P11Potent antagonist of αvβ3-vitronectin interaction; antiangiogenic CAS# 848644-86-0 |
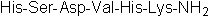
- USP7-USP47 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4113
CAS No.:1247825-37-1
- NSC 632839 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2088
CAS No.:157654-67-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 848644-86-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90488969 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H48N12O9 | M.Wt | 720.78 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in 20% acetonitrile - 0.1% acetic acid | ||
| Sequence | HSDVHK (Modifications: Lys-6 = C-terminal amide) | ||
| Chemical Name | (3S)-3-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-4-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1,6-diamino-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)N)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CC2=CN=CN2)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FSVRGWKWZIRBPC-KESUXUJOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H48N12O9/c1-15(2)24(30(51)40-20(8-17-11-35-14-37-17)27(48)38-19(25(33)46)5-3-4-6-31)42-28(49)21(9-23(44)45)39-29(50)22(12-43)41-26(47)18(32)7-16-10-34-13-36-16/h10-11,13-15,18-22,24,43H,3-9,12,31-32H2,1-2H3,(H2,33,46)(H,34,36)(H,35,37)(H,38,48)(H,39,50)(H,40,51)(H,41,47)(H,42,49)(H,44,45)/t18-,19-,20-,21-,22-,24-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent antagonist of the integrin αvβ3-vitronectin interaction (IC50 = 25.72 nM). Blocks proliferation and induces apoptosis in HUVECs; antiangiogenic. |

P11 Dilution Calculator

P11 Molarity Calculator

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- A 582941
Catalog No.:BCC7920
CAS No.:848591-90-2
- Vasicinolone
Catalog No.:BCN4394
CAS No.:84847-50-7
- NCH 51
Catalog No.:BCC2422
CAS No.:848354-66-5
- AS 602801
Catalog No.:BCC1369
CAS No.:848344-36-5
- SSR128129E
Catalog No.:BCC4498
CAS No.:848318-25-2
- EX-527 R-enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC5595
CAS No.:848193-69-1
- EX-527 S-enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC5594
CAS No.:848193-68-0
- Alvelestat
Catalog No.:BCC4058
CAS No.:848141-11-7
- HKI 357
Catalog No.:BCC6046
CAS No.:848133-17-5
- 3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4393
CAS No.:84812-00-0
- threo-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1331
CAS No.:848031-94-7
- 5-Epilithospermoside
Catalog No.:BCN4392
CAS No.:84799-31-5
- Stigmasta-4,25-dien-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN4395
CAS No.:848669-08-9
- Stigmasta-4,22,25-trien-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN4396
CAS No.:848669-09-0
- BIIB021
Catalog No.:BCC2124
CAS No.:848695-25-0
- Gnetin D
Catalog No.:BCN3380
CAS No.:84870-53-1
- p-Hydroxyphenethyl trans-ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN3995
CAS No.:84873-15-4
- Pulsatilla camphor
Catalog No.:BCN8184
CAS No.:90921-11-2
- Betulinic acid 3β-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)]-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCC8303
CAS No.:848784-87-2
- AZD8931 (Sapitinib)
Catalog No.:BCC3734
CAS No.:848942-61-0
- UFP-101
Catalog No.:BCC5775
CAS No.:849024-68-6
- Floribundasaponin A
Catalog No.:BCN1330
CAS No.:37341-36-9
- Glaucogenin C mono-D-thevetoside
Catalog No.:BCN7089
CAS No.:849201-84-9
- Foretinib (GSK1363089)
Catalog No.:BCC1263
CAS No.:849217-64-7
Effect of Maternal +/-Citalopram Exposure on P11 Expression and Neurogenesis in the Mouse Fetal Brain.[Pubmed:28076682]
ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017 May 17;8(5):1019-1025.
Fetal exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) has been associated with increased risk of adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes. In the adult brain, SSRI therapy regulates P11 (s100a10) expression and alters neurogenesis. The protein P11 indirectly regulates 5-HT signaling through 5-HT1B/D receptors. In the fetal brain, signaling through these receptors modulates axonal circuit formation. We determined whether P11 is expressed in the fetal mouse brain, and whether maternal SSRI exposure affects fetal P11 expression and neurogenesis. The SSRI +/- citalopram was administered to pregnant mice from gestational day 8 to 17. Results show that P11 is expressed in fetal thalamic neurons and thalamocortical axons. Furthermore, P11 protein expression is significantly decreased in the fetal thalamus after in utero +/-citalopram exposure compared to untreated controls, and neurogenesis is significantly decreased in specific fetal brain regions. These findings reveal differential regulation of P11 expression and altered neurogenesis in the fetal brain as a result of maternal SSRI exposure.
Alterations of p11 in brain tissue and peripheral blood leukocytes in Parkinson's disease.[Pubmed:28137881]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 7;114(10):2735-2740.
Individuals with Parkinson's disease (PD) often suffer from comorbid depression. P11 (S100A10), a member of the S100 family of proteins, is expressed widely throughout the body and is involved in major depressive disorder and antidepressant response. Central P11 levels are reduced in postmortem tissue from depressed individuals; however, P11 has not yet been investigated in PD patients with depression or those without depression. We investigated P11 levels in postmortem PD brains and assessed whether peripheral P11 levels correlate with disease severity. Substantia nigra, putamen, and cortical P11 protein levels were assessed in postmortem brain samples from PD patients and matched controls. In a different set of postmortem brains, P11 mRNA expression was measured in dopaminergic cells from the substantia nigra. Both P11 protein and mRNA levels were decreased in PD patients. Peripheral P11 protein levels were investigated in distinct leukocyte populations from PD patients with depression and those without depression. Monocyte, natural killer (NK) cell, and cytotoxic T-cell P11 levels were positively associated with the severity of PD, and NK cell P11 levels were positively associated with depression scores. Given that inflammation plays a role in both PD and depression, it is intriguing that peripheral P11 levels are altered in immune cells in both conditions. Our data provide insight into the pathological alterations occurring centrally and peripherally in PD. Moreover, if replicated in other cohorts, P11 could be an easily accessible biomarker for monitoring the severity of PD, especially in the context of comorbid depression.
Mantle cell lymphoma with a novel t(11;12)(q13;p11.2): a proposed alternative mechanism of CCND1 up-regulation.[Pubmed:28132860]
Hum Pathol. 2017 Jun;64:207-212.
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is typically characterized by t(11;14), which places the IGH@ enhancer elements upstream of CCND1. This fusion results in up-regulation of CCND1 and consequently its protein product cyclin D1. Recent studies have shown that in MCL, mutations or translocations occurring within the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of the CCND1 gene can result in a truncated mRNA transcript that is more stable and associated with more aggressive disease. We identified a case of MCL showing cyclin D1 overexpression by immunohistochemistry and a t(11;12)(q13;P11.2) by conventional cytogenetic studies. Next-generation genomic sequencing indicated a chromosomal break through the CCND1 3'-UTR and fusion with a non-coding region of chromosome 12. We suggest that, in the absence of the typical CCND1/IGH@ fusion, this rearrangement promotes MCL pathogenesis by eliminating miRNA interaction elements within the 3'-UTR of the CCND1 mRNA transcript consequently resulting in CCND1 overexpression.
Pharmacoproteomic analysis of a novel cell-permeable peptide inhibitor of tumor-induced angiogenesis.[Pubmed:21558493]
Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Aug;10(8):M110.005264.
P11, a novel peptide ligand containing a PDZ-binding motif (Ser-Asp-Val) with high affinity to integrin alpha(v)beta(3) was identified from a hexapeptide library (PS-SPCL) using a protein microarray chip-based screening system. Here, we investigated the inhibitory mechanism of P11 (HSDVHK) on tumor-induced angiogenesis via a pharmacoproteomic approach. P11 was rapidly internalized by, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) via an integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-mediated event. Caveolin and clathrin appeared to be involved in the P11 uptake process. The cell-penetrating P11 resulted in suppression of bFGF-induced HUVEC proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Phosphorylation of extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK1/2) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) in bFGF-stimulated HUVECs was inhibited by cell-permeable P11. Proteomic analysis via antibody microarray showed up-regulation of p53 in P11-treated HUVECs, resulting in induction of apoptosis via activation of caspases-3, -8, and -9. Several lines of experimental evidence strongly suggest that the molecular mechanism of P11, a novel anti-angiogenic agent, inhibits bFGF-induced HUVEC proliferation via mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase and extracellular-signal regulated kinase inhibition as well as p53-mediated apoptosis related with activation of caspases.
Site-specific inhibition of integrin alpha v beta 3-vitronectin association by a ser-asp-val sequence through an Arg-Gly-Asp-binding site of the integrin.[Pubmed:19882657]
Proteomics. 2010 Jan;10(1):72-80.
A functional proteomic technology using protein chip and molecular simulation was used to demonstrate a novel biomolecular interaction between P11, a peptide containing the Ser-Asp-Val (SDV) sequence and integrin alpha v beta 3. P11 (HSDVHK) is a novel antagonistic peptide of integrin alpha v beta 3 screened from hexapeptide library through protein chip system. An in silico docking study and competitive protein chip assay revealed that the SDV sequence of P11 is able to create a stable inhibitory complex onto the vitronectin-binding site of integrin alpha v beta 3. The Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD)-binding site recognition by P11 was site specific because the P11 was inactive for the complex formation of a denatured form of integrin-vitronectin. P11 showed a strong antagonism against alpha v beta 3-GRGDSP interaction with an IC(50) value of 25.72+/-3.34 nM, whereas the value of GRGDSP peptide was 1968.73+/-444.32 nM. The binding-free energies calculated from the docking simulations for each P11 and RGD peptide were -3.99 and -3.10 kcal/mol, respectively. The free energy difference between P11 and RGD corresponds to approximately a 4.5-fold lower K(i) value for the P11 than the RGD peptide. The binding orientation of the docked P11 was similar to the crystal structure of the RGD in alpha v beta 3. The analyzed docked poses suggest that a divalent metal-ion coordination was a common driving force for the formation of both SDV/alpha v beta 3 and RGD/alpha v beta 3 complexes. This is the first report on the specific recognition of the RGD-binding site of alpha v beta 3 by a non-RGD containing peptide using a computer-assisted proteomic approach.
High-throughput screening of novel peptide inhibitors of an integrin receptor from the hexapeptide library by using a protein microarray chip.[Pubmed:15634795]
J Biomol Screen. 2004 Dec;9(8):687-94.
Protein microarray is an emerging technology that makes high-throughput analysis possible for protein-protein interactions and analysis of proteome and biomarkers in parallel. The authors investigated the application of a novel protein microarray chip, ProteoChip, in new drug discovery. Integrin alpha(v)beta(3) microarray immobilized on the ProteoChip was employed to screen new active peptides against the integrin from multiple hexapeptide sublibraries of a positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial library (PS-SPCL). The integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-vitronectin interaction was successfully demonstrated on the integrin microarray in a dose-dependent manner and was inhibited not only by the synthetic RGD peptide but also by various integrin antagonists on the integrin microarray chip. Novel peptide ligands with high affinity to the integrin were also identified from the peptide libraries with this chip-based screening system by a competitive inhibition assay in a simultaneous and high-throughput fashion. The authors have confirmed antiangiogenic functions of the novel peptides thus screened through an in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis assay. These results provide evidence that the ProteoChip is a promising tool for high-throughput screening of lead molecules in new drug development.


