ISO-1Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) inhibitor CAS# 478336-92-4 |
- Gatifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1064
CAS No.:112811-59-3
- Dexrazoxane HCl (ICRF-187, ADR-529)
Catalog No.:BCC1087
CAS No.:149003-01-0
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1117
CAS No.:25316-40-9
- Etoposide
Catalog No.:BCC1151
CAS No.:33419-42-0
- Genistein
Catalog No.:BCN5499
CAS No.:446-72-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 478336-92-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6098948 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H13NO4 | M.Wt | 235.24 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | MIF Antagonist | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
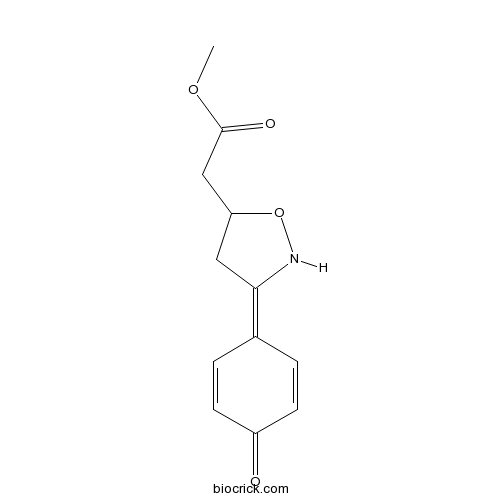
| Chemical Name | methyl 2-[3-(4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)-1,2-oxazolidin-5-yl]acetate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)CC1CC(=C2C=CC(=O)C=C2)NO1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CLVQGFPQFNASJH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H13NO4/c1-16-12(15)7-10-6-11(13-17-10)8-2-4-9(14)5-3-8/h2-5,10,13H,6-7H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) inhibitor (IC50 = 7 μM); inhibits MIF tautomerase activity in vitro and in vivo. Protective against mouse models of streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus; blocks anti-inflammatory response following LPS exposure and increases survival. Inhibits airway remodeling in a mouse model of chronic asthma. Cell permeable; orally bioavailable. |

ISO-1 Dilution Calculator

ISO-1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.251 mL | 21.2549 mL | 42.5098 mL | 85.0196 mL | 106.2744 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8502 mL | 4.251 mL | 8.502 mL | 17.0039 mL | 21.2549 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4251 mL | 2.1255 mL | 4.251 mL | 8.502 mL | 10.6274 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.085 mL | 0.4251 mL | 0.8502 mL | 1.7004 mL | 2.1255 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0425 mL | 0.2125 mL | 0.4251 mL | 0.8502 mL | 1.0627 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
ISO-1 is an inhibitor of MIF d-dopachrome tautomerase activity with an IC50 of about 7 uM. IC50 value: 7 uM [1] Target: MIF inhibitor in vitro: ISO-1 inhibited MIF tautomerase activity in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of about 7 μM, but the non-hydroxylated phenyl analog (compound 2) was 10–15 times less potent. In accordance with this potential mechanism(s), treatment of the transfected cells with ISO-1 inhibited the release of arachidonic acid in a dose-dependent manner [1]. ISO-1 significantly inhibits the cytokine activity in vitro. Moreover, ISO-1 inhibits tumor necrosis factor release from macrophages isolated from LPStreated wild type mice but has no effect on cytokine release from MIFdeficient macrophages [2]. in vivo: Administration of ISO-1 resulted in a significant reduction in implant size and vascularity (as assessed by Flk1 mRNA expression) which was not associated with an alteration in the reproductive cycle in mice [3].
References:
[1]. Lubetsky JB, et al. The tautomerase active site of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a potential target for discovery of novel anti-inflammatory agents. J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 12;277(28):24976-82.
[2]. Al-Abed Y, et al. ISO-1 binding to the tautomerase active site of MIF inhibits its pro-inflammatory activity and increases survival in severe sepsis. J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 4;280(44):36541-4.
[3]. Nothnick WB, et al. Inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor reduces endometriotic implant size in mice with experimentally induced disease. J Endometr. 2011 Sep 30;3(3):135-142.
- 4-Hydroxymethylphenol 1-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN7750
CAS No.:478314-67-9
- Gabapentin enacarbil
Catalog No.:BCC4239
CAS No.:478296-72-9
- R-1479
Catalog No.:BCC1878
CAS No.:478182-28-4
- Isoerysenegalensein E
Catalog No.:BCN3978
CAS No.:478158-77-9
- PHA 543613 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5972
CAS No.:478149-53-0
- Pseudococaine
Catalog No.:BCN1902
CAS No.:478-73-9
- Berbamine
Catalog No.:BCN5543
CAS No.:478-61-5
- Rhein
Catalog No.:BCN5947
CAS No.:478-43-3
- Droserone
Catalog No.:BCN7985
CAS No.:478-40-0
- Eleutherin
Catalog No.:BCN8475
CAS No.:478-36-4
- Pseudoaspidin
Catalog No.:BCN6386
CAS No.:478-28-4
- Lucidin
Catalog No.:BCC1709
CAS No.:478-08-0
- CP 339818 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7048
CAS No.:478341-55-8
- Kisspeptin 10 (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC6132
CAS No.:478507-53-8
- Zopfiellamide A
Catalog No.:BCN1865
CAS No.:478945-64-1
- Angiotensin 1/2 (1-6)
Catalog No.:BCC1036
CAS No.:47896-63-9
- Calcium-Sensing Receptor Antagonists I
Catalog No.:BCC1448
CAS No.:478963-79-0
- Coumestrol
Catalog No.:BCN3949
CAS No.:479-13-0
- Dyphylline
Catalog No.:BCC2297
CAS No.:479-18-5
- Atranorin
Catalog No.:BCN5544
CAS No.:479-20-9
- Cotoin
Catalog No.:BCN5545
CAS No.:479-21-0
- Indirubin
Catalog No.:BCN2385
CAS No.:479-41-4
- Canthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN5546
CAS No.:479-43-6
- Artemetin
Catalog No.:BCN5547
CAS No.:479-90-3
The MIF Antagonist ISO-1 Attenuates Corticosteroid-Insensitive Inflammation and Airways Hyperresponsiveness in an Ozone-Induced Model of COPD.[Pubmed:26752192]
PLoS One. 2016 Jan 11;11(1):e0146102.
INTRODUCTION: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is an inflammatory cytokine associated with acute and chronic inflammatory disorders and corticosteroid insensitivity. Its expression in the airways of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a relatively steroid insensitive inflammatory disease is unclear, however. METHODS: Sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) macrophages and serum were obtained from non-smokers, smokers and COPD patients. To mimic oxidative stress-induced COPD, mice were exposed to ozone for six-weeks and treated with ISO-1, a MIF inhibitor, and/or dexamethasone before each exposure. BAL fluid and lung tissue were collected after the final exposure. Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) and lung function were measured using whole body plethysmography. HIF-1alpha binding to the Mif promoter was determined by Chromatin Immunoprecipitation assays. RESULTS: MIF levels in sputum and BAL macrophages from COPD patients were higher than those from non-smokers, with healthy smokers having intermediate levels. MIF expression correlated with that of HIF-1alpha in all patients groups and in ozone-exposed mice. BAL cell counts, cytokine mRNA and protein expression in lungs and BAL, including MIF, were elevated in ozone-exposed mice and had increased AHR. Dexamethasone had no effect on these parameters in the mouse but ISO-1 attenuated cell recruitment, cytokine release and AHR. CONCLUSION: MIF and HIF-1alpha levels are elevated in COPD BAL macrophages and inhibition of MIF function blocks corticosteroid-insensitive lung inflammation and AHR. Inhibition of MIF may provide a novel anti-inflammatory approach in COPD.
Effect of an Ala81His mutation on the Met80 loop dynamics of iso-1-cytochrome c.[Pubmed:25671560]
Biochemistry. 2015 Mar 10;54(9):1729-42.
An A81H variant of yeast ISO-1-cytochrome c is prepared to test the hypothesis that the steric size of the amino acid at sequence position 81 of cytochrome c, which has evolved from Ala in yeast to Ile in mammals, slows the dynamics of the opening of the heme crevice. The A81H mutation is used both to increase steric size and to provide a probe of the dynamics of the heme crevice through measurement of the thermodynamics and kinetics of the His81-mediated alkaline conformational transition of A81H ISO-1-cytochrome c. Thermodynamic measurements show that the native conformer is more stable than the His81-heme alkaline conformer for A81H ISO-1-cytochrome c. DeltaGu degrees (H2O) is approximately 1.9 kcal/mol for formation of the His81-heme alkaline conformer. By contrast, for K79H ISO-1-cytochrome c, the native conformer is less stable than the His79-heme alkaline conformer. DeltaGu degrees (H2O) is approximately -0.34 kcal/mol for formation of the His79-heme alkaline conformer. pH jump and gated electron transfer kinetics demonstrate that this stabilization of the native conformer in A81H ISO-1-cytochrome c arises primarily from a decrease in the rate constant for formation of the His81-heme alkaline conformer, kf,His81, relative to kf,His79 for formation of the His79-heme alkaline conformer, which forms by a mechanism similar to that observed for the His81-heme alkaline conformer. The result is discussed in terms of the effect of global protein stability on protein dynamics and in terms of optimization of the sequence of cytochrome c for its role as a peroxidase in the early stages of apoptosis in higher eukaryotes.
The response of Omega-loop D dynamics to truncation of trimethyllysine 72 of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c depends on the nature of loop deformation.[Pubmed:25948392]
J Biol Inorg Chem. 2015 Jul;20(5):805-19.
Trimethyllysine 72 (tmK72) has been suggested to play a role in sterically constraining the heme crevice dynamics of yeast ISO-1-cytochrome c mediated by the Omega-loop D cooperative substructure (residues 70-85). A tmK72A mutation causes a gain in peroxidase activity, a function of cytochrome c that is important early in apoptosis. More than one higher energy state is accessible for the Omega-loop D substructure via tier 0 dynamics. Two of these are alkaline conformers mediated by Lys73 and Lys79. In the current work, the effect of the tmK72A mutation on the thermodynamic and kinetic properties of wild-type ISO-1-cytochrome c (yWT versus WT*) and on variants carrying a K73H mutation (yWT/K73H versus WT*/K73H) is studied. Whereas the tmK72A mutation confers increased peroxidase activity in wild-type yeast ISO-1-cytochrome c and increased dynamics for formation of a previously studied His79-heme alkaline conformer, the tmK72A mutation speeds return of the His73-heme alkaline conformer to the native state through destabilization of the His73-heme alkaline conformer relative to the native conformer. These opposing behaviors demonstrate that the response of the dynamics of a protein substructure to mutation depends on the nature of the perturbation to the substructure. For a protein substructure which mediates more than one function of a protein through multiple non-native structures, a mutation could change the partitioning between these functions. The current results suggest that the tier 0 dynamics of Omega-loop D that mediates peroxidase activity has similarities to the tier 0 dynamics required to form the His79-heme alkaline conformer.
Characterization of pre-molten globule state of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c and its deletants at pH 6.0 and 25 degrees C.[Pubmed:25450045]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2015 Jan;72:1406-18.
To understand the role of five extra N-terminal residues, we prepared wild type (WT) yeast ISO-1-cytochrome c (y-cyt-c) and its deletants by subsequently deleting these residues. Denaturation of all these proteins induced by LiCl was followed by observing changes in molar absorption coefficient at 405 nm (Deltavarepsilon405), the mean residue ellipticity at 222 nm ([theta]222), and the difference mean residue ellipticity at 409 nm (Delta[theta]409) near physiological pH and temperature (pH 6.0 and 25 degrees C). It was observed that in each case LiCl induces biphasic transition, N (native) state <--> X (intermediate) state <--> D (denatured) state. The intermediate (X) was characterized by the far-UV, near-UV and Soret circular dichroism, ANS (8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid) binding and dynamic light scattering measurements. These measurements led us to conclude that X state of each protein has structural characteristics of PMG (pre-molten globule) state. Thermodynamic stability of all proteins was also determined. It was observed that the N-terminal extension stabilizes the native WT protein but it has no effect on the stability of PMG state. Another state was observed for each protein, in the presence of 0.33 M Na2SO4 at pH 2.1, which when characterized showed all structural characteristics of MG (molten globule) state.
ISO-1, a macrophage migration inhibitory factor antagonist, inhibits airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma.[Pubmed:20485865]
Mol Med. 2010 Sep-Oct;16(9-10):400-8.
Airway remodeling is the process of airway structural change that occurs in patients with asthma in response to persistent inflammation and leads to increasing disease severity. Drugs that decrease this persistent inflammation play a crucial role in managing asthma episodes. Mice sensitized (by intraperitoneal administration) and then challenged (by inhalation) with ovalbumin (OVA) develop an extensive eosinophilic inflammatory response, goblet cell hyperplasia, collagen deposition, airway smooth muscle thickening, and airway wall area increase, similar to pathologies observed in human asthma. We used OVA-sensitized/challenged mice as a murine model of chronic allergic airway inflammation with subepithelial fibrosis (i.e., asthma). In this OVA mouse model, mRNA and protein of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) are upregulated, a response similar to what has been observed in the pathogenesis of acute inflammation in human asthma. We hypothesized that MIF induces transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) synthesis, which has been shown to play an important role in asthma and airway remodeling. To explore the role of MIF in the development of airway remodeling, we evaluated the effects of an MIF small-molecule antagonist, (S,R)3-(4-hy-droxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-isoxazole acetic acid methyl ester (ISO-1), on pathologies associated with the airway-remodeling process in the OVA mouse model. We found that administration of ISO-1 significantly mitigated all symptoms caused by OVA treatment. In addition, the treatment of OVA-sensitized mice with the MIF antagonist ISO-1 significantly reduced TGF-beta1 mRNA levels in pulmonary tissue and its protein level in bronchial alveolar lavage fluid supernatants. We believe the repression of MIF in the ISO-1 treatment group led to the significant suppression observed in the inflammatory responses associated with the allergen-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in our murine asthma (OVA) model. Our results implicate a possible function of MIF in the pathogenesis of chronic asthma and suggest that MIF might be an important therapeutic target for airway remodeling.
ISO-1 binding to the tautomerase active site of MIF inhibits its pro-inflammatory activity and increases survival in severe sepsis.[Pubmed:16115897]
J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 4;280(44):36541-4.
MIF is a proinflammatory cytokine that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of sepsis, arthritis, and other inflammatory diseases. Antibodies against MIF are effective in experimental models of inflammation, and there is interest in strategies to inhibit its deleterious cytokine activities. Here we identify a mechanism of inhibiting MIF pro-inflammatory activities by targeting MIF tautomerase activity. We designed small molecules to inhibit this tautomerase activity; a lead molecule, "ISO-1 ((S,R)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-isoxazole acetic acid methyl ester)," significantly inhibits the cytokine activity in vitro. Moreover, ISO-1 inhibits tumor necrosis factor release from macrophages isolated from LPStreated wild type mice but has no effect on cytokine release from MIFdeficient macrophages. The therapeutic importance of the MIF inhibition by ISO-1 is demonstrated by the significant protection from sepsis, induced by cecal ligation and puncture in a clinically relevant time frame. These results identify ISO-1 as the first small molecule inhibitor of MIF proinflammatory activities with therapeutic implications and indicate the potential of the MIF active site as a novel target for therapeutic interventions in human sepsis.
Critical role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor activity in experimental autoimmune diabetes.[Pubmed:15790730]
Endocrinology. 2005 Jul;146(7):2942-51.
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a proinflammatory cytokine that plays a pivotal role in several immunoinflammatory and autoimmune diseases. In this study we examined the role of MIF in the development of immunoinflammatory diabetes induced in susceptible strains of mice by multiple low doses of streptozotocin. We found that MIF protein was significantly elevated in islet cells during the development of diabetes, and that targeting MIF activity with either neutralizing antibody or the pharmacological inhibitor (S,R)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-isoxazole acetic acid methyl ester, markedly reduced clinical and histopathological features of the disease, such as hyperglycemia and insulitis. Lymphocytes from mice treated with the MIF inhibitors exhibited reduction of both islet antigen-specific proliferative responses and adhesive cell-cell interactions. Neutralization of MIF also down-regulated the ex vivo secretion of the proinflammatory mediators, TNF-alpha, interferon-gamma, and nitric oxide, while augmenting that of the antiinflammatory cytokine, IL-10. This study provides the first in vivo evidence for a critical role for MIF in the immune-mediated beta-cell destruction in an animal model of human type 1 diabetes mellitus and identifies a new therapeutic strategy for the prevention and treatment of this disease in humans that is based on the selective inhibition of MIF activity.
The tautomerase active site of macrophage migration inhibitory factor is a potential target for discovery of novel anti-inflammatory agents.[Pubmed:11997397]
J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 12;277(28):24976-82.
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is an immunoregulatory protein that is a potential therapeutic target for a number of inflammatory diseases. Evidence exists that an unexpected catalytic active site of MIF may have a biological function. To gain further insight into the role of the catalytic active site, a series of mutational, structural, and biological activity studies were performed. The insertion of an alanine between Pro-1 and Met-2 (PAM) abolishes a non-physiological catalytic activity, and this mutant is defective in the in vitro glucocorticoid counter-regulatory activity of MIF. The crystal structure of MIF complexed to (S,R)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-isoxazole acetic acid methyl ester (ISO-1), an inhibitor of MIF d-dopachrome tautomerase activity, reveals that ISO-1 binds to the same position of the active site as p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid, a substrate of MIF. ISO-1 inhibits several MIF biological activities, further establishing a role for the catalytic active site of MIF.


