CP 339818 hydrochlorideNon-peptide, potent KV1.3 channel blocker CAS# 478341-55-8 |
- WR 1065
Catalog No.:BCC2417
CAS No.:14653-77-1
- PRIMA-1MET
Catalog No.:BCC2414
CAS No.:5291-32-7
- PRIMA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2413
CAS No.:5608-24-2
- Pifithrin-μ
Catalog No.:BCC2412
CAS No.:64984-31-2
- NSC 319726
Catalog No.:BCC2242
CAS No.:71555-25-4
- JNJ-26854165 (Serdemetan)
Catalog No.:BCC2240
CAS No.:881202-45-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 478341-55-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71433722 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H23ClN2 | M.Wt | 326.9 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 20 mM in water | ||
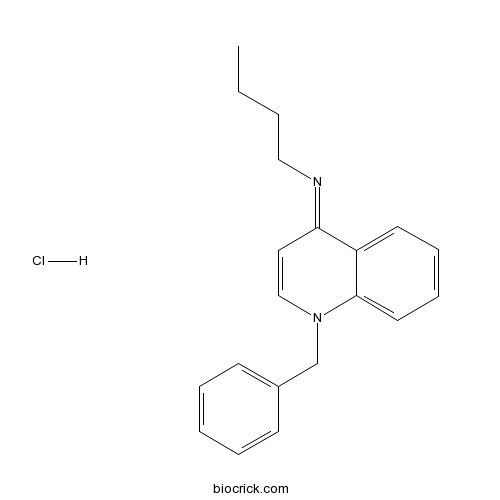
| Chemical Name | 1-benzyl-N-butylquinolin-4-imine;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCCCN=C1C=CN(C2=CC=CC=C12)CC3=CC=CC=C3.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HDAMNMJLKSDNJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H22N2.ClH/c1-2-3-14-21-19-13-15-22(16-17-9-5-4-6-10-17)20-12-8-7-11-18(19)20;/h4-13,15H,2-3,14,16H2,1H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, non-peptide KV1.3 channel antagonist that preferentially binds to the C-type inactivated state of the channel (IC50 ~ 200 nM). Inhibits KV1.4 with an IC50 of ~ 300 nM. Selective over KV1.1, KV1.2, KV1.5, KV1.6, KV3.1-4, and KV4.2. |

CP 339818 hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

CP 339818 hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.059 mL | 15.2952 mL | 30.5904 mL | 61.1808 mL | 76.476 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6118 mL | 3.059 mL | 6.1181 mL | 12.2362 mL | 15.2952 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3059 mL | 1.5295 mL | 3.059 mL | 6.1181 mL | 7.6476 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0612 mL | 0.3059 mL | 0.6118 mL | 1.2236 mL | 1.5295 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.153 mL | 0.3059 mL | 0.6118 mL | 0.7648 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- ISO-1
Catalog No.:BCC5427
CAS No.:478336-92-4
- 4-Hydroxymethylphenol 1-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN7750
CAS No.:478314-67-9
- Gabapentin enacarbil
Catalog No.:BCC4239
CAS No.:478296-72-9
- R-1479
Catalog No.:BCC1878
CAS No.:478182-28-4
- Isoerysenegalensein E
Catalog No.:BCN3978
CAS No.:478158-77-9
- PHA 543613 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5972
CAS No.:478149-53-0
- Pseudococaine
Catalog No.:BCN1902
CAS No.:478-73-9
- Berbamine
Catalog No.:BCN5543
CAS No.:478-61-5
- Rhein
Catalog No.:BCN5947
CAS No.:478-43-3
- Droserone
Catalog No.:BCN7985
CAS No.:478-40-0
- Eleutherin
Catalog No.:BCN8475
CAS No.:478-36-4
- Pseudoaspidin
Catalog No.:BCN6386
CAS No.:478-28-4
- Kisspeptin 10 (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC6132
CAS No.:478507-53-8
- Zopfiellamide A
Catalog No.:BCN1865
CAS No.:478945-64-1
- Angiotensin 1/2 (1-6)
Catalog No.:BCC1036
CAS No.:47896-63-9
- Calcium-Sensing Receptor Antagonists I
Catalog No.:BCC1448
CAS No.:478963-79-0
- Coumestrol
Catalog No.:BCN3949
CAS No.:479-13-0
- Dyphylline
Catalog No.:BCC2297
CAS No.:479-18-5
- Atranorin
Catalog No.:BCN5544
CAS No.:479-20-9
- Cotoin
Catalog No.:BCN5545
CAS No.:479-21-0
- Indirubin
Catalog No.:BCN2385
CAS No.:479-41-4
- Canthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN5546
CAS No.:479-43-6
- Artemetin
Catalog No.:BCN5547
CAS No.:479-90-3
- Vitexicarpin
Catalog No.:BCN5020
CAS No.:479-91-4
Regulation of mammalian Shaker-related K+ channels: evidence for non-conducting closed and non-conducting inactivated states.[Pubmed:9490854]
J Physiol. 1998 Jan 15;506 ( Pt 2):291-301.
1. Using the whole-cell recording mode we have characterized two non-conducting states in mammalian Shaker-related voltage-gated K+ channels induced by the removal of extracellular potassium, K+o. 2. In the absence of K+o, current through Kv1.4 was almost completely abolished due to the presence of a charged lysine residue at position 533 at the entrance to the pore. Removal of K+o had a similar effect on current through Kv1.3 when the histidine at the homologous position (H404) was protonated (pH 6.0). Channels containing uncharged residues at the corresponding position (Kv1.1: Y; Kv1.2: V) did not exhibit this behaviour. 3. To characterize the nature of the interaction between Kv1.3 and K+o concentration ([K+]o), we replaced H404 with amino acids of different character, size and charge. Substitution of hydrophobic residues (A, V and L) either in all four subunits or in only two subunits in the tetramer made the channel insensitive to the removal of K+o, possibly by stabilizing the channel complex. Replacement of H404 with the charged residue arginine, or the polar residue asparagine, enhanced the sensitivity of the channel to 0 mM K+o, possibly by making the channel unstable in the absence of K+o. Mutation at a neighbouring position (400) had a similar effect. 4. The effect of removing K+o on current amplitude does not seem to be correlated with the rate of C-type inactivation since the slowly inactivating G380F mutant channel exhibited a similar [K+]o dependence as the wild-type Kv1.3 channel. 5. CP-339,818, a drug that recognizes only the inactivated conformation of Kv1.3, could not block current in the absence of K+o unless the channels were inactivated through depolarizing pulses. 6. We conclude that removal of K+o induces the Kv1.3 channel to transition to a non-conducting 'closed' state which can switch into a non-conducting 'inactivated' state upon depolarization.
Novel nonpeptide agents potently block the C-type inactivated conformation of Kv1.3 and suppress T cell activation.[Pubmed:8967992]
Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;50(6):1672-9.
The nonpeptide agent CP-339,818 (1-benzyl-4-pentylimino-1,4-dihydroquinoline) and two analogs (CP-393,223 and CP-394,322) that differ only with respect to the type of substituent at the N1 position, potently blocked the Kv1.3 channel in T lymphocytes. A fourth compound (CP-393,224), which has a smaller and less-lipophilic group at N1, was 100-200-fold less potent, suggesting that a large lipophilic group at this position is necessary for drug activity. CP-339,818 blocked Kv1.3 from the outside with a IC50 value of approximately 200 nM and 1:1 stoichiometry and competitively inhibited 125I-charybdotoxin from binding to the external vestibule of Kv1.3. This drug inhibited Kv1.3 in a use-dependent manner by preferentially blocking the C-type inactivated state of the channel. CP-339,818 was a significantly less potent blocker of Kv1.1, Kv1.2, Kv1.5, Kv1.6, Kv3.1-4, and Kv4.2; the only exception was Kv1.4, a cardiac and neuronal A-type K+ channel. CP-339,818 had no effect on two other T cell channels (I(CRAC) and intermediate-conductance K(Ca)) implicated in T cell mitogenesis. This drug suppresses human T cell activation, suggesting that blockade of Kv1.3 alone is sufficient to inhibit this process.


