N-MethyltaurineCAS# 107-68-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 107-68-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 7882 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C3H9NO3S | M.Wt | 139.17 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(methylamino)ethanesulfonic acid | ||
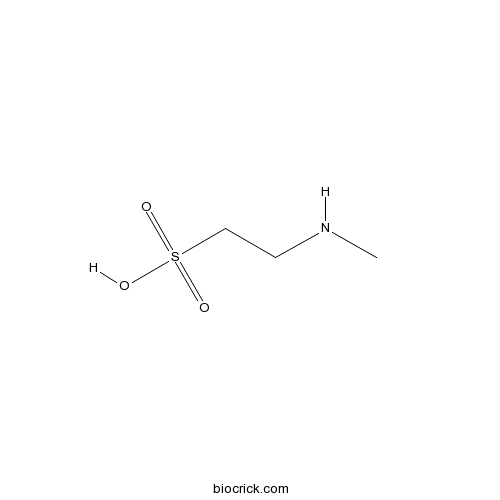
| SMILES | CNCCS(=O)(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SUZRRICLUFMAQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C3H9NO3S/c1-4-2-3-8(5,6)7/h4H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,5,6,7) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. The presence of N-Methyltaurine conjugated bile acids that are resistant to bacterial attack; the excreted N-Methyltaurine could be utilized by other bacteria in cocultures. 2. N-Methyltaurine conjugated bile acids are resistant to bacterial deconjugation and dehydroxylation, and such resistance to bacterial enzymes should aid in the maintenance of high concentrations of bile acids during lipid digestion. |

N-Methyltaurine Dilution Calculator

N-Methyltaurine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.1855 mL | 35.9273 mL | 71.8546 mL | 143.7091 mL | 179.6364 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.4371 mL | 7.1855 mL | 14.3709 mL | 28.7418 mL | 35.9273 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.7185 mL | 3.5927 mL | 7.1855 mL | 14.3709 mL | 17.9636 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1437 mL | 0.7185 mL | 1.4371 mL | 2.8742 mL | 3.5927 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0719 mL | 0.3593 mL | 0.7185 mL | 1.4371 mL | 1.7964 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Betaine
Catalog No.:BCN6303
CAS No.:107-43-7
- Taurine
Catalog No.:BCN1750
CAS No.:107-35-7
- Propylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1814
CAS No.:107-10-8
- Boc-isoleucinol
Catalog No.:BCC3096
CAS No.:106946-74-1
- Adefovir
Catalog No.:BCC8808
CAS No.:106941-25-7
- Boc-D-Leucinol
Catalog No.:BCC2723
CAS No.:106930-51-2
- Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)
Catalog No.:BCC2156
CAS No.:1069-66-5
- 5-Allyl-3-methoxy-6-methyl-7-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)bicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-ene-2,8-dione
Catalog No.:BCN1632
CAS No.:106894-43-3
- BIBP 3226 trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC7456
CAS No.:1068148-47-9
- Diethyl Acetamidomalonate
Catalog No.:BCC2841
CAS No.:1068-90-2
- Otophylloside B
Catalog No.:BCN7267
CAS No.:106758-54-7
- 24-Deacetylalisol O
Catalog No.:BCN3365
CAS No.:1067510-31-9
- 3-Methyl-1-butylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1810
CAS No.:107-85-7
- H-ß-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2851
CAS No.:107-95-9
- Sarcosine
Catalog No.:BCN2744
CAS No.:107-97-1
- Granisetron HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1060
CAS No.:107007-99-8
- Amyloid Beta-Peptide (12-28) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1044
CAS No.:107015-83-8
- O-Phosphorylethanolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1759
CAS No.:1071-23-4
- EIT hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6824
CAS No.:1071-37-0
- Apo-12'-Lycopenal
Catalog No.:BCC8298
CAS No.:1071-52-9
- Adipic dihydrazide
Catalog No.:BCC8810
CAS No.:1071-93-8
- 8,9-Dihydroxy-10-isobutyryloxythymol
Catalog No.:BCN7974
CAS No.:107109-97-7
- Perindopril Erbumine
Catalog No.:BCC3586
CAS No.:107133-36-8
- Pyrocincholic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN5873
CAS No.:107160-24-7
Amphoteric surfactant N-oleoyl-N-methyltaurine utilized by Pseudomonas alcaligenes with excretion of N-methyltaurine.[Pubmed:18783436]
FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008 Nov;288(1):112-7.
The amphoteric surfactant N-oleoyl-N-Methyltaurine, which is in use in skin-care products, was utilized by aerobic bacteria as the sole source of carbon or of nitrogen in enrichment cultures. One isolate, which was identified as Pseudomonas alcaligenes, grew with the xenobiotic compound as the sole source of carbon and energy. The sulfonate moiety, N-Methyltaurine, was excreted quantitatively during growth, while the fatty acid was dissimilated. The initial degradative reaction was shown to be hydrolytic and inducible. This amidase reaction could be demonstrated with crude cell extracts. The excreted N-Methyltaurine could be utilized by other bacteria in cocultures. Complete degradation of similar natural compounds in bacterial communities seems likely.
N-Methyltaurine N-acyl amidated bile acids and deoxycholic acid in the bile of angelfish (Pomacanthidae): a novel bile acid profile in Perciform fish.[Pubmed:24291417]
Steroids. 2014 Feb;80:15-23.
Two novel N-acyl amidated bile acids, N-Methyltaurine conjugated cholic acid and N-Methyltaurine conjugated deoxycholic acid, were found to be major biliary bile acids in two species of angelfish the regal (Pygoplites diacanthus) and the blue-girdled (Pomacanthus navarchus) angelfish. The identification was based on their having MS and NMR spectra identical to those of synthetic standards. A survey of biliary bile acids of 10 additional species of angelfish found 7 with N-Methyltaurine conjugation. In all 12 species, conjugated deoxycholic acid (known to be formed by bacterial 7-dehydroxylation of cholic acid) was a major bile acid. In all previous studies of biliary bile acids in fish, deoxycholic acid has been present in only trace proportions. In addition, bile acid conjugation with N-Methyltaurine has not been detected previously in any known vertebrate. N-Methyltaurine conjugated bile acids are resistant to bacterial deconjugation and dehydroxylation, and such resistance to bacterial enzymes should aid in the maintenance of high concentrations of bile acids during lipid digestion. Our findings suggest that these species of angelfish have a novel microbiome in their intestine containing anaerobic bacteria, and describe the presence of N-Methyltaurine conjugated bile acids that are resistant to bacterial attack.
Hypotaurine, N-methyltaurine, taurine, and glycine betaine as dominant osmolytes of vestimentiferan tubeworms from hydrothermal vents and cold seeps.[Pubmed:11073799]
Physiol Biochem Zool. 2000 Sep-Oct;73(5):629-37.
Organic osmolytes, solutes that regulate cell volume, occur at high levels in marine invertebrates. These are mostly free amino acids such as taurine, which are "compatible" with cell macromolecules, and methylamines such as trimethylamine oxide, which may have a nonosmotic role as a protein stabilizer, and which is higher in many deep-sea animals. To better understand nonosmotic roles of osmolytes, we used high-performance liquid chromatography and (1)H-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to analyze vestimentiferans (vestimentum tissue) from unusual marine habitats. Species from deep hydrothermal vents were Riftia pachyptila of the East Pacific Rise (2,636 m) and Ridgeia piscesae of the Juan de Fuca Ridge (2,200 m). Species from cold hydrocarbon seeps were Lamellibrachia sp. and an unnamed escarpid species from subtidal sediment seeps (540 m) off Louisiana and Lamellibrachia barhami from bathyal tectonic seeps (1,800-2,000 m) off Oregon. Riftia were dominated by hypotaurine (152 mmol/kg wet wt), an antioxidant, and an unidentified solute with an NMR spectrum consistent with a methylamine. Ridgeia were dominated by betaine (N-trimethylglycine; 109 mmol/kg), hypotaurine (64 mmol/kg), and taurine (61 mmol/kg). The escarpids were dominated by taurine (138 mmol/kg) and hypotaurine (69 mmol/kg). Both Lamellibrachia populations were dominated by N-Methyltaurine (209-252 mmol/kg), not previously reported as a major osmolyte, which may be involved in methane and sulfate metabolism. Trunk and plume tissue of the Oregon Lamellibrachia were nearly identical to vestimentum in osmolyte composition. The methylamines may also stabilize proteins against pressure; they were significantly higher in the three deeper-dwelling groups.
The sulfonated osmolyte N-methyltaurine is dissimilated by Alcaligenes faecalis and by Paracoccus versutus with release of methylamine.[Pubmed:16549680]
Microbiology. 2006 Apr;152(Pt 4):1179-86.
Selective enrichments yielded bacterial cultures able to utilize the osmolyte N-Methyltaurine as sole source of carbon and energy or as sole source of fixed nitrogen for aerobic growth. Strain MT1, which degraded N-Methyltaurine as a sole source of carbon concomitantly with growth, was identified as a strain of Alcaligenes faecalis. Stoichiometric amounts of methylamine, whose identity was confirmed by matrix-assisted, laser-desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry, and of sulfate were released during growth. Inducible N-Methyltaurine dehydrogenase, sulfoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase (Xsc) and a sulfite dehydrogenase could be detected. Taurine dehydrogenase was also present and it was hypothesized that taurine dehydrogenase has a substrate range that includes N-Methyltaurine. Partial sequences of a tauY-like gene (encoding the putative large component of taurine dehydrogenase) and an xsc gene were obtained by PCR with degenerate primers. Strain N-MT utilized N-Methyltaurine as a sole source of fixed nitrogen for growth and could also utilize the compound as sole source of carbon. This bacterium was identified as a strain of Paracoccus versutus. This organism also expressed inducible (N-methyl)taurine dehydrogenase, Xsc and a sulfite dehydrogenase. The presence of a gene cluster with high identity to a larger cluster from Paracoccus pantotrophus NKNCYSA, which is now known to dissimilate N-Methyltaurine via Xsc, allowed most of the overall pathway, including transport and excretion, to be defined. N-Methyltaurine is thus another compound whose catabolism is channelled directly through sulfoacetaldehyde.


