H 89 2HClPotent PKA inhibitor CAS# 130964-39-5 |
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Hydroxyfasudil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1636
CAS No.:155558-32-0
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 130964-39-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5702541 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H22BrCl2N3O2S | M.Wt | 519.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Protein kinase inhibitor H-89 dihydrochloride | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (96.29 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
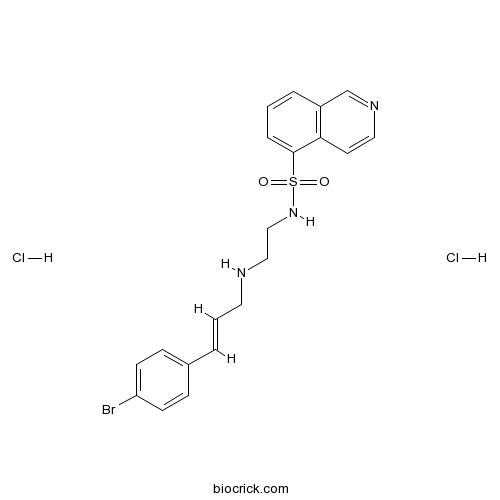
| Chemical Name | N-[2-[[(E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)prop-2-enyl]amino]ethyl]isoquinoline-5-sulfonamide;dihydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC2=C(C=CN=C2)C(=C1)S(=O)(=O)NCCNCC=CC3=CC=C(C=C3)Br.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GELOGQJVGPIKAM-WTVBWJGASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H20BrN3O2S.2ClH/c21-18-8-6-16(7-9-18)3-2-11-22-13-14-24-27(25,26)20-5-1-4-17-15-23-12-10-19(17)20;;/h1-10,12,15,22,24H,11,13-14H2;2*1H/b3-2+;; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Protein kinase A inhibitor that also inhibits several other kinases (IC50 values are 80, 120, 135, 270, 2600 and 2800 nM for S6K1, MSK1, PKA, ROCKII, PKBα and MAPKAP-K1b). Exhibits antinociceptive activity. Also available as part of the PKATM. |

H 89 2HCl Dilution Calculator

H 89 2HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9257 mL | 9.6287 mL | 19.2574 mL | 38.5149 mL | 48.1436 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3851 mL | 1.9257 mL | 3.8515 mL | 7.703 mL | 9.6287 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1926 mL | 0.9629 mL | 1.9257 mL | 3.8515 mL | 4.8144 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0385 mL | 0.1926 mL | 0.3851 mL | 0.7703 mL | 0.9629 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0193 mL | 0.0963 mL | 0.1926 mL | 0.3851 mL | 0.4814 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
H 89 2HCl is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase A (Ki values= 48 nM).
PKA (protein kinase A), also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase, is composed of two regulatory subunits and two catalytic subunits. It has several cellular functions including regulation of glycogen, glucose and lipid metabolism.
In PC12 cells treated with H-89 and nerve growth factor, forskolin and dibutyryl cAMP. H-89 caused a forskolin-induced protein phosporlylation inhibition in a dose-dependent manner. This inhibition also occurred when H-89 was added before the addition of dibutyryl cAMP. Pretreatment of PC12D cells with H-89 (30 mM) inhibited significantly cAMP-dependent histone IIb phosphorylation activity in cell lysates but did not affect other protein phosphorylation activity. [1]
H89 was also used as a tool to determine whether differential profiling of tissue phosphoproteins can be used to detect treatment-related effects of a protein kinase A inhibitor in vivo with rat liver. [2]
References:
1. Chijiwa T, Mishima A, Hagiwara M et al. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and
protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5267-72.
Davis MA, Hinerfeld D, Joseph S et al. Proteomic analysis of rat liver phosphoproteins after treatment with protein kinase inhibitor H89 (N-(2-[p-bromocinnamylamino-]ethyl)-5-isoquinoline
-sulfonamide). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Aug;318(2):589-95.
- Marumoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7702
CAS No.:1309604-34-9
- Wittifuran X
Catalog No.:BCN4794
CAS No.:1309478-07-6
- K145
Catalog No.:BCC4305
CAS No.:1309444-75-4
- GPR40 Activator 1
Catalog No.:BCC4125
CAS No.:1309435-60-6
- Cerberic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN4715
CAS No.:1309362-77-3
- CX-4945 sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5586
CAS No.:1309357-15-0
- Entacapone
Catalog No.:BCC2217
CAS No.:130929-57-6
- 7-O-Acetylneocaesalpin N
Catalog No.:BCN7332
CAS No.:1309079-08-0
- N4-Benzoylcytidine
Catalog No.:BCC9072
CAS No.:13089-48-0
- Fmoc-Val-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3572
CAS No.:130878-68-1
- 1beta,10beta-Epoxydehydroleucodin
Catalog No.:BCN7331
CAS No.:130858-00-3
- ent-kaurane-3,16,17-triol
Catalog No.:BCN6164
CAS No.:130855-22-0
- (±)-CPSI 1306
Catalog No.:BCC6161
CAS No.:1309793-47-2
- Sephin1
Catalog No.:BCC3980
CAS No.:13098-73-2
- MRS 4062 triethylammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6134
CAS No.:1309871-50-8
- 15-Methoxymkapwanin
Catalog No.:BCN6498
CAS No.:1309920-99-7
- VU 0360172 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6141
CAS No.:1309976-62-2
- alpha-Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN6166
CAS No.:131-03-3
- Dimethyl phthalate
Catalog No.:BCN6167
CAS No.:131-11-3
- Pimpinellin
Catalog No.:BCN6168
CAS No.:131-12-4
- N-Acetylneuraminic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2204
CAS No.:131-48-6
- Oxybenzone
Catalog No.:BCC5445
CAS No.:131-57-7
- Meptyldinocap
Catalog No.:BCC5468
CAS No.:131-72-6
- 8-Epiloganic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8956
CAS No.:82509-41-9
The many faces of H89: a review.[Pubmed:17214602]
Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2006 Fall-Winter;24(3-4):261-74.
H89 is marketed as a selective and potent inhibitor of protein kinase A (PKA). Since its discovery, it has been used extensively for evaluation of the role of PKA in the heart, osteoblasts, hepatocytes, smooth muscle cells, neuronal tissue, epithelial cells, etc. Despite the frequent use of H89, its mode of specific inhibition of PKA is still not completely understood. It has also been shown that H89 inhibits at least 8 other kinases, while having a relatively large number of PKA-independent effects which may seriously compromise interpretation of data. Thus, while recognizing its kinase inhibiting properties, it is advised that H89 should not be used as the single source of evidence of PKA involvement. H-89 should be used in conjunction with other PKA inhibitors, such as Rp-cAMPS or PKA analogs.
Involvement of cAMP response element-binding protein activation in salivary secretion.[Pubmed:16785762]
Pathobiology. 2006;73(1):1-7.
OBJECTIVE: Saliva secretion is mediated by cAMP and the calcium signaling pathway in salivary acinar cells. The PKA signaling pathway plays an important role in protein secretion through the activation of cAMP, in fluid secretion through the elevation of intracellular calcium and in the activation of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB), which is involved in these signaling cascades. In this study, we investigated whether the activation of CREB plays a part in the salivary secretion in mice. METHODS: We examined CREB activation by assessing phosphorylation at the serine-133 position using Western blotting. RESULTS: Carbachol (a muscarinic acetylcholine agonist) and isoproterenol (a beta-adrenergic agonist) markedly activated CREB in parotid acinar cells. Carbachol and isoproterenol-induced CREB phosphorylation was blocked by atropine (a muscarinic acetylcholine antagonist) and propranolol (a beta-adrenergic antagonist), respectively. The PKA inhibitor H89 inhibited CREB activation, but the PLC inhibitor U73122 did not. Moreover, carbachol- and isoproterenol-stimulated amylase secretion from parotid acinar cells was inhibited by H89 and adenoviral dominant-negative CREB. CONCLUSION: These results indicate that the muscarinic and beta-adrenergic activation of CREB was mediated through the PKA pathway and that CREB is involved in protein secretion from parotid acinar cells.
Amyloid beta -peptide inhibition of the PKA/CREB pathway and long-term potentiation: reversibility by drugs that enhance cAMP signaling.[Pubmed:12244210]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):13217-21.
Changes in hippocampal function seem critical for cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Although there is eventual loss of synapses in both AD and animal models of AD, deficits in spatial memory and inhibition of long-term potentiation (LTP) precede morphological alterations in the models, suggesting earlier biochemical changes in the disease. In the studies reported here we demonstrate that amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta) treatment of cultured hippocampal neurons leads to the inactivation of protein kinase A (PKA) and persistence of its regulatory subunit PKAIIalpha. Consistent with this, CREB phosphorylation in response to glutamate is decreased, and the decrease is reversed by rolipram, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor that raises cAMP and leads to the dissociation of the PKA catalytic and regulatory subunits. It is likely that a similar mechanism underlies Alphabeta inhibition of LTP, because rolipram and forskolin, agents that enhance the cAMP-signaling pathway, can reverse this inhibition. This reversal is blocked by H89, an inhibitor of PKA. These observations suggest that Alphabeta acts directly on the pathways involved in the formation of late LTP and agents that enhance the cAMP/PKA/CREB-signaling pathway have potential for the treatment of AD.
Biphasic modulation of nociceptive processing by the cyclic AMP-protein kinase A signalling pathway in sheep spinal cord.[Pubmed:11514065]
Neurosci Lett. 2001 Aug 31;309(3):157-60.
A role for the cyclic AMP (cAMP)-protein kinase A (PKA) transduction cascade in nociceptive processing has been identified. This study examined the effects of intrathecal treatment with the cAMP analogue 8-Bromo-cAMP and the PKA inhibitor H-89 dihydrochloride on nociceptive thresholds to mechanical stimulation in six adult sheep to define further the role of cAMP in spinal nociception. Treatment with 420 nmol 8-Br-cAMP induced significant hypoalgesia to noxious stimulation, while a 10-fold higher dose (4.2 micromol) induced mechanical hyperalgesia. Both of these behaviours were blocked by H-89 (38-380 nmol). Treatment with high dose H-89 (380 nmol) alone significantly increased nociceptive thresholds. These results demonstrate that activation of the cAMP-PKA signalling pathway modulates acute nociceptive events in spinal cord in a biphasic manner, and suggest that significant tonic activity exists in this pathway.


