under the confines of the study protocol. This study certainly provides new ideas for intensifying studies to unravel elusive central mechanism of amelioration involving use of DPI, EBL or Pro in plants with confirmed As-toxicity.
24-epibrassinolide stimulates imidacloprid detoxification by modulating the gene expression of Brassica juncea L.[Pubmed:28245791]
BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Feb 28;17(1):56.
BACKGROUND: Pesticides cause oxidative stress to plants and their residues persist in plant parts, which are a major concern for the environment as well as human health. Brassinosteroids (BRs) are known to protect plants from abiotic stress conditions including pesticide toxicity. The present study demonstrated the effects of seed-soaking with 24-Epibrassinolide (EBR) on physiological responses of 10-day old Brassica juncea seedlings grown under imidacloprid (IMI) toxicity. RESULTS: In the seedlings raised from EBR-treated seeds and grown under IMI toxicity, the contents of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anion (O(.)2(-)) were decreased, accompanied by enhanced activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), guaiacol peroxidase (POD) and the content of glutathione (GSH). As compared to controls, the gene expressions of SOD, CAT, GR, POD, NADH (NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase), CXE (carboxylesterase), GSH-S (glutathione synthase), GSH-T (glutathione transporter-1), P450 (cytochrome P450 monooxygenase) and GST1-3,5-6 were enhanced in the seedlings raised from EBR-treated seeds and grown in IMI supplemented substratum. However, expression of RBO (respiratory burst oxidase, the gene responsible for H2O2 production) was decreased in seedlings raised from EBR treated seeds and grown under IMI toxicity. Further, the EBR seed treatment decreased IMI residues by more than 38% in B. juncea seedlings. CONCLUSIONS: The present study revealed that EBR seed soaking can efficiently reduce oxidative stress and IMI residues by modulating the gene expression of B. juncea under IMI stress. In conclusion, exogenous EBR application can protect plants from pesticide phytotoxicity.
Calreticulin is a fine tuning molecule in epibrassinolide-induced apoptosis through activating endoplasmic reticulum stress in colon cancer cells.[Pubmed:28112451]
Mol Carcinog. 2017 Jun;56(6):1603-1619.
Epibrassinolide (EBR), a member of brassinostreoids plant hormones with cell proliferation promoting role in plants, is a natural polyhydroxysteroid with structural similarity to steroid hormones of vertebrates. EBR has antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing effect in various cancer cells. Although EBR has been shown to affect survival and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathways in a p53-independent manner, the exact molecular targets of EBR are still under investigation. Our recent SILAC (Stable Isotope Labeling by Amino Acids in Cell Culture) data showed that the most significantly altered protein after EBR treatment was calreticulin (CALR). CALR, a chaperone localized in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen, plays role in protein folding and buffering Ca(2+) ions. The alteration of CALR may cause ER stress and unfolded protein response correspondingly the induction of apoptosis. Unfolded proteins are conducted to 26S proteasomal degradation following ubiquitination. Our study revealed that EBR treatment caused ER stress and UPR by altering CALR expression causing caspase-dependent apoptosis in HCT 116, HT29, DLD-1, and SW480 colon cancer cells. Furthermore, 48 h EBR treatment did not caused UPR in Fetal Human Colon cells (FHC) and Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast cells (MEF). In addition our findings showed that HCT 116 colon cancer cells lacking Bax and Puma expression still undergo UPR and related apoptosis. CALR silencing and rapamycin co-treatment prevented EBR-induced UPR and apoptosis, whereas 26S proteasome inhibition further increased the effect of EBR in colon cancer cells. All these findings showed that EBR is an ER stress and apoptotic inducer in colon cancer cells without affecting non-malignant cells.
Exogenously Applied 24-Epibrassinolide (EBL) Ameliorates Detrimental Effects of Salinity by Reducing K+ Efflux via Depolarization-Activated K+ Channels.[Pubmed:28340062]
Plant Cell Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;58(4):802-810.
This study has investigated mechanisms conferring beneficial effects of exogenous application of 24-Epibrassinolides (EBL) on plant growth and performance under saline conditions. Barley seedlings treated with 0.25 mg l-1 EBL showed significant improvements in root hair length, shoot length, shoot fresh weight and relative water content when grown in the presence of 150 mM NaCl in the growth medium. In addition, EBL treatment significantly decreased the Na+ content in both shoots (by approximately 50%) and roots. Electrophysiological experiments revealed that pre-treatment with EBL for 1 and 24 h suppressed or completely prevented the NaCl-induced K+ leak in the elongation zone of barley roots, but did not affect root sensitivity to oxidative stress. Further experiments using Arabidopsis loss-of-function gork1-1 (lacking functional depolarization-activated outward-rectifying K+ channels in the root epidermal cells) and akt1 (lacking inward-rectifying K+ uptake channel) mutants showed that NaCl-induced K+ loss in the elongation zone of roots was reduced by EBL pre-treatment 50- to 100-fold in wild-type Col-0 and akt1, but only 10-fold in the gork1-1 mutant. At the same time, EBL treatment shifted vanadate-sensitive H+ flux towards net efflux. Taken together, these data indicate that exogenous application of EBL effectively improves plant salinity tolerance by prevention of K+ loss via regulating depolarization-activated K+ channels.


