IsotaxiresinolCAS# 26194-57-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 26194-57-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9841162 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H22O6 | M.Wt | 346.38 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
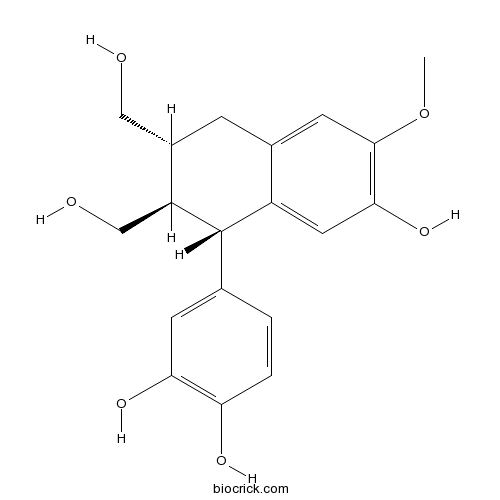
| Chemical Name | 4-[(1S,2R,3R)-7-hydroxy-2,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)-6-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-1-yl]benzene-1,2-diol | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(C(C(CC2=C1)CO)CO)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GQLVRVYXAHDDLB-PJFSTRORSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H22O6/c1-25-18-6-11-4-12(8-20)14(9-21)19(13(11)7-17(18)24)10-2-3-15(22)16(23)5-10/h2-3,5-7,12,14,19-24H,4,8-9H2,1H3/t12-,14-,19-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Isotaxiresinol may be useful for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, especially for prevention of bone fracture induced by estrogen deficiency. 2. Isotaxiresinol prevents d-GalN/LPS-induced hepatic injury by inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis through the blocking of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma production by activated macrophages and direct inhibition of the apoptosis induced by TNF-alpha. |
| Targets | IFN-γ | TNF-α |

Isotaxiresinol Dilution Calculator

Isotaxiresinol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.887 mL | 14.435 mL | 28.87 mL | 57.7401 mL | 72.1751 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5774 mL | 2.887 mL | 5.774 mL | 11.548 mL | 14.435 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2887 mL | 1.4435 mL | 2.887 mL | 5.774 mL | 7.2175 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0577 mL | 0.2887 mL | 0.5774 mL | 1.1548 mL | 1.4435 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0289 mL | 0.1444 mL | 0.2887 mL | 0.5774 mL | 0.7218 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- SB269970 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5056
CAS No.:261901-57-9
- Foliamenthoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5138
CAS No.:26187-80-4
- 6-Prenylsakuranetin
Catalog No.:BCN7883
CAS No.:261776-61-8
- 6-Methyl-8-prenylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN6860
CAS No.:261776-60-7
- 3,19-Dihydroxy-6,23-dioxo-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1471
CAS No.:261768-88-1
- Beesioside Q
Catalog No.:BCC8301
CAS No.:261767-91-3
- Denudatine
Catalog No.:BCN5406
CAS No.:26166-37-0
- CGS 35066
Catalog No.:BCC5916
CAS No.:261619-50-5
- Naproxen Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC6490
CAS No.:26159-34-2
- 3,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN2257
CAS No.:26153-38-8
- Linderene acetate
Catalog No.:BCN8042
CAS No.:26146-28-1
- Linderene
Catalog No.:BCN2779
CAS No.:26146-27-0
- CALP2
Catalog No.:BCC5898
CAS No.:261969-04-4
- CALP3
Catalog No.:BCC5900
CAS No.:261969-05-5
- Cl-HOBt
Catalog No.:BCC2829
CAS No.:26198-19-6
- 3alpha-Acetoxy-20-oxo-29-norlupane-23,28-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6507
CAS No.:262272-76-4
- 3,6-Dihydroxy-1,7-dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN6394
CAS No.:262292-34-2
- H-D-Aib-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3151
CAS No.:2623-91-8
- Debenzoylgalloylpaeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCC8927
CAS No.:262350-51-6
- Mudanpioside J
Catalog No.:BCC9050
CAS No.:262350-52-7
- Torcetrapib
Catalog No.:BCC2330
CAS No.:262352-17-0
- 7,15-Dihydroxypodocarp-8(14)-en-13-one
Catalog No.:BCN1470
CAS No.:262355-96-4
- Cyclofenil
Catalog No.:BCC7839
CAS No.:2624-43-3
- BVD 10
Catalog No.:BCC5882
CAS No.:262418-00-8
Secoisolariciresinol and isotaxiresinol inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent hepatic apoptosis in mice.[Pubmed:15043992]
Life Sci. 2004 Apr 16;74(22):2781-92.
The effects of secoisolariciresinol (1) and Isotaxiresinol (2), two major lignans isolated from the wood of Taxus yunnanensis, on tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-dependent hepatic apoptosis induced by D-galactosamine (d-GalN)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were investigated in mice. Co-administration of d-GalN (700 mg/kg) and LPS (10 microg/kg) resulted in a typical hepatic apoptosis characterized by DNA fragmentation and the formation of apoptotic bodies. Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase (sGPT) and glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (sGOT) levels were also raised at 8 h after d-GalN/LPS intoxication due to a severe necrosis of hepatocytes. Pre-administration of 1 or 2 (50, 10 mg/kg, i.p.) 12 and 1 h before d-GalN/LPS significantly reduced DNA fragmentation and prevented chromatin condensation, apoptotic body formation and hepatitis. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) secreted from LPS-activated macrophages are important mediators of hepatocyte apoptosis in this model. Pre-treatment with 1 or 2 significantly inhibited the elevation of serum TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma levels. In a separate experiment, both lignans had a significant dose-dependent protective effect on d-GalN/TNF-alpha-induced cell death in primary cultured mouse hepatocytes and TNF-alpha-mediated cell death in murine L929 fibrosarcoma cells. These results indicated that 1 and 2 prevent d-GalN/LPS-induced hepatic injury by inhibiting hepatocyte apoptosis through the blocking of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma production by activated macrophages and direct inhibition of the apoptosis induced by TNF-alpha.
In vivo anti-osteoporotic activity of isotaxiresinol, a lignan from wood of Taxus yunnanensis.[Pubmed:16360931]
Phytomedicine. 2006 Jan;13(1-2):37-42.
Isotaxiresinol, the main lignan isolated from the water extract of wood of Taxus yunnanensis, was investigated for its effect on bone loss, on serum biochemical markers for bone remodeling and on uterine tissue, using ovariectomized (OVX) rats as the model of postmenopausal osteoporosis. After oral administration of Isotaxiresinol (50 and 100mg/kg/d) for 6 weeks, bone mineral content (BMC) and bone mineral density (BMD) in total and cortical bones were increased as compared to those of OVX control rats, and decreases of three bone strength indexes induced by OVX surgery were prevented. Serum biochemical markers for bone remodeling revealed that Isotaxiresinol slightly increased bone formation and significantly inhibited bone resorption without side effect on uterine tissue. These results suggest that Isotaxiresinol may be useful for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, especially for prevention of bone fracture induced by estrogen deficiency.


