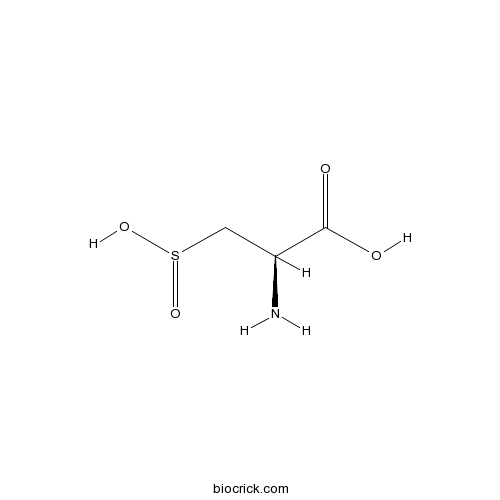
L-Cysteinesulfinic acidmGlu and NMDA agonist CAS# 1115-65-7 |
- Qingyangshengenin A
Catalog No.:BCN8126
CAS No.:106644-33-1
- Demethylzeylasteral
Catalog No.:BCN2282
CAS No.:107316-88-1
- Asarinin
Catalog No.:BCN2769
CAS No.:133-05-1
- Magnoflorine Iodide
Catalog No.:BCN2911
CAS No.:4277-43-4
- Magnoflorine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2405
CAS No.:6681-18-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1115-65-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1549098 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C3H7NO4S | M.Wt | 153.15 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-amino-3-sulfinopropanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(C(C(=O)O)N)S(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ADVPTQAUNPRNPO-REOHCLBHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C3H7NO4S/c4-2(3(5)6)1-9(7)8/h2H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/t2-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Agonist at mGlu1a and mGlu5a subtypes expressed in clonal RGT cell lines. Also agonist at NMDA and PLD-coupled mGlu receptors. |

L-Cysteinesulfinic acid Dilution Calculator

L-Cysteinesulfinic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.5295 mL | 32.6477 mL | 65.2955 mL | 130.5909 mL | 163.2387 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.3059 mL | 6.5295 mL | 13.0591 mL | 26.1182 mL | 32.6477 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.653 mL | 3.2648 mL | 6.5295 mL | 13.0591 mL | 16.3239 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1306 mL | 0.653 mL | 1.3059 mL | 2.6118 mL | 3.2648 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0653 mL | 0.3265 mL | 0.653 mL | 1.3059 mL | 1.6324 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-Ala-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2687
CAS No.:1115-59-9
- Ac-DL-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2999
CAS No.:1115-47-5
- 25-Anhydroalisol F
Catalog No.:BCN3361
CAS No.:1114895-01-0
- Amlodipine Besylate
Catalog No.:BCC4397
CAS No.:111470-99-6
- Naltrindole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6773
CAS No.:111469-81-9
- Axinysone B
Catalog No.:BCN7713
CAS No.:1114491-60-9
- Pinocembrin diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN5997
CAS No.:111441-88-4
- Azadirachtin
Catalog No.:BCC8123
CAS No.:11141-17-6
- Zileuton
Catalog No.:BCC2515
CAS No.:111406-87-2
- Lestaurtinib
Catalog No.:BCC2440
CAS No.:111358-88-4
- Sappanol
Catalog No.:BCN3735
CAS No.:111254-19-4
- Episappanol
Catalog No.:BCN7940
CAS No.:111254-18-3
- Metformin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4799
CAS No.:1115-70-4
- Nyasicoside
Catalog No.:BCN5998
CAS No.:111518-94-6
- Nyasicol
Catalog No.:BCN5999
CAS No.:111518-95-7
- Fmoc-D-Phg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3316
CAS No.:111524-95-9
- 3',5-Dihydroxy-4',5',6,7-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1620
CAS No.:111537-41-8
- Anonamine
Catalog No.:BCN2139
CAS No.:111566-66-6
- Cyanidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3023
CAS No.:111613-04-8
- GSK1838705A
Catalog No.:BCC3787
CAS No.:1116235-97-2
- Elastase Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1225
CAS No.:111682-13-4
- Remacemide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7129
CAS No.:111686-79-4
- Demethoxyfumitremorgin C
Catalog No.:BCN7240
CAS No.:111768-16-2
- H-Glu-Oet.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2685
CAS No.:1118-89-4
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid modulates cardiovascular function in the periaqueductal gray area of rat.[Pubmed:9781935]
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1998 Oct;32(4):650-3.
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid (CSA) involvement in modulating periaqueductal gray (PAG) pressor neurons has been evaluated in the rat. Intra-PAG CSA induced an increase in mean blood pressure partially antagonized by (2S)-alpha-ethylglutamic acid (EGA), a group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) antagonist. Conversely, the NMDA antagonist, DL-AP5, or the mGluRs antagonists, (+)-MCPG, UPF523, or (RS)-alpha-methylserine-O-phosphate (MSOP), were devoid of any activity on the CSA effect. These data show that the excitatory amino acid CSA, probably by stimulating an mGluR, contributes with glutamate in modulating cardiovascular function at the PAG matter.
Sulphur-containing amino acids are agonists for group 1 metabotropic receptors expressed in clonal RGT cell lines.[Pubmed:9681926]
Neuropharmacology. 1998;37(3):277-87.
Comparison of the pharmacological effects of a range of sulphur-containing amino acids on human mGluR1alpha and mGluR5a has been undertaken. cDNAs of each mGluR were transfected into a Syrian hamster tumour cell line AV12-664 that was previously transfected with the rat glutamate-aspartate transporter protein (GLAST). The L-isomers of cysteine sulphinic acid (CSA), homocysteine sulphinic acid (HCSA), cysteic acid (CA) and serine-O-sulphate (SOS) stimulated PI hydrolysis in human mGluR1alpha and mGluR5a cells with full agonist effects. D-CSA, the only active D-isomer, was a partial agonist for mGluR5a whereas L-sulphocysteine (S-CYS) showed weak agonist-like effects at high concentrations on both mGluR1alpha and mGluR5a. L-Homocysteic acid was inactive on both mGluR1alpha and mGluR5a cells. Treatment of mGluR cultures with glutamate pyruvate transaminase did not alter the potencies of the S-amino acids on PI hydrolysis responses. Inhibitor constants (Ki) obtained for L-HCSA, L-CSA, L-CA and L-SOS in [3H]glutamate receptor binding studies with mGluR1alpha cells indicated that L-HCSA, L-CSA, L-CA and L-SOS can bind specifically to mGluR1 with L-HCSA showing the highest affinity. These results confirm that certain endogenously produced S-amino acids may interact directly with group 1 mGluRs.
Sulphur-containing excitatory amino acid-stimulated inositol phosphate formation in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells is mediated predominantly by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.[Pubmed:8008194]
Neuroscience. 1994 Mar;59(2):299-308.
The stimulatory effect of excitatory sulphur-containing amino acids on inositol phosphate formation was investigated in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells. L-Cysteine sulphinate (CSA), L-cysteate (CA), L-homocysteine sulphinate (HCSA), L-homocysteate (HCA) and S-sulpho-L-cysteine (SSC) dose-dependently stimulated the formation of [3H]inositol phosphates exhibiting EC50 values in the range 60-200 microM and maximal effects of six- to 17-fold that of basal [3H]inositol phosphate levels. Endogenous L-glutamate spontaneously released into the extracellular medium or following exposure of cells to HCSA, HCA or SSC did not contribute significantly to formation of [3H]inositol phosphates, whereas 10% of the total [3H]inositol phosphates accumulated following exposure to CSA and CA was due to released L-glutamate. The selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist, D,L-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (APV, 500 microM) attenuated by 20% (HCSA) to between 80 and 100% (CSA, CA, SSC, HCA) the formation of [3H]inositol phosphates induced by 1 mM sulphur-containing amino acids. When, however, HCSA was used at 100 microM (a concentration near to its EC50 for phosphoinositide hydrolysis), APV inhibited induced responses by 70%. Sulphur-containing amino acid-stimulated [3H]inositol phosphate formation was unaffected by the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX, 10 microM). Inhibition of sulphur-containing amino acid-stimulated [3H]inositol phosphate formation by co-administration of APV and CNQX was similar to that obtained in the presence of APV alone. CSA-, CA-, SSC- and HCA-stimulated [3H]inositol phosphate formation was markedly reduced by removal of Ca2+ from the extracellular medium whereas that stimulated by HCSA was less affected. A similar inhibitory profile was observed when the levels of sulphur-containing amino acid-induced increases in intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) were measured in the presence of 500 microM APV; 1 mM HCSA-induced responses being inhibited by only 30% whereas responses to the remaining sulphur-containing amino acid (also at 1 mM) were inhibited by > 45%. When the sulphur-containing amino acids were used at concentrations approximating their EC50 values for phosphoinositide hydrolysis, APV inhibited the induced increases in [Ca2+]i by 70-100%. HCA and SSC co-administered with the less efficacious but selective metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist, (+-)-1-aminocyclopentane-trans-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (trans-ACPD) at maximally effective concentrations (1 mM) of each agonist stimulated [3H]inositol phosphate formation in an additive manner.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)


