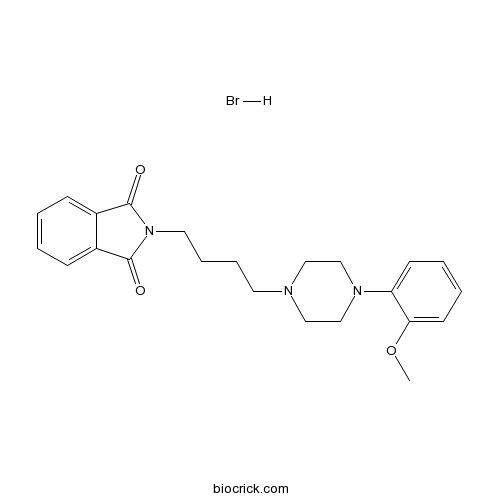
NAN-190 hydrobromide5-HT1A antagonist CAS# 115338-32-4 |
- Alvimopan monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1349
CAS No.:1383577-62-5
- Alvimopan
Catalog No.:BCC1347
CAS No.:156053-89-3
- Alvimopan dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1348
CAS No.:170098-38-1
- ADL5859 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1265
CAS No.:850173-95-4
- Cebranopadol
Catalog No.:BCC1467
CAS No.:863513-91-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 115338-32-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 107966 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H28BrN3O3 | M.Wt | 474.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (35.14 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butyl]isoindole-1,3-dione;hydrobromide | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=CC=C1N2CCN(CC2)CCCCN3C(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4C3=O.Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AXRUEPFPTQYHQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H27N3O3.BrH/c1-29-21-11-5-4-10-20(21)25-16-14-24(15-17-25)12-6-7-13-26-22(27)18-8-2-3-9-19(18)23(26)28;/h2-5,8-11H,6-7,12-17H2,1H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 5-HT1A antagonist. |

NAN-190 hydrobromide Dilution Calculator

NAN-190 hydrobromide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1079 mL | 10.5396 mL | 21.0793 mL | 42.1585 mL | 52.6981 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4216 mL | 2.1079 mL | 4.2159 mL | 8.4317 mL | 10.5396 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2108 mL | 1.054 mL | 2.1079 mL | 4.2159 mL | 5.2698 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0422 mL | 0.2108 mL | 0.4216 mL | 0.8432 mL | 1.054 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0211 mL | 0.1054 mL | 0.2108 mL | 0.4216 mL | 0.527 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Dihydroniloticin
Catalog No.:BCN6032
CAS No.:115334-05-9
- Phellochin
Catalog No.:BCN6031
CAS No.:115334-04-8
- Isosalvipuberulin
Catalog No.:BCN6030
CAS No.:115321-32-9
- 3-Bromo-N-phenylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN2260
CAS No.:1153-85-1
- A 1120
Catalog No.:BCC7775
CAS No.:1152782-19-8
- Dofetilide
Catalog No.:BCC3770
CAS No.:115256-11-6
- VX-661
Catalog No.:BCC1241
CAS No.:1152311-62-0
- 8-pCPT-2-O-Me-cAMP-AM
Catalog No.:BCC6305
CAS No.:1152197-23-3
- Z-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2760
CAS No.:1152-62-1
- Z-Asp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2793
CAS No.:1152-61-0
- ICI 199,441 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6792
CAS No.:115199-84-3
- Caprarioside
Catalog No.:BCN7278
CAS No.:1151862-69-9
- Siguazodan
Catalog No.:BCC6954
CAS No.:115344-47-3
- Kanshone A
Catalog No.:BCN7279
CAS No.:115356-18-8
- 2,2-Dimethyl-6-phenylpyrano[3,4-b]pyran-8-one
Catalog No.:BCN7280
CAS No.:1153624-36-2
- Kanshone B
Catalog No.:BCN7700
CAS No.:115370-61-1
- EIPA
Catalog No.:BCC7672
CAS No.:1154-25-2
- Molidustat (BAY85-3934)
Catalog No.:BCC6412
CAS No.:1154028-82-6
- Niloticin
Catalog No.:BCN6033
CAS No.:115404-57-4
- Risedronate Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC2501
CAS No.:115436-72-1
- Sootepin D
Catalog No.:BCN6034
CAS No.:1154518-97-4
- Glaucin B
Catalog No.:BCN6035
CAS No.:115458-73-6
- 5,6,7,7a-Tetrahydrothieno[3,2-c]pyridine-2(4H)-one hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8721
CAS No.:115473-15-9
- Z-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2781
CAS No.:1155-62-0
Resveratrol Improves Brain-Gut Axis by Regulation of 5-HT-Dependent Signaling in the Rat Model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome.[Pubmed:30800058]
Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Feb 8;13:30.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is at high risk of co-morbid depression and anxiety, which reduces patients' quality of life and increases the burden of health care costs. However, the pathophysiological mechanisms responsible for IBS still remain unknown. This study investigated the effects of resveratrol on stress-related depression, anxiety, intestinal and visceral dysfunction in rat model of IBS. Rats received chronic acute combining stress (CACS) for 22 days exhibited depression/anxiety-like behavior, visceral hypersensitivity and altered intestinal motility, as measured by the forced swimming, marble bury, abdominal withdrawal reflex (AWR) and intestinal tract motility (ITM) tests. These abnormalities were accompanied by reduced 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) level in the hippocampus and increased 5-HT expression in the gut (ileum and colon) after CACS. Chronic treatment of IBS rats with resveratrol dose-dependently normalized CACS-induced both central nervous and peripheral dysfunction, which were consistent with its differentially regulating 5-HT contents in the brain and intestine. Pretreatment with the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist NAN-190 hydrobromide (NAN-190) prevented such effects. While sub-threshold of 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT potentiated the effects of low dose of resveratrol (10 mg/kg) on CACS-related behavioral abnormalities. Furthermore, resveratrol markedly increased PKA, p-cAMP-response element binding protein (p-CREB) and brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in the hippocampus of IBS rats, while decreased PKA, pCREB and BDNF levels were found in the ileum and colon. These effects were prevented by NAN-190, which were consistent with the behavioral changes. The present results suggested that resveratrol improved anti-IBS-like effects on depression, anxiety, visceral hypersensitivity and intestinal motility abnormality through regulating 5-HT1A-dependent PKA-CREB-BDNF signaling in the brain-gut axis.
Electroacupuncture inhibition of hyperalgesia in an inflammatory pain rat model: involvement of distinct spinal serotonin and norepinephrine receptor subtypes.[Pubmed:22628394]
Br J Anaesth. 2012 Aug;109(2):245-52.
BACKGROUND: Although acupuncture analgesia is well documented, its mechanisms have not been thoroughly clarified. We previously showed that electroacupuncture (EA) activates supraspinal serotonin- and norepinephrine-containing neurones that project to the spinal cord. This study investigates the involvement of spinal alpha(2)-adrenoceptors (alpha2-ARs) and 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptors (5-HTRs) in EA effects on an inflammatory pain rat model. METHODS: Inflammatory hyperalgesia was induced by injecting complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA, 0.08 ml) into the plantar surface of one hind paw and assessed by paw withdrawal latency (PWL) to a noxious thermal stimulus. The selective alpha2a-AR antagonist BRL-44408, alpha2b-AR antagonist imiloxan hydrochloride, 5-HT2B receptor (5-HT2BR) antagonist SB204741, 5-HT3R antagonist LY278584, or 5-HT1AR antagonists NAN-190 hydrobromide, or WAY-100635 were intrathecally administered 20 min before EA or sham EA, which was given 2 h post-CFA at acupoint GB30. RESULTS: EA significantly increased PWL compared with sham [7.20 (0.46) vs 5.20 (0.43) s]. Pretreatment with alpha2a-AR [5.35 (0.45) s] or 5-HT1AR [5.22 (0.38) s] antagonists blocked EA-produced anti-hyperalgesia; alpha2b-AR, 5-HT2BR, and 5-HT3R antagonist pretreatment did not. Sham plus these antagonists did not significantly change PWL compared with sham plus vehicle, indicating that the antagonists had little effect on PWL. Immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that alpha2a-ARs are on primary afferents and 5-HT1ARs are localized in N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA) subunit NR1-containing neurones in the spinal dorsal horn. CONCLUSIONS: The data show that alpha2a-ARs and 5-HT1ARs are involved in the EA inhibition of inflammatory pain and that the NMDA receptors are involved in EA action.
Involvement of spinal serotonin receptors in electroacupuncture anti-hyperalgesia in an inflammatory pain rat model.[Pubmed:21556842]
Neurochem Res. 2011 Oct;36(10):1785-92.
We previously showed that electroacupuncture (EA) activates medulla-spinal serotonin-containing neurons. The present study investigated the effects of intrathecal 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine creatinine sulfate, a selective neurotoxin for serotonergic terminals, the 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor (5-HT1AR) antagonist NAN-190 hydrobromide and the 5-HT2C receptor (5-HT2CR) antagonist SB-242,084 on EA anti-hyperalgesia. EA was given twice at acupoint GB30 after complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA) injection into hind paw. CFA-induced hyperalgesia was measured by assessing hind paw withdrawal latency (PWL) to a noxious thermal stimulus 30 min post-EA. Serotonin depletion and the 5-HT1AR antagonist blocked EA anti-hyperalgesia; the 5-HT2CR antagonist did not. Immunohistochemical staining showed that spinal 5-HT1AR was expressed and that 5-HT2CR was absent in naive and CFA-injected animals 2.5 h post-CFA. These results show a correlation between EA anti-hyperalgesia and receptor expression. Collectively, the data show that EA activates supraspinal serotonin neurons to release 5-HT, which acts on spinal 5-HT1AR to inhibit hyperalgesia.
Effects of the putative 5-HT1A receptor antagonist NAN-190 on free feeding and on feeding induced by the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT in the rat.[Pubmed:1397037]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug 14;219(1):105-12.
The effects of the putative 5-HT1A receptor antagonist NAN-190 on feeding and spontaneous locomotor activity in rats were examined. The drug elicited a robust, dose-dependent (0.01-10 mg/kg) increase in food consumption in free feeding animals. Microstructural analysis of feeding induced by NAN-190 (3 mg/kg) revealed that the drug increased the duration of feeding and number of feeding bouts but decreased the feeding rate. The increase in feeding induced by 3 mg/kg of NAN-190 was not apparent until 2-4 h after injection. This prolonged latency to onset of the feeding response appeared to be due to response competition. Thus, a 'neuroleptic-like' action of the drug on spontaneous motor activity was observed during the the initial 2 h following injection. A dopamine receptor antagonist action of NAN-190 was also indicated by the results of studies in which the drug was observed to block oral stereotypy induced by the dopamine receptor agonist apomorphine. In interaction studies, NAN-190 (0.1 and 10 mg/kg) failed to block the feeding response induced by the prototypical 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT (0.0625 and 1.0 mg/kg) and indeed, appeared to have an additive effect with 8-OH-DPAT on consummatory behaviour. These data suggest that NAN-190 may act as a partial agonist rather than an antagonist at the 5-HT1A receptor and also provide the first evidence that the drug has dopamine receptor antagonist properties in vivo.
Arylpiperazine derivatives as high-affinity 5-HT1A serotonin ligands.[Pubmed:3172131]
J Med Chem. 1988 Oct;31(10):1968-71.
Although simple arylpiperazines are commonly considered to be moderately selective for 5-HT1B serotonin binding sites, N4-substitution of such compounds can enhance their affinity for 5-HT1A sites and/or decrease their affinity for 5-HT1B sites. A small series of 4-substituted 1-arylpiperazines was prepared in an attempt to develop agents with high affinity for 5-HT1A sites. Derivatives where the aryl portion is phenyl, 2-methoxyphenyl, or 1-naphthyl, and the 4-substituent is either a phthalimido or benzamido group at a distance of four methylene units away from the piperazine 4-position, display high affinity for these sites. One of these compounds, 1-(2-methoxyphenyl)-4-[4-(2-phthalimido)butyl]piperazine (18), possesses a higher affinity than 5-HT and represents the highest affinity (Ki = 0.6 nM) agent yet reported for 5-HT1A sites.


