ML 9 hydrochlorideMyosin light chain kinase inhibitor CAS# 105637-50-1 |
- TAK-438
Catalog No.:BCC1182
CAS No.:1260141-27-2
- Istaroxime
Catalog No.:BCC1660
CAS No.:203737-93-3
- Dynasore
Catalog No.:BCC1088
CAS No.:304448-55-3
- Istaroxime hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1661
CAS No.:374559-48-5
- 20-HETE
Catalog No.:BCC1301
CAS No.:79551-86-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 105637-50-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 108047 | Appearance | Powder |
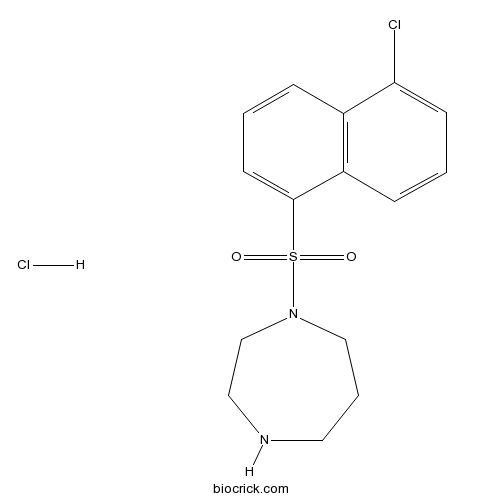
| Formula | C15H18Cl2N2O2S | M.Wt | 361.29 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-(5-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)sulfonyl-1,4-diazepane;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | C1CNCCN(C1)S(=O)(=O)C2=CC=CC3=C2C=CC=C3Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZNRYCIVTNLZOGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H17ClN2O2S.ClH/c16-14-6-1-5-13-12(14)4-2-7-15(13)21(19,20)18-10-3-8-17-9-11-18;/h1-2,4-7,17H,3,8-11H2;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective MLCK inhibitor (Ki values are 4, 32 and 54 μM for MLCK, PKA and PKC respectively). Also inhibits STIM1-plasma membrane interactions, preventing store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE). |

ML 9 hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

ML 9 hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7679 mL | 13.8393 mL | 27.6786 mL | 55.3572 mL | 69.1965 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5536 mL | 2.7679 mL | 5.5357 mL | 11.0714 mL | 13.8393 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2768 mL | 1.3839 mL | 2.7679 mL | 5.5357 mL | 6.9196 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0554 mL | 0.2768 mL | 0.5536 mL | 1.1071 mL | 1.3839 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0277 mL | 0.1384 mL | 0.2768 mL | 0.5536 mL | 0.692 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- Fasudil (HA-1077) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2542
CAS No.:105628-07-7
- Prostephanaberrine
Catalog No.:BCN4736
CAS No.:105608-27-3
- BMY 14802 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5759
CAS No.:105565-55-7
- Ginsenoside Rh3
Catalog No.:BCN1071
CAS No.:105558-26-7
- Fmoc-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3094
CAS No.:105496-31-9
- Calceolarioside B
Catalog No.:BCN2787
CAS No.:105471-98-5
- Risedronate
Catalog No.:BCC4711
CAS No.:105462-24-6
- 7-Epitaxol
Catalog No.:BCN2514
CAS No.:105454-04-4
- Tamoxifen
Catalog No.:BCN1634
CAS No.:10540-29-1
- Spiroxatrine
Catalog No.:BCC6728
CAS No.:1054-88-2
- Bis(3-ethyl-5-methyl-4-maleimidophenyl)methane
Catalog No.:BCC8881
CAS No.:105391-33-1
- Mizolastine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4132
CAS No.:1056596-82-7
- CYT387
Catalog No.:BCC2196
CAS No.:1056634-68-4
- CYT387 sulfate salt
Catalog No.:BCC1506
CAS No.:1056636-06-6
- AT13148
Catalog No.:BCC5360
CAS No.:1056901-62-2
- Androstanolone 17-benzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8825
CAS No.:1057-07-4
- AL 8697
Catalog No.:BCC8037
CAS No.:1057394-06-5
- Ganoderic acid C6
Catalog No.:BCN3257
CAS No.:105742-76-5
- Methyl ganoderate C6
Catalog No.:BCN3259
CAS No.:105742-81-2
- Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3545
CAS No.:105751-13-1
- Sitostenone
Catalog No.:BCN5868
CAS No.:1058-61-3
- E-3810
Catalog No.:BCC1541
CAS No.:1058137-23-7
- Nateglinide
Catalog No.:BCC5005
CAS No.:105816-04-4
In vivo comet assay of acrylonitrile, 9-aminoacridine hydrochloride monohydrate and ethanol in rats.[Pubmed:26212299]
Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Jul;786-788:104-13.
As part of the Japanese Center for the Validation of Alternative Methods (JaCVAM)-initiative international validation study of the in vivo rat alkaline comet assay, we examined the ability of acrylonitrile, 9-aminoacridine hydrochloride monohydrate (9-AA), and ethanol to induce DNA damage in the liver and glandular stomach of male rats. Acrylonitrile is a genotoxic carcinogen, 9-AA is a genotoxic non-carcinogen, and ethanol is a non-genotoxic carcinogen. Positive results were obtained in the liver cells of male rats treated with known genotoxic compounds, acrylonitrile and 9-AA.
Stability of i.v. admixture containing metoclopramide, diphenhydramine hydrochloride, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate in 0.9% sodium chloride injection.[Pubmed:25404598]
Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014 Dec 1;71(23):2061-5.
PURPOSE: The chemical stability of a sterile admixture containing metoclopramide 1.6 mg/mL, diphenhydramine hydrochloride 2 mg/mL, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate 0.16 mg/mL in 0.9% sodium chloride injection was evaluated. METHODS: Triplicate samples were prepared and stored at room temperature without light protection for a total of 48 hours. Aliquots from each sample were tested for chemical stability immediately after preparation and at 1, 4, 8, 24, and 48 hours using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis. Metoclopramide, diphenhydramine hydrochloride, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate were selectively monitored using multiple-reaction monitoring. Samples were diluted differently for quantitation using three individual LC-MS/MS methods. To determine the drug concentration of the three compounds in the samples, three calibration curves were constructed by plotting the peak area or the peak area ratio versus the concentration of the calibration standards of each tested compound. Apixaban was used as an internal standard. Linearity of the calibration curve was evaluated by the correlation coefficient r(2). RESULTS: Constituents of the admixture of metoclopramide 1.6 mg/mL, diphenhydramine hydrochloride 2 mg/mL, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate 0.16 mg/mL in 0.9% sodium chloride injection retained more than 90% of their initial concentrations over 48 hours of storage at room temperature without protection from light. The observed variability in concentrations of these three compounds was within the limits of assay variability. CONCLUSION: An i.v. admixture containing metoclopramide 1.6 mg/mL, diphenhydramine hydrochloride 2 mg/mL, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate 0.16 mg/mL in 0.9% sodium chloride injection was chemically stable for 48 hours when stored at room temperature without light protection.
Long-term stability of morphine hydrochloride in 0.9% NaCl infusion polyolefin bags after freeze-thaw treatment and in polypropylene syringes at 5 degrees C + 3 degrees C.[Pubmed:24881344]
Int J Pharm Compd. 2014 Jan-Feb;18(1):78-82.
The aim of this study was to investigate the long-term stability of morphine hydrochloride in 0.9% NaCI infusion polyolefin bags and polypropylene syringes after storage at 5 degrees C + 3 degrees C and to evaluate the influence of initial freezing and microwave thawing on this stability. Ten polyolefin bags and five polypropylene syringes containing 100 mL of 1 mg/mL of morphine hydrochloride solution in 0.9% NaCI were prepared under aseptic conditions. Five polyolefin bags were frozen at -20 degrees C for 90 days before storage. Immediately after the preparation and after thawing, 2 mL of each bag were withdrawn for the initial concentration measurements. All polyolefin bags and polypropylene syringes were then refrigerated at 5 degrees C + 3 degrees C for 58 days during which the morphine concentrations were measured periodically by high-performance liquid chromatography using a reversed-phase column, naloxone as internal standard, a mobile phase consisting of 5% acetonitrile and 95% of KH2PO4 buffer (pH 3.50), and detection with diode array detector at 254 nm. Visual and microscopic observations and spectrophotometric and pH measurements were also performed. Solutions were considered stable if the concentration remained superior to 90% of the initial concentration. The degradation products peaks were not quantitatively significant and were resolved from the native drug. Polyolefin bag and polypropylene syringe solutions were stable when stored at 5 degrees C + 3 degrees C during these 58 days. No color change or precipitation in the solutions was observed. The physical stability was confirmed by visual, microscopic, and spectrophotometric inspection. There was no significant change in pH during storage. Freezing and microwave thawing didn't influence the infusion stability. Morphine hydrochloride infusions may be prepared in advance by centralized intravenous additive service, frozen in polyolefin bags, and microwave thawed before storage under refrigeration until 58 days either in polyolefin bags or polypropylene syringes. Such treatment could improve safety and management.
Stability of Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride, Lorazepam, and Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Stored in Polypropylene Syringes.[Pubmed:26625573]
Int J Pharm Compd. 2015 Jul-Aug;19(4):344-7.
Chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting is problematic for many patients undergoing chemotherapy. Multiple-drug treatments have been developed to mitigate chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting. A patient-controlled infusion of diphenhydramine hydrochloride, lorazepam, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate has been studied in patients who are refractory to first-line therapy. Unfortunately, the physical and chemical compatibility of this three-drug combination is not available in the published literature. Chemical compatibility was evaluated using high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. Visual observation was employed to detect change in color, clarity, or gas evolution. Turbidity and pH measurements were performed in conjunction with visual observation at hours 0, 24, and 48. Results showed that diphenhydramine hydrochloride 4 mg/mL, lorazepam 0.16 mg/mL, and dexamethasone sodium phosphate 0.27 mg/mL in 0.9% sodium chloride stored in polypropylene syringes were compatible, and components retained greater than 95% of their original concentration over 48 hours when stored at room temperature.
STIM and Orai: the long-awaited constituents of store-operated calcium entry.[Pubmed:19187978]
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Mar;30(3):118-28.
Rapid changes in cytosolic Ca(2+) concentrations [Ca(2+)](i) are the most commonly used signals in biology to regulate a whole host of cellular functions including contraction, secretion and gene activation. A widely utilized form of Ca(2+) influx is termed store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) owing to its control by the Ca(2+) content of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The underlying molecular mechanism of SOCE has eluded identification until recently when two groups of proteins, the ER Ca(2+) sensors stromal interaction molecule (STIM)1 and STIM2 and the plasma-membrane channels Orai1, Orai2 and Orai3, have been identified. These landmark discoveries have enabled impressive progress in clarifying how these proteins work in concert and what developmental and cellular processes require their participation most. As we begin to better understand the biology of the STIM and Orai proteins, the attention to the pharmacological tools to influence their functions quickly follow suit. Here, we briefly summarize recent developments in this exciting area of Ca(2+) signaling.
Effects of HA1077, a protein kinase inhibitor, on myosin phosphorylation and tension in smooth muscle.[Pubmed:1874276]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar 26;195(2):267-72.
We examined the effects of HA1077, a potent inhibitor of protein kinases in vitro, on the relationship between tension and myosin-light chain (MLC20) phosphorylation in the initial phase of contraction of the rabbit aorta. The dose-response curve of HA1077 for MLC20 phosphorylation was to the left of the tension curve produced by 40 mM K+. In contrast, the potassium dose-response (15-100 mM) curves for tension and MLC20 phosphorylation were virtually identical. The nifedipine dose-response (1-3000 nM) curves for tension and MLC20 phosphorylation after 40 mM K(+)-stimulation were much the same. HA1077 inhibited the contraction induced by 30 microM prostaglandin F2 alpha (ED50 = 50 microM). Stimulation with prostaglandin F2 alpha induced both mono (MLC-P) and diphosphorylation (MLC-P2) of MLC20. In the presence of various concentrations of HA1077 (1-300 microM), the dose-response curves for MLC-P and MLC-P2 were also to the left of the tension curve. HA1077 inhibited MLC-P2 (ED50 less than microM) more effectively than it inhibited MLC-P (ED50 = 2.1 microM). These observations indicate that the relationship between tension and MLC20 phosphorylation involves inhibition of protein kinases by HA1077. The mechanism underlying the formation of MLC-P2 induced by prostaglandin F2 alpha may differ from that underlying MLC-P formation.


