GNF-7Type II Bcr-Abl inhibitor CAS# 839706-07-9 |
- Lestaurtinib
Catalog No.:BCC2440
CAS No.:111358-88-4
- GW441756
Catalog No.:BCC5093
CAS No.:504433-23-2
- TLQP 21
Catalog No.:BCC2405
CAS No.:869988-94-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 839706-07-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11478363 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C28H24F3N7O2 | M.Wt | 547.53 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 33 mg/mL (60.27 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
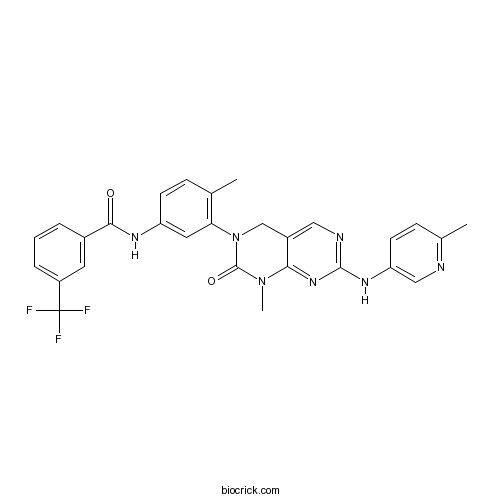
| Chemical Name | N-[4-methyl-3-[1-methyl-7-[(6-methylpyridin-3-yl)amino]-2-oxo-4H-pyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidin-3-yl]phenyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC(=CC=C2)C(F)(F)F)N3CC4=CN=C(N=C4N(C3=O)C)NC5=CN=C(C=C5)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SZNYUUZOQHNEKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H24F3N7O2/c1-16-7-9-21(34-25(39)18-5-4-6-20(11-18)28(29,30)31)12-23(16)38-15-19-13-33-26(36-24(19)37(3)27(38)40)35-22-10-8-17(2)32-14-22/h4-14H,15H2,1-3H3,(H,34,39)(H,33,35,36) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ras signaling inhibitor; inhibits Ack1 and germinal center kinase (GCK). Suppresses proliferation, and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in leukemia cells harboring NRAS mutations. Prolongs survival in a leukemia cell xenotransplantation model in mice. |

GNF-7 Dilution Calculator

GNF-7 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8264 mL | 9.1319 mL | 18.2638 mL | 36.5277 mL | 45.6596 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3653 mL | 1.8264 mL | 3.6528 mL | 7.3055 mL | 9.1319 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1826 mL | 0.9132 mL | 1.8264 mL | 3.6528 mL | 4.566 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0365 mL | 0.1826 mL | 0.3653 mL | 0.7306 mL | 0.9132 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0183 mL | 0.0913 mL | 0.1826 mL | 0.3653 mL | 0.4566 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: The IC50 of GNF-7 is 0.005, 0.001, and 0.008 μM in Colo205, SW620, and TrkC-Ba/F3 cells, respectively.
GNF-7 is the type-II inhibitor of T315I-Bcr-Abl [1]. BCR-ABL, constitutively activated tyrosine kinase, is an oncogene associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and some cases of acute lymphocytic leukemia in humans.
In vitro: GNF-7 showed excellent growth inhibitory activity against some human cancer cells. The IC50 of GNF-7 is 0.005, 0.001, and 0.008 μM when tested in Colo205, SW620, and TrkC-Ba/F3 cell line, respectively. GNF-7 showed little effect on HEK293T cells, a normal cell line [1]. After treated for 24 h (7.5 mg/kg QD or 15 mg/kg QD), GNF-7 significantly decreased disease burden in mice and prolonged overall survival compared to vehicle-controls [2].
In vivo: In acute myelogenous leukemia and lymphoblastic leukemia models, GNF-7 potently and selectively inhibited NRAS-dependent cells [2]. In the T315I-Bcr-Abl-Ba/F3 cell line bioluminescent xenograft mouse model, oral administration of GNF-7 with 10 or 20 mg/kg exhibited significant efficacy against T315I-Bcr-Abl without appreciable toxicity [1].
References:
1. Choi H G, Ren P, Adrian F, et al. A type-II kinase inhibitor capable of inhibiting the T315I “gatekeeper” mutant of Bcr-Abl[J]. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2010, 53(15): 5439-5448.
2. Nonami A, Sattler M, Weisberg E, et al. Identification of novel therapeutic targets in acute leukemias with NRAS mutations using a pharmacologic approach[J]. Blood, 2015, 125(20): 3133-3143.
- 4-Epicommunic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4382
CAS No.:83945-57-7
- Flavidinin
Catalog No.:BCN3599
CAS No.:83925-00-2
- Flavidin
Catalog No.:BCN6438
CAS No.:83924-98-5
- Mometasone furoate
Catalog No.:BCC4801
CAS No.:83919-23-7
- Isogomisin O
Catalog No.:BCN4381
CAS No.:83916-76-1
- 13-Hydroxylabda-8(17),14-dien-18-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1332
CAS No.:83915-59-7
- 12-Acetoxyabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4380
CAS No.:83905-81-1
- Gramodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2155
CAS No.:83905-67-3
- Azithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC4385
CAS No.:83905-01-5
- TCS 2312
Catalog No.:BCC7541
CAS No.:838823-31-7
- WIKI4
Catalog No.:BCC2455
CAS No.:838818-26-1
- Cetirizine DiHCl
Catalog No.:BCC4517
CAS No.:83881-52-1
- Pluripotin
Catalog No.:BCC6178
CAS No.:839707-37-8
- 2,7-Dimethyl-1,4-dihydroxynaphthalene 1-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7611
CAS No.:839711-70-5
- Cariprazine
Catalog No.:BCC1453
CAS No.:839712-12-8
- Hexestrol
Catalog No.:BCC4484
CAS No.:84-16-2
- Rutaecarpine
Catalog No.:BCN4385
CAS No.:84-26-4
- Ophiohayatone C
Catalog No.:BCN3608
CAS No.:84-33-3
- Syrosingopine
Catalog No.:BCN5365
CAS No.:84-36-6
- Stylopine
Catalog No.:BCN3715
CAS No.:84-39-9
- Tectoquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3481
CAS No.:84-54-8
- Anthraflavic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8831
CAS No.:84-60-6
- Anthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8832
CAS No.:84-65-1
- Diisobutyl phthalate
Catalog No.:BCN7148
CAS No.:84-69-5
First SAR Study for Overriding NRAS Mutant Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia.[Pubmed:30153003]
J Med Chem. 2018 Sep 27;61(18):8353-8373.
GNF-7, a multitargeted kinase inhibitor, served as a dual kinase inhibitor of ACK1 and GCK, which provided a novel therapeutic strategy for overriding AML expressing NRAS mutation. This SAR study with GNF-7 derivatives, designed to target NRAS mutant-driven AML, led to identification of the extremely potent inhibitors, 10d, 10g, and 11i, which possess single-digit nanomolar inhibitory activity against both ACK1 and GCK. These substances strongly suppress proliferation of mutant NRAS expressing AML cells via apoptosis and AKT/mTOR signaling blockade. Compound 11i is superior to GNF-7 in terms of kinase inhibitory activity, cellular activity, and differential cytotoxicity. Moreover, 10k possessing a favorable mouse pharmacokinetic profile prolonged life-span of Ba/F3-NRAS-G12D injected mice and significantly delayed tumor growth of OCI-AML3 xenograft model without causing the prominent level of toxicity found with GNF-7. Taken together, this study provides insight into the design of novel ACK1 and GCK dual inhibitors for overriding NRAS mutant-driven AML.
Discovery of 2-((3-Amino-4-methylphenyl)amino)-N-(2-methyl-5-(3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamido)phe nyl)-4-(methylamino)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide (CHMFL-ABL-053) as a Potent, Selective, and Orally Available BCR-ABL/SRC/p38 Kinase Inhibitor for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.[Pubmed:26789553]
J Med Chem. 2016 Mar 10;59(5):1984-2004.
Starting from a dihydropyrimidopyrimidine core scaffold based compound 27 (GNF-7), we discovered a highly potent (ABL1: IC50 of 70 nM) and selective (S score (1) = 0.02) BCR-ABL inhibitor 18a (CHMFL-ABL-053). Compound 18a did not exhibit apparent inhibitory activity against c-KIT kinase, which is the common target of currently clinically used BCR-ABL inhibitors. Through significant suppression of the BCR-ABL autophosphorylation (EC50 about 100 nM) and downstream mediators such as STAT5, Crkl, and ERK's phosphorylation, 18a inhibited the proliferation of CML cell lines K562 (GI50 = 14 nM), KU812 (GI50 = 25 nM), and MEG-01 (GI50 = 16 nM). A pharmacokinetic study revealed that 18a had over 4 h of half-life and 24% bioavailability in rats. A 50 mg/kg/day dosage treatment could almost completely suppress tumor progression in the K562 cells inoculated xenograft mouse model. As a potential useful drug candidate for CML, 18a is under extensive preclinical safety evaluation now.
Hybrid pyrimidine alkynyls inhibit the clinically resistance related Bcr-Abl(T315I) mutant.[Pubmed:26195136]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Sep 1;25(17):3458-63.
A series of pyrimidine alkynyl derivatives were designed and synthesized as new Bcr-Abl inhibitors by hybriding the structural moieties from GNF-7, ponatinib and nilotinib. One of the most potent compounds 4e strongly suppresses Bcr-Abl(WT) and Bcr-Abl(T315I) kinase with IC50 values of 5.0 and 9.0 nM, and inhibits the proliferation of K562 and murine Ba/F3 cells ectopically expressing Bcr-Abl(T315I) cells with IC50 values of 2 and 50 nM, respectively. It also displays good pharmacokinetics properties with an oral bioavailability of 35.3% and T(1/2) value of 48.7 h, and demonstrates significantly suppression on tumor growth in xenografted mice of K562 and Ba/F3 cells expressing Bcr-Abl(T315I). These inhibitors may serve as lead compounds for further developing new anticancer drugs overcoming the clinically acquired resistance against current Bcr-Abl inhibitors.
Identification of novel therapeutic targets in acute leukemias with NRAS mutations using a pharmacologic approach.[Pubmed:25833960]
Blood. 2015 May 14;125(20):3133-43.
Oncogenic forms of NRAS are frequently associated with hematologic malignancies and other cancers, making them important therapeutic targets. Inhibition of individual downstream effector molecules (eg, RAF kinase) have been complicated by the rapid development of resistance or activation of bypass pathways. For the purpose of identifying novel targets in NRAS-transformed cells, we performed a chemical screen using mutant NRAS transformed Ba/F3 cells to identify compounds with selective cytotoxicity. One of the compounds identified, GNF-7, potently and selectively inhibited NRAS-dependent cells in preclinical models of acute myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mechanistic analysis revealed that its effects were mediated in part through combined inhibition of ACK1/AKT and of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 2 (germinal center kinase). Similar to genetic synthetic lethal approaches, these results suggest that small molecule screens can be used to identity novel therapeutic targets in cells addicted to RAS oncogenes.
A type-II kinase inhibitor capable of inhibiting the T315I "gatekeeper" mutant of Bcr-Abl.[Pubmed:20604564]
J Med Chem. 2010 Aug 12;53(15):5439-48.
The second generation of Bcr-Abl inhibitors nilotinib, dasatinib, and bosutinib developed to override imatinib resistance are not active against the T315I "gatekeeper" mutation. Here we describe a type-II T315I inhibitor 2 (GNF-7), based upon a 3,4-dihydropyrimido[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2(1H)-one scaffold which is capable of potently inhibiting wild-type and T315I Bcr-Abl as well as other clinically relevant Bcr-Abl mutants such as G250E, Q252H, Y253H, E255K, E255V, F317L, and M351T in biochemical and cellular assays. In addition, compound 2 displayed significant in vivo efficacy against T315I-Bcr-Abl without appreciable toxicity in a bioluminescent xenograft mouse model using a transformed T315I-Bcr-Abl-Ba/F3 cell line that has a stable luciferase expression. Compound 2 is among the first type-II inhibitors capable of inhibiting T315I to be described and will serve as a valuable lead to design the third generation Bcr-Abl kinase inhibitors.


