(-)-Huperzine ANMDA receptor antagonist/AChE inhibitor CAS# 102518-79-6 |
- DAPT (GSI-IX)
Catalog No.:BCC3618
CAS No.:208255-80-5
- Semagacestat (LY450139)
Catalog No.:BCC3610
CAS No.:425386-60-3
- AR-A014418
Catalog No.:BCC1366
CAS No.:487021-52-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 102518-79-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 854026 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C15H18N2O | M.Wt | 242.32 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Huperzine A;(-)-huperzine A;(-)-huperazine A;Selagine | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (412.68 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
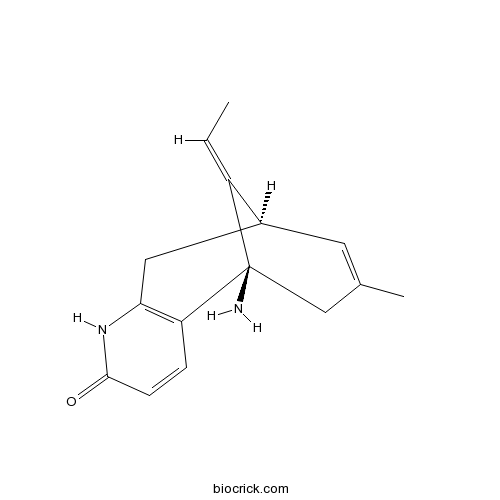
| Chemical Name | (1R,9R,13E)-1-amino-13-ethylidene-11-methyl-6-azatricyclo[7.3.1.02,7]trideca-2(7),3,10-trien-5-one | ||
| SMILES | CC=C1C2CC3=C(C1(CC(=C2)C)N)C=CC(=O)N3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZRJBHWIHUMBLCN-YQEJDHNASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H18N2O/c1-3-11-10-6-9(2)8-15(11,16)12-4-5-14(18)17-13(12)7-10/h3-6,10H,7-8,16H2,1-2H3,(H,17,18)/b11-3+/t10-,15+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | (-)-Huperzine A is a naturally occurring potent reversible AChE inhibitor that penetrates the blood-brain barrier, it also has several neuroprotective effects including modification of beta-amyloid peptide, reduction of oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and induction and regulation of nerve growth factor. |
| Targets | AChE | NGF | NMDA receptor |
| In vivo | A combination of [+] and [-]-Huperzine A improves protection against soman toxicity compared to [+]-Huperzine A in guinea pigs.[Pubmed: 23123250]Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Mar 25;203(1):120-4.The neuropathologic mechanisms after exposure to lethal doses of nerve agent are complex and involve multiple biochemical pathways. Effective treatment requires drugs that can simultaneously protect by reversible binding to the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and blocking cascades of seizure related brain damage, inflammation, neuronal degeneration as well as promoting induction of neuroregeneration. (-)-Huperzine A ([-]-Hup A), is a naturally occurring potent reversible AChE inhibitor that penetrates the blood-brain barrier. It also has several neuroprotective effects including modification of beta-amyloid peptide, reduction of oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and induction and regulation of nerve growth factor.
|
| Structure Identification | Org Lett. 2013 Feb 15;15(4):882-5.A novel synthesis of (-)-huperzine A via tandem intramolecular aza-Prins cyclization-cyclobutane fragmentation.[Pubmed: 23346936]The acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (-)-Huperzine A was synthesized from (S)-4-hydroxycyclohex-2-enone in 17 steps by a route that involved two cyclobutane fragmentations. The first of these employed a retro-aldol cleavage to generate the α-pyridone ring of huperzine A, and the second invoked a novel intramolecular aza-Prins reaction in tandem with stereocontrolled scission of a cyclobutylcarbinyl cation to create the aminobicyclo[3.3.1]nonene framework of the natural alkaloid. Org Lett. 2012 Sep 7;14(17):4446-9.An efficient total synthesis of (-)-huperzine A.[Pubmed: 22900755]The total synthesis of Lycopodium alkaloid (-)-Huperzine A has been accomplished in 10 steps with 17% overall yield from commercially abundant (R)-pulegone. The synthetic route features an efficient synthesis of 4 via a Buchwald-Hartwig coupling reaction, a dianion-mediated highly stereoselective alkylation of 4, and a rare example of an intramolecular Heck reaction of an enamine-type substrate. The stereoselective β-elimination and the accompanying Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement are of particular interest. |

(-)-Huperzine A Dilution Calculator

(-)-Huperzine A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1268 mL | 20.6339 mL | 41.2677 mL | 82.5355 mL | 103.1694 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8254 mL | 4.1268 mL | 8.2535 mL | 16.5071 mL | 20.6339 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4127 mL | 2.0634 mL | 4.1268 mL | 8.2535 mL | 10.3169 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0825 mL | 0.4127 mL | 0.8254 mL | 1.6507 mL | 2.0634 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0413 mL | 0.2063 mL | 0.4127 mL | 0.8254 mL | 1.0317 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
Three different models were used to evaluate the intestinal permeability of huperzine A, including in vitro Caco-2 and parallel artificial membrane permeation assay models and the ex vivo Ussing chamber model, in which results suggest the permeability rate was strongly ionization dependent and increased with elevation of the donor medium PH. Though the majority of huperzine A passes through intestinal border through passive transcellular diffusion, a small fraction depending on the degree of ionization is absorbed by the paracellular route.
Abstract
Huperzine A, an AchEl used to treat cognitive deterioration associated with AD, has side effects associated with increased cholinergic activity in the gastrointestinal system. Following oral administration of huperine A to mice, a single dose significantly inhibited the AChE activity in the stomach and duodenum and significantly increased the gastrointestinal motility; while multiple doses caused no significant changes in both.
Abstract
Cineole and terpineol synergistically increased the transdermal delivery of huperzine from microemulsions in Franz-type diffusion cells through increasing the partition and diffusion coefficients of huperzine A, in which ATR-FTIR analysis revealed the mechanism of the synergistic effects was due to increasing the disorderliness and fluidity of SC lipid alkyl chains, disrupting the structure of keratin in SC, and extracting SC lipids.
Abstract
Huperzine A is a novel reversible and selective AchE inhibition that is isolated from Chinese herb Hyperzia serrate (Thunb) Trev.
Abstract
As a drug extracted from a Chinese herb to treat Alzheimer’s disease, huperzine A was evaluated for its beneficial and harmful effects.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(−)-Huperzine A (HupA) is an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor with an IC50 value of 82 nmol/L [1] and acts as an antagonist of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor [2].
AChE is the key brain enzyme responsible for the rapid degradation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. AChE inhibitors are probably useful in the amelioration of the Alzheimer’s symptomatology [3].
It was found that NMDA markedly reduced AChE activities [4]. In rat dissociated hippocampal neurons, HupA inhibited the NMDA-induced current. In neurons, 100 µM HupA, NMDA-induced currents were 55.7 ± 4.9% of the control values. The binding molecular ratio of NMDA receptor: HupA is 1:1. The inhibition of NMDA receptor by HupA is not competitive [5]. HupA significantly increased the phosphorylation levels of both glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3α protein and GSK-3β protein in APPsw-overexpressing cells [2]. Activated GSK-3 consequently decreased acetylcholine (ACh) level in the striatum [6].
Treated with doses of (−)-huperzine A, AChE−/− mice showed no toxic symptoms and had normal levels of AChE. This demonstrated the specificity of (−)-huperzine A as an inhibitor of AChE at the dose used in vivo [7]. In rat whole brain, oral administration of HupA at a dose of 1.5 μmol/kg (3.6 mg/kg) obtained a maximum inhibition of AChE at 60 min and this maximum inhibition was maintained for 360 min [8].
References:
[1]. MA Xiao-Chao, XIN Jian, WANG Hai-Xue, et al. Acute effects of huperzine A and tacrine on rat liver. Acta Pharmacol ogica Sinica, 2003, 24(3):247-250.
[2]. Zhong Ming Qian and Ya Ke. Huperzine A: is it an effective disease-modifying drug for Alzheimer's disease? Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2014, 6:216.
[3]. V. Rajendran, Suo-Bao Rong, Ashima Saxena, et al. Synthesis of a hybrid analog of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors huperzine A and huperzine B. Tetrahedron Letters, 2001, 42: 5359-5361.
[4]. J. R. Delfs, D. M. Saroff, Y. Nishida, et al. Effects of NMDA and its antagonists on ventral horn cholinergic neurons in organotypic roller tube spinal cord cultures. J. Neural Transm., 1997, 104(1):31-51.
[5]. J. M. Zhang and G. Y. Hu. Huperzine A, a nootropic alkaloid, inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced current in rat dissociated hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience, 2001, 105(3):663-9.
[6]. L. Zhao, C. B. Chu, J. F. Li, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 reduces acetylcholine level in striatum via disturbing cellular distribution of choline acetyltransferase in cholinergic interneurons in rats. Neuroscience, 2013, 255:203-11.
[7]. Ellen G. Duysen, Bin Li, Sultan Darvesh, et al. Sensitivity of butyrylcholinesterase knockout mice to (−)-huperzine A and donepezil suggests humans with butyrylcholinesterase deficiency may not tolerate these Alzheimer’s disease drugs and indicates butyrylcholinesterase function in neurotransmission. Toxicology, 2007, 233:60-69.
[8]. Rui Wang, Han Yan and Xi-can Tang. Progress in studies of huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2006, 27:1-26.
- SGI-1776 free base
Catalog No.:BCC2232
CAS No.:1025065-69-3
- Periglaucine B
Catalog No.:BCN7053
CAS No.:1025023-05-5
- Periglaucine A
Catalog No.:BCN5839
CAS No.:1025023-04-4
- GK921
Catalog No.:BCC8057
CAS No.:1025015-40-0
- Kushenol N
Catalog No.:BCN2984
CAS No.:102490-65-3
- RN 1747
Catalog No.:BCC7769
CAS No.:1024448-59-6
- Fmoc-Phg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3312
CAS No.:102410-65-1
- Jasplakinolide
Catalog No.:BCC7485
CAS No.:102396-24-7
- AF-DX 116
Catalog No.:BCC6939
CAS No.:102394-31-0
- Glyburide
Catalog No.:BCC4784
CAS No.:10238-21-8
- Negsehisandrin G
Catalog No.:BCN2674
CAS No.:1023744-69-5
- Naringin
Catalog No.:BCN6312
CAS No.:10236-47-2
- 2,3,23-Trihydroxy-12-oleanen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1638
CAS No.:102519-34-6
- R788 disodium
Catalog No.:BCC3695
CAS No.:1025687-58-4
- Methyl lucidente G
Catalog No.:BCN8269
CAS No.:102607-20-5
- Ganoderic acid L
Catalog No.:BCN8204
CAS No.:102607-24-9
- Saprorthoquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3147
CAS No.:102607-41-0
- Pantoprazole
Catalog No.:BCC5432
CAS No.:102625-70-7
- SC-9
Catalog No.:BCC6646
CAS No.:102649-78-5
- SC-10
Catalog No.:BCC6643
CAS No.:102649-79-6
- RO-3
Catalog No.:BCC7548
CAS No.:1026582-88-6
- LB-100
Catalog No.:BCC5532
CAS No.:1026680-07-8
- Labd-13-ene-8,15-diol
Catalog No.:BCN5840
CAS No.:10267-31-9
- VX-222 (VCH-222, Lomibuvir)
Catalog No.:BCC2108
CAS No.:1026785-59-0
A novel synthesis of (-)-huperzine A via tandem intramolecular aza-Prins cyclization-cyclobutane fragmentation.[Pubmed:23346936]
Org Lett. 2013 Feb 15;15(4):882-5.
The acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (-)-Huperzine A was synthesized from (S)-4-hydroxycyclohex-2-enone in 17 steps by a route that involved two cyclobutane fragmentations. The first of these employed a retro-aldol cleavage to generate the alpha-pyridone ring of huperzine A, and the second invoked a novel intramolecular aza-Prins reaction in tandem with stereocontrolled scission of a cyclobutylcarbinyl cation to create the aminobicyclo[3.3.1]nonene framework of the natural alkaloid.
Total synthesis of (-)-huperzine A.[Pubmed:19873983]
Org Lett. 2009 Nov 19;11(22):5354-6.
The total synthesis of (-)-Huperzine A was accomplished in 23 steps from a commercially available anhydride. Our synthetic route features a facile construction of the bicyclo[3.3.1] skeleton equipped with proper functionalities to introduce the remaining substructures.
A combination of [+] and [-]-Huperzine A improves protection against soman toxicity compared to [+]-Huperzine A in guinea pigs.[Pubmed:23123250]
Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Mar 25;203(1):120-4.
The neuropathologic mechanisms after exposure to lethal doses of nerve agent are complex and involve multiple biochemical pathways. Effective treatment requires drugs that can simultaneously protect by reversible binding to the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and blocking cascades of seizure related brain damage, inflammation, neuronal degeneration as well as promoting induction of neuroregeneration. [-]-Huperzine A ([-]-Hup A), is a naturally occurring potent reversible AChE inhibitor that penetrates the blood-brain barrier. It also has several neuroprotective effects including modification of beta-amyloid peptide, reduction of oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and induction and regulation of nerve growth factor. Toxicities at higher doses restrict the neuroporotective ability of [-]-Hup A for treatment. The synthetic stereoisomer, [+]-Hup A, is less toxic due to poor AChE inhibition and is suitable for both pre-/post-exposure treatments of nerve agent toxicity. [+]-Hup A block the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-induced seizure in rats, reduce excitatory amino acid induced neurotoxicity and also prevent soman induced toxicity with minimum performance decrement. Unique combinations of two stereo-isomers of Hup A may provide an excellent pre/post-treatment drug for the nerve agent induced seizure/status epilepticus. We investigated a combination of [+]-Hup A with a small dose of [-]-Hup A ([+] and [-]-Hup A) against soman toxicity. Our data showed that pretreatment with a combination [+] and [-]-Hup A significantly increased the survival rate and reduced behavioral abnormalities after exposure to 1.2 x LD(50) soman compared to [+]-Hup A in guinea pigs. In addition, [+] and [-]-Hup A pretreatment inhibited the development of high power of EEG better than [+]-Hup A pretreatment alone. These data suggest that a combination of [+] and [-]-Hup A offers better protection than [+]-Hup A and serves as a potent medical countermeasure against lethal dose nerve agent toxicity in guinea pigs.
An efficient total synthesis of (-)-huperzine A.[Pubmed:22900755]
Org Lett. 2012 Sep 7;14(17):4446-9.
The total synthesis of Lycopodium alkaloid (-)-Huperzine A has been accomplished in 10 steps with 17% overall yield from commercially abundant (R)-pulegone. The synthetic route features an efficient synthesis of 4 via a Buchwald-Hartwig coupling reaction, a dianion-mediated highly stereoselective alkylation of 4, and a rare example of an intramolecular Heck reaction of an enamine-type substrate. The stereoselective beta-elimination and the accompanying Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement are of particular interest.


