OfloxacinFluoroquinolones,antibiotics CAS# 82419-36-1 |
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- CA 074
Catalog No.:BCC1141
CAS No.:134448-10-5
- Cathepsin Inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4896
CAS No.:225120-65-0
- L 006235
Catalog No.:BCC2361
CAS No.:294623-49-7
- Balicatib
Catalog No.:BCC5139
CAS No.:354813-19-7
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 82419-36-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4583 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H20FN3O4 | M.Wt | 361.37 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 4 mg/mL (11.07 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
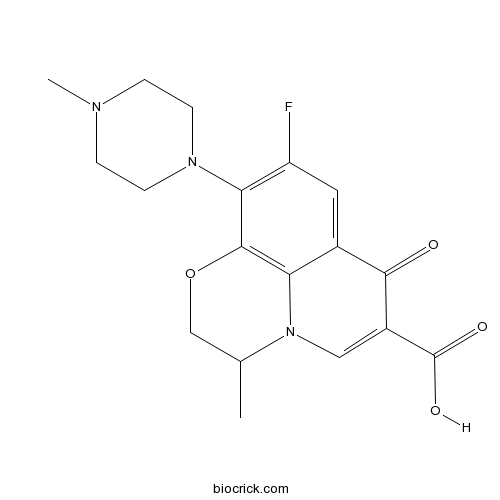
| SMILES | CC1COC2=C3N1C=C(C(=O)C3=CC(=C2N4CCN(CC4)C)F)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GSDSWSVVBLHKDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H20FN3O4/c1-10-9-26-17-14-11(16(23)12(18(24)25)8-22(10)14)7-13(19)15(17)21-5-3-20(2)4-6-21/h7-8,10H,3-6,9H2,1-2H3,(H,24,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone whose primary mechanism of action is inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase.
Target: DNA gyrase
Ofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone whose primary mechanism of action is inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase. In vitro it has a broad spectrum of activity against aerobic Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, although it is poorly active against anaerobes [1]. Ofloxacin, like other 4-quinolones, is unusual among front line drugs available to treat bacterial infections since it affects bacterial DNA synthesis, rather than cell wall or protein synthesis [2].
Ofloxacin (20 mg/kg), norfloxacin (40 mg/kg), pefloxacin mesylate dihydrate (40 mg/kg)and ciprofloxacin (50 mg/kg) were administered by gavage twice daily for three consecutive weeks. 6 weeks after treatment, the test animals were euthanised and Achilles tendon specimens were collected. A computer monitored tensile testing machine was utilised for biomechanical testing. The mean elastic modulus of the control group was significantly higher than that of the norfloxacin and pefloxacin groups (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). The mean yield force (YF) of the control group was significantly higher than those of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and pefloxacin groups (p<0.001, p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). The mean ultimate tensile force (UTF) of the control group was significantly higher than of the ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and pefloxacin groups (p<0.001, p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively). Hyaline degeneration and fibre disarrangement were observed in the tendons of the ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and ofloxacin treated-groups, whereas myxomatous degeneration was observed only in the ciprofloxacin and pefloxacin groups [3].
Clinical indications: Bacterial infection; Bacterial respiratory tract infection; Bacterial urinary tract infection
Toxicity: tendinopathy; hepatotoxicity; dysglycemia References: | |||||

Ofloxacin Dilution Calculator

Ofloxacin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7672 mL | 13.8362 mL | 27.6725 mL | 55.3449 mL | 69.1812 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5534 mL | 2.7672 mL | 5.5345 mL | 11.069 mL | 13.8362 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2767 mL | 1.3836 mL | 2.7672 mL | 5.5345 mL | 6.9181 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0553 mL | 0.2767 mL | 0.5534 mL | 1.1069 mL | 1.3836 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0277 mL | 0.1384 mL | 0.2767 mL | 0.5534 mL | 0.6918 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ofloxacin is a fluorinated quinolone antibacterial. Ofloxacin functions by inhibiting DNA gyrase, a Topo II (topoisomerase II) and Topo IV (Topo II alpha).
- Ganciclovir
Catalog No.:BCC4908
CAS No.:82410-32-0
- Humantenirine
Catalog No.:BCN4850
CAS No.:82375-30-2
- Humantenine
Catalog No.:BCN4358
CAS No.:82375-29-9
- Heliocurassavinine
Catalog No.:BCN2050
CAS No.:82374-02-5
- 2,3,5,4'-Tetrahydroxyl diphenylethylene-2-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1340
CAS No.:82373-94-2
- Humantenmine
Catalog No.:BCN4357
CAS No.:82354-38-9
- Heliocurassavicine
Catalog No.:BCN2049
CAS No.:82354-34-5
- Heliocoromandaline
Catalog No.:BCN2046
CAS No.:82354-33-4
- Coelonin
Catalog No.:BCN3600
CAS No.:82344-82-9
- SN 2
Catalog No.:BCC6325
CAS No.:823218-99-1
- Styraxlignolide F
Catalog No.:BCN3416
CAS No.:823214-06-8
- Breyniaionoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7112
CAS No.:823182-23-6
- 20-O-Acetylingenol-3-angelate
Catalog No.:BCN8469
CAS No.:82425-35-2
- Gomisin L1
Catalog No.:BCN7039
CAS No.:82425-43-2
- Gomisin L2
Catalog No.:BCN7032
CAS No.:82425-44-3
- Gomisin M2
Catalog No.:BCN4359
CAS No.:82425-45-4
- Maglifloenone
Catalog No.:BCN4360
CAS No.:82427-77-8
- Agomelatine L(+)-Tartaric acid
Catalog No.:BCC4211
CAS No.:824393-18-2
- Pulchinenoside E3
Catalog No.:BCN8187
CAS No.:824401-07-2
- Arteannuin A
Catalog No.:BCN4361
CAS No.:82442-48-6
- Hispanone
Catalog No.:BCN7404
CAS No.:82462-67-7
- 3-Oxotirucalla-7,24-dien-21-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4568
CAS No.:82464-35-5
- R(+)-Gomisin M1
Catalog No.:BCN4362
CAS No.:82467-50-3
- Neokadsuranin
Catalog No.:BCN7816
CAS No.:115181-68-5
Molecular characteristics of ofloxacin mono-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from new and previously treated tuberculosis patients.[Pubmed:28317169]
J Clin Lab Anal. 2018 Jan;32(1).
BACKGROUND: Ofloxacin (OFX) resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) isolates have been increasingly observed and are a major concern in recent years. This study investigated the genetic mutations associated with OFX resistance among clinical OFX mono-resistant MTB isolates from new and previously treated tuberculosis patients. METHODS: A total of 50 unrelated OFX mono-resistant MTB isolates were analyzed. For all isolates, the quinolone resistance determining regions of gyrA and gyrB were PCR amplified and sequenced. RESULTS: Single mutations in the quinolone resistance determining regions of gyrA (positions D94A, G, N, and Y; A90V; and S91P) and gyrB (positions T539A and E540D) were observed in 62% (31/50) and 4% (2/50) of all OFX mono-resistant isolates, respectively. No differences were detected between the proportions of isolates with mutations in gyrA/gyrB from new and previously treated tuberculosis patients (P=.820). CONCLUSIONS: Although mutations in gyrB were rare, they were as important as mutations in gyrA in predicting OFX resistance in MTB in Tianjin, China.
Effect of iNOS inhibitor LNMMA along with antibiotics Chloramphenicol or Ofloxacin in murine peritoneal macrophages regulates S.aureus infection as well as inflammation: An in vitro study.[Pubmed:28242423]
Microb Pathog. 2017 Apr;105:307-320.
Death due to sepsis by S. aureus is rapidly increasing because of their potent weaponries against macrophage mediated killing. Macrophages serve as intracellular reservoirs of S. aureus. Although significant resources have been invested during the last decade in new treatments for sepsis, only antibiotic therapy has failed to improve outcomes. Moreover the host pathogen interaction resulted in host cell death triggering inflammation. So, successful therapy requires amalgamation of therapies to delineate pathogen along with providing protection to host cell. With this idea, LNMMA, the iNOS inhibitor is used along with antibiotics Ofloxacin or Chloramphenicol on S. aureus infected mouse peritoneal macrophage. ROS like H2O2, O2(-) production has been measured. NO inhibition by iNOS inhibitor and antioxidant levels has been analysed. COX2, TLR2 and iNOS expression along with proinflammatory cytokine level was studied. It was found that the use of iNOS inhibitor LNMMA along with antibiotics not only enhances bacterial clearance but also decreases proinflammatory responses in Staphylococcus aureus infected macrophages. Inhibition of TLR2 as well as COX2 has also been found in combined treatment groups. The use of iNOS inhibitor LNMMA plus Ofloxacin or Chloramphenicol pretreatment enhanced bacterial clearance by increasing ROS. Decreases in NO protect the cell from harmful peroxynitril as well as inflammatory damage by changes in iNOS, COX2 activity along with reduced proinflammatory cytokines like TNFalpha, IFNgamma, IL1-beta etc. Changes in antioxidant level has been found. This in-vitro realm of augmented bacterial clearance and regulated inflammation may be considered as a novel and important therapeutic intervention.
Detection of ofloxacin resistance by nitrate reductase assay in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from extrapulmonary tuberculosis.[Pubmed:28303821]
Indian J Med Microbiol. 2017 Jan-Mar;35(1):69-73.
CONTEXT: Increased use of fluoroquinolones to treat community-acquired infections has led to the decreased susceptibility to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. There is a paucity of data on Ofloxacin (OFX) resistance detection by nitrate reductase assay (NRA). Hence, the present study was carried out to find the efficacy of NRA for detection of OFX resistance in M. tuberculosis isolated from extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) cases. AIMS: (1) To compare sensitivity, specificity and median time required to obtain results by NRA with economic variant proportion method (PM) for detection of OFX resistance.(2) To determine the extent of OFX resistance in clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis. SETTINGS AND DESIGN: Seventy-three M. tuberculosis isolates from cases of EPTB were subjected to economic variant of PM for isoniazid, rifampicin and OFX. NRA was done for detection of OFX resistance. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: Seventy-three isolates from clinical samples of suspected EPTB received in the Department of Microbiology were included in the study. Drug susceptibility test was performed on Lowenstein-Jensen medium with and without drugs. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS USED: Of turnaround time was done by Mann-Whitney test on SPSS (version 19, released in 2010, IBM Corp, Armonk NY),P < 0.05. RESULTS: OFX resistance was seen in nine isolates. The sensitivity and specificity of OFX resistance by NRA was 100% and 96.87%, respectively. Median time required to obtain results by NRA was 10 days as compared to 28 days by PM. CONCLUSIONS: NRA is a specific and sensitive method for detection of OFX resistance in resource-restricted settings.
Double Mutants in DNA Gyrase Lead to Ofloxacin Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.[Pubmed:28247939]
J Cell Biochem. 2017 Sep;118(9):2950-2957.
Fluoroquinolones are among the most important classes of highly effective antibacterial drugs, exhibiting wide range of activity to cure infectious diseases. Ofloxacin is second generation fluoroquinolone approved by FDA for the treatment of tuberculosis by selectively inhibiting DNA gyrase. However, the emergence of drug resistance owing to mutations in DNA gyrase poses intimidating challenge for the effective therapy of this drug. The double mutants GyrA(A90V) GyrB(D500N) and GyrA(A90V) GyrB(T539N) are reported to be implicated in conferring higher levels of OFX resistance. The present study was designed to unravel the molecular principles behind development of resistance by the bug against fluoroquinolones. Our results highlighted that polar interactions play critical role in the development of drug resistance and highlight the significant correlation between the free energy calculations predicted by MM-PBSA and stability of the ligand-bound complexes. Modifications at the OFX binding pocket due to amino acid substitution leads to fewer hydrogen bonds in mutants DNA gyrase-OFX complex, which determined the low susceptibility of the ligand in inhibiting the mutant protein. This study provides a structural rationale to the mutation-based resistance to Ofloxacin and will pave way for development potent fluoroquinolone-based resistant-defiant drugs. J. Cell. Biochem. 118: 2950-2957, 2017. (c) 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.


