Latrunculin AInhibitor of actin assembly and polymerization CAS# 76343-93-6 |
- CUDC-101
Catalog No.:BCC2149
CAS No.:1012054-59-9
- Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)
Catalog No.:BCC2156
CAS No.:1069-66-5
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- Belinostat (PXD101)
Catalog No.:BCC2153
CAS No.:414864-00-9
- Trichostatin A (TSA)
Catalog No.:BCC3605
CAS No.:58880-19-6
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 76343-93-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 445420 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H31NO5S | M.Wt | 421.55 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in DMSO | ||
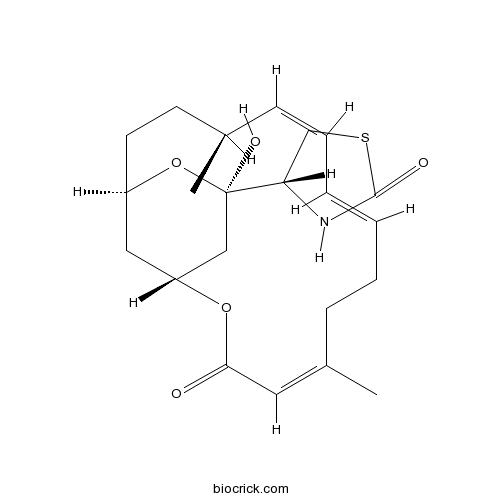
| Chemical Name | (4R)-4-[(1R,4S,5Z,7E,11Z,15R,17R)-17-hydroxy-4,11-dimethyl-13-oxo-14,18-dioxabicyclo[13.3.1]nonadeca-5,7,11-trien-17-yl]-1,3-thiazolidin-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCC2CC(CC(O2)(C3CSC(=O)N3)O)OC(=O)C=C(CCC=CC=C1)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DDVBPZROPPMBLW-IZGXTMSKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H31NO5S/c1-15-7-5-3-4-6-8-16(2)11-20(24)27-18-12-17(10-9-15)28-22(26,13-18)19-14-29-21(25)23-19/h3-5,7,11,15,17-19,26H,6,8-10,12-14H2,1-2H3,(H,23,25)/b4-3+,7-5-,16-11-/t15-,17-,18-,19+,22-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Reversible inhibitor of actin assembly; blocks actin adenine nucleotide exchange. Complexes with actin in vitro and interacts with actin monomers only, unlike cytochalasins. Prevents actin repolymerization into filaments and disrupts the actin cytoskeleton. |

Latrunculin A Dilution Calculator

Latrunculin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3722 mL | 11.861 mL | 23.722 mL | 47.444 mL | 59.3049 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4744 mL | 2.3722 mL | 4.7444 mL | 9.4888 mL | 11.861 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2372 mL | 1.1861 mL | 2.3722 mL | 4.7444 mL | 5.9305 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0474 mL | 0.2372 mL | 0.4744 mL | 0.9489 mL | 1.1861 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1186 mL | 0.2372 mL | 0.4744 mL | 0.593 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- DL-AP5
Catalog No.:BCC6552
CAS No.:76326-31-3
- Sodium Nitrite
Catalog No.:BCC4723
CAS No.:7632-00-0
- Olaparib (AZD2281, Ku-0059436)
Catalog No.:BCC2206
CAS No.:763113-22-0
- Polyphyllin G
Catalog No.:BCN1054
CAS No.:76296-75-8
- Polyphyllin F
Catalog No.:BCN2589
CAS No.:76296-74-7
- Polyphyllin E
Catalog No.:BCN2588
CAS No.:76296-73-6
- Polyphyllin II
Catalog No.:BCN1052
CAS No.:76296-72-5
- Polyphyllin C
Catalog No.:BCN2587
CAS No.:76296-71-4
- 7-Deoxy-10-hydroxyloganetin
Catalog No.:BCN7578
CAS No.:76267-48-6
- Fmoc-Met(O)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3530
CAS No.:76265-70-8
- Fmoc-Lys(Tfa)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3524
CAS No.:76265-69-5
- Yukovanol
Catalog No.:BCN3699
CAS No.:76265-12-8
- (1S)-(+)-Menthyl chloroformate
Catalog No.:BCN4972
CAS No.:7635-54-3
- Euphorbia factor Ti2
Catalog No.:BCN3782
CAS No.:64180-96-7
- Dihydroxyaflavinine
Catalog No.:BCN7387
CAS No.:76410-56-5
- Sodium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7580
CAS No.:7647-14-5
- Cesium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2399
CAS No.:7647-17-8
- Effusanin E
Catalog No.:BCN3234
CAS No.:76470-15-0
- Effusanin B
Catalog No.:BCN3391
CAS No.:76470-16-1
- Kuwanon H
Catalog No.:BCN2945
CAS No.:76472-87-2
- Morachalcone A
Catalog No.:BCN4311
CAS No.:76472-88-3
- Dihydrocurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN6297
CAS No.:76474-56-1
- Galeopsin
Catalog No.:BCN7358
CAS No.:76475-16-6
- Croverin
Catalog No.:BCN2518
CAS No.:76475-17-7
Molecular Dynamics Simulation Reveal the Mechanism of Resistance of Mutant Actins to Latrunculin A - Insight into Specific Modifications to Design Novel Drugs to Overcome Resistance.[Pubmed:27484118]
Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2016;12(2):107-18.
BACKGROUND: Mutant actins D157E and R183A-D184A are reported to resist the anticancer drug Latrunculin A (LAT); though identified, the mechanism of resistance is not clearly understood. OBJECTIVE: To design better molecules that can overcome the resistance caused by mutations it is important to define precise pharmacophoric regions in LAT based on the mechanism of resistance on the mutant actin -LAT interactions. METHODS: To address this we have conducted 20 nano seconds (ns) simulation of mutant actins - LAT complex and compared it with the 20ns simulation of wild actin - LAT complex. Functions as the binding free energy, distance between LAT and binding site residues, LAT and actin domains, dihedral angle analysis, motional correlation were studied of these simulations. RESULTS: Grounded on these studies, four sites in LAT are identified to be crucial for modification. Bulkier ring moieties containing nitrogen in place of the double bonded oxygen in the macrocyclic lactone ring may be considered to establish interactions with Glu214. The nitrogen in 2-thiazolidinone moiety can be substituted with a hydrophobic ring to stabilise the interaction with the Asp157Glu and the oxygen in the cyclohexane of LAT with hydrophilic groups to strengthen their interaction with Tyr69. The nitrogen of the 2-thiazolidinone moiety can be replaced with nitrogen containing rings to improve inhibition of the actin polymerisation. Apart from this chemical groups on the sulphur of 2-thiazolidinone moiety to improve the hydrophobic interaction with actin is also identified for modification. CONCLUSION: Based on this a combinatorial library of 46 LAT analogs was generated and docked with the wild and mutant actins to identify potent leads to become anti-actin anticancer drugs.
Latrunculin A - Insight into Specific Modifications to Design Novel Drugs to Overcome Resistance.[Pubmed:27146706]
Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2016 May 5. pii: CAD-EPUB-75422.
Mutant actins D157E and R183A-D184A are reported to resist the anticancer drug Latrunculin A (LAT); though identified, the mechanism of resistance is not clearly understood. To design a better molecule that can overcome the resistance caused by mutations it is important to define precise pharmacophoric regions in LAT based on the mechanism of resistance on the mutant actin -LAT interactions. To address this we have conducted 20 nano seconds (ns) simulation of mutant actins - LAT complex and compared it with the 20ns simulation of wild actin - LAT complex. Functions as the binding free energy, distance between LAT and binding site residues, LAT and actin domains, dihedral angle analysis, motional correlation were studied for these simulations. Grounded on these observations and studies, four sites in LAT are identified to be crucial for modification. Bulkier ring moieties containing nitrogen in place of the double bonded oxygen in the macrocyclic lactone ring may be considered to establish interactions with Glu214. The nitrogen in 2-thiazolidinone moiety can be substituted with a hydrophobic ring to stabilize the interaction with the Asp157 which is mutated to Glu157and the oxygen in the cyclohexane of LAT with hydrophilic atoms or groups to strengthen their interaction with Tyr69. The nitrogen of the 2-thiazolidinone moiety can be replaced with aromatic nitrogen containing rings to improve inhibition of the actin polymerisation. Apart from this, chemical groups on the sulphur of 2-thiazolidinone moiety to improve the hydrophobic interaction with actin and saturating the double bonds between carbons 10 and 11 to control the conformational flexibility of the LAT are also identified for modification. Based on this a combinatorial library of 46 LAT analogs was generated and docked with the wild and mutant actins to identify potent leads to become anti-actin anticancer drugs.
Latrunculin A-Induced Perturbation of the Actin Cytoskeleton Mediates Pap1p-Dependent Induction of the Caf5p Efflux Pump in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.[Pubmed:28040778]
G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Feb 9;7(2):723-730.
As part of an earlier study aimed at uncovering gene products with roles in defending against Latrunculin A (LatA)-induced cytoskeletal perturbations, we identified three members of the oxidative stress response pathway: the Pap1p AP-1-like transcription factor, the Imp1p alpha-importin, and the Caf5p efflux pump. In this report, we characterize the pathway further and show that Pap1p translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus in an Imp1p-dependent manner upon LatA treatment. Moreover, preventing this translocation, through the addition of a nuclear export signal (NES), confers the same characteristic LatA-sensitive phenotype exhibited by pap1Delta cells. Lastly, we show that the caf5 gene is induced upon exposure to LatA and that Pap1p is required for this transcriptional upregulation. Importantly, the expression of trr1, a Pap1p target specifically induced in response to oxidative stress, is not significantly altered by LatA treatment. Taken together, these results suggest a model in which LatA-mediated cytoskeletal perturbations are sensed, triggering the Imp1p-dependent translocation of Pap1p to the nucleus and the induction of the caf5 gene (independently of oxidative stress).
A Genetic Screen for Fission Yeast Gene Deletion Mutants Exhibiting Hypersensitivity to Latrunculin A.[Pubmed:27466272]
G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Oct 13;6(10):3399-3408.
Fission yeast cells treated with low doses of the actin depolymerizing drug, Latrunculin A (LatA), delay entry into mitosis via a mechanism that is dependent on both the Clp1p and Rad24p proteins. During this delay, cells remain in a cytokinesis-competent state that is characterized by continuous repair and/or reestablishment of the actomyosin ring. In this manner, cells ensure the faithful completion of the preceding cytokinesis in response to perturbation of the cell division machinery. To uncover other genes with a role in this response, or simply genes with roles in adapting to LatA-induced stress, we carried out a genome-wide screen and identified a group of 38 gene deletion mutants that are hyper-sensitive to the drug. As expected, we found genes affecting cytokinesis and/or the actin cytoskeleton within this set (ain1, acp2, imp2). We also identified genes with roles in histone modification (tra1, ngg1), intracellular transport (apl5, aps3), and glucose-mediated signaling (git3, git5, git11, pka1, cgs2). Importantly, while the identified gene deletion mutants are prone to cytokinesis failure in the presence of LatA, they are nevertheless fully capable of cell division in the absence of the drug. These results indicate that fission yeast cells make use of a diverse set of regulatory modules to counter abnormal cytoskeletal perturbations, and furthermore, that these modules act redundantly to ensure cell survival and proliferation.
Actin-latrunculin A structure and function. Differential modulation of actin-binding protein function by latrunculin A.[Pubmed:10859320]
J Biol Chem. 2000 Sep 8;275(36):28120-7.
Latrunculin A is used extensively as an agent to sequester monomeric actin in living cells. We hypothesize that additional activities of Latrunculin A may be important for its biological activity. Our data are consistent with the formation of a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with an equilibrium dissociation constant of 0.2 to 0.4 micrometer and provide no evidence that the actin-Latrunculin A complex participates in the elongation of actin filaments. Profilin and Latrunculin A bind independently to actin, whereas binding of thymosin beta(4) to actin is inhibited by Latrunculin A. Potential implications of this differential effect on actin-binding proteins are discussed. From a structural perspective, if Latrunculin A binds to actin at a site that sterically influences binding by thymosin beta(4), then the observation that Latrunculin A inhibits nucleotide exchange on actin implies an allosteric effect on the nucleotide binding cleft. Alternatively, if, as previously postulated, Latrunculin A binds in the nucleotide cleft of actin, then its ability to inhibit binding by thymosin beta(4) is a surprising result that suggests that significant allosteric changes affect the thymosin beta(4) binding site. We show that Latrunculin A and actin form a crystalline structure with orthorhombic space group P2(1)2(1)2(1) and diffraction to 3.10 A. A high resolution structure with optimized crystallization conditions should provide insight regarding these remarkable allosteric properties.


