RisedronateCAS# 105462-24-6 |
- Methylcobalamin
Catalog No.:BCC5188
CAS No.:13422-55-4
- TPT-260 Dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5172
CAS No.:2076-91-7
- Miglustat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5186
CAS No.:210110-90-0
- Tirapazamine
Catalog No.:BCC5184
CAS No.:27314-97-2
- Amifampridine
Catalog No.:BCC5185
CAS No.:54-96-6
- Miglustat
Catalog No.:BCC5187
CAS No.:72599-27-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 105462-24-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5245 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C7H11NO7P2 | M.Wt | 283.11 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Risedronate | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
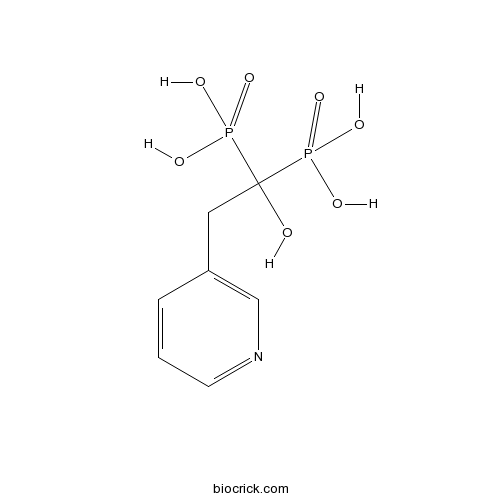
| Chemical Name | (1-hydroxy-1-phosphono-2-pyridin-3-ylethyl)phosphonic acid | ||
| SMILES | OC(Cc1cccnc1)([P](O)(O)=O)[P](O)(O)=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IIDJRNMFWXDHID-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H11NO7P2/c9-7(16(10,11)12,17(13,14)15)4-6-2-1-3-8-5-6/h1-3,5,9H,4H2,(H2,10,11,12)(H2,13,14,15) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Risedronic acid (Risedronate ) is a pyridinyl biphosphonate which inhibits osteoclast-mediated bone resorption.
Target: Others
Risedronate, which was promoted in Croatia a few months ago, is the latest (III) generation of bisphosphonates, the most efficient anti-resorption drugs that inhibit osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and change the bone metabolism. Risedronate is hence the first line of bisphosphonates for the reduction of vertebral and non-vertebral fracture risks in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis or those with a high risk of osteoporosis. It also efficiently prevents bone loss or improves bone density in men and women on a long-term corticosteroid therapy .
The administration of 20 and 25 mg/kg risedronate for 4 days led to decreases of parasitemia of 68.9% and 83.6%, respectively. On the seventh day of treatment the inhibitions were 63% and 88.9% with 20 and 25 mg/kg, respectively. After recovering the parasitemia, a dose-response curve was obtained for estimating the ID50 (dose causing 50% inhibition), equivalent to 17 ± 1.8 mg/kg after 7 days of treatment. Four days after the interruption of treatment (11 days postinfection), the parasitemias of the groups treated with 10, 15, 20, and 25 mg/kg/day were 15.3%, 15.9%, 15.2%, and 5.7%, respectively. Conversely, the group that received PBS presented parasitemia of 25.6%. Among the groups treated with risedronate, only the animals that received 25 mg/kg had a significant inhibition of 77.8% (see Table S1 in the supplemental material), demonstrating that even after treatment discontinuation, the parasitemia of the animals remained low in relation to that of the controls . References: | |||||

Risedronate Dilution Calculator

Risedronate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5322 mL | 17.661 mL | 35.322 mL | 70.6439 mL | 88.3049 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7064 mL | 3.5322 mL | 7.0644 mL | 14.1288 mL | 17.661 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3532 mL | 1.7661 mL | 3.5322 mL | 7.0644 mL | 8.8305 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0706 mL | 0.3532 mL | 0.7064 mL | 1.4129 mL | 1.7661 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0353 mL | 0.1766 mL | 0.3532 mL | 0.7064 mL | 0.883 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Risedronic acid (Risedronate ) is a pyridinyl biphosphonate which inhibits osteoclast-mediated bone resorption.
- 7-Epitaxol
Catalog No.:BCN2514
CAS No.:105454-04-4
- Tamoxifen
Catalog No.:BCN1634
CAS No.:10540-29-1
- Spiroxatrine
Catalog No.:BCC6728
CAS No.:1054-88-2
- Bis(3-ethyl-5-methyl-4-maleimidophenyl)methane
Catalog No.:BCC8881
CAS No.:105391-33-1
- Shuterin
Catalog No.:BCN8068
CAS No.:105377-77-3
- Tyrphostin 9
Catalog No.:BCC4471
CAS No.:10537-47-0
- Tanshinlactone
Catalog No.:BCN5867
CAS No.:105351-70-0
- 5,7,4'-Tri-O-methylcatechin
Catalog No.:BCN3951
CAS No.:105330-59-4
- Neocaesalpin O
Catalog No.:BCN7266
CAS No.:1053189-53-9
- Aloeresin D
Catalog No.:BCN2850
CAS No.:105317-67-7
- Ganodermatriol
Catalog No.:BCC8177
CAS No.:105300-28-5
- 3'-Deoxy-4-O-methylepisappanol
Catalog No.:BCN3676
CAS No.:1052714-12-1
- Calceolarioside B
Catalog No.:BCN2787
CAS No.:105471-98-5
- Fmoc-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3094
CAS No.:105496-31-9
- Ginsenoside Rh3
Catalog No.:BCN1071
CAS No.:105558-26-7
- BMY 14802 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5759
CAS No.:105565-55-7
- Prostephanaberrine
Catalog No.:BCN4736
CAS No.:105608-27-3
- Fasudil (HA-1077) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2542
CAS No.:105628-07-7
- Hydroxyfasudil
Catalog No.:BCC1635
CAS No.:105628-72-6
- ML 9 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6644
CAS No.:105637-50-1
- Mizolastine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4132
CAS No.:1056596-82-7
- CYT387
Catalog No.:BCC2196
CAS No.:1056634-68-4
- CYT387 sulfate salt
Catalog No.:BCC1506
CAS No.:1056636-06-6
- AT13148
Catalog No.:BCC5360
CAS No.:1056901-62-2
Risedronate therapy in patients with mild-to-moderate chronic kidney disease with osteoporosis: post-hoc analysis of data from the risedronate phase III clinical trials.[Pubmed:28201994]
BMC Nephrol. 2017 Feb 15;18(1):66.
BACKGROUND: The clinical effect of bisphosphonate treatment has not been clearly evaluated by kidney function in Japanese Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) patients with osteoporosis. This study analyzed the data from three Risedronate Japanese phase III trials. The clinical effect of Risedronate therapy was evaluated in CKD patients with osteoporosis. METHODS: The Japanese clinical trials involved 852 subjects who received Risedronate (2.5 mg once daily or 17.5 mg once weekly) and whose estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were calculable and at >/= 30 mL/min. The subjects were divided into subgroups according to the eGFR level: >/= 90 mL/min/1.73 m(2), >/= 60 to < 90 mL/min/1.73 m(2), >/= 30 to < 60 mL/min/1.73 m(2). Lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD), bone turnover markers (BTMs) and adverse events were evaluated at 48 weeks. RESULTS: Adverse event incidence was similar among three subgroups. There was also no exacerbation of impaired kidney function associated with Risedronate administration in the subjects with eGFR above 30 mL/min/1.73 m(2). Risedronate administration induced a significant increase in lumbar spine BMD and significant inhibition of BTMs in three subgroups. CONCLUSIONS: The Risedronate therapy showed similar clinical effects in CKD patients with osteoporosis compared to those without CKD.
Effect of Sequential Treatment with Bisphosphonates After Teriparatide in Ovariectomized Rats: A Direct Comparison Between Risedronate and Alendronate.[Pubmed:28337514]
Calcif Tissue Int. 2017 Jul;101(1):102-110.
Teriparatide (TPTD), a recombinant human parathyroid hormone N-terminal fragment (1-34), is a widely used bone anabolic drug for osteoporosis. Sequential treatment with antiresorptives such as bisphosphonates after TPTD discontinuation is generally recommended. However, relative effects of bisphosphonates have not been determined. In the present study, we directly compared effects of Risedronate (RIS) and alendronate (ALN) on bone mineral density (BMD), bone turnover, structural property and strength in ovariectomized (OVX) rats, when administered after TPTD. Female Sprague Dawley rats were divided into one sham-operated and eight ovariectomized groups. TPTD, RIS, and ALN were given subcutaneously twice per week for 4 or 8 weeks after 4 week treatment with TPTD. TPTD significantly increased BMD (+9.6%) in OVX rats after 4 weeks of treatment. 8 weeks after TPTD withdrawal, vehicle-treated group showed a blunted BMD increase of +8.4% from the baseline. In contrast, 8 weeks of treatment with RIS and ALN significantly increased BMD to 17.4 and 21.8%, respectively. While ALN caused a consistently larger increase in BMD, sequential treatment with RIS resulted in lower Tb.Sp compared to ALN in the fourth lumbar vertebra as well as in greater stiffness in compression test. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that sequential therapy with ALN and RIS after TPTD both improved bone mass and structure. Our results further suggest that RIS may have a greater effect on improving bone quality and stiffness than ALN despite less prominent effect on BMD. Further studies are necessary to determine clinical relevance of these findings to fracture rate.


