SSR128129Eallosteric inhibitor of FGFR1, orally-active CAS# 848318-25-2 |
- Amyloid Beta-peptide (25-35) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1027
CAS No.:131602-53-4
- Adrenorphin
Catalog No.:BCC1021
CAS No.:88377-68-8
- Adrenorphin, Free Acid
Catalog No.:BCC1011
CAS No.:88866-92-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 848318-25-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 68853159 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H15N2NaO4 | M.Wt | 346.31 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | SSR | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 54 mg/mL (155.93 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
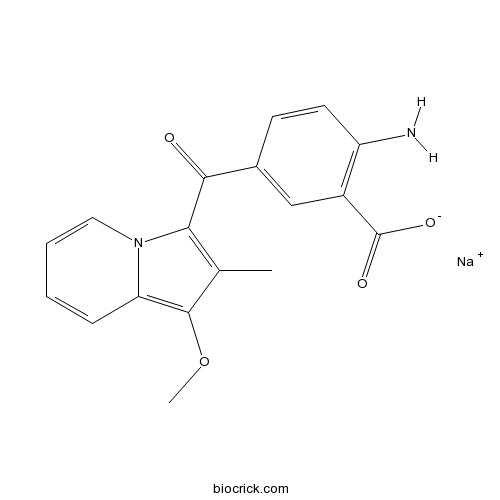
| Chemical Name | sodium;2-amino-5-(1-methoxy-2-methylindolizine-3-carbonyl)benzoate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(N2C=CC=CC2=C1OC)C(=O)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)N)C(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JFBMSTWZURKQOC-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16N2O4.Na/c1-10-15(20-8-4-3-5-14(20)17(10)24-2)16(21)11-6-7-13(19)12(9-11)18(22)23;/h3-9H,19H2,1-2H3,(H,22,23);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | SSR128129E is an orally available and allosteric FGFR inhibitor with an IC50 of 1.9 μM for FGFR1.In Vitro:SSR128129E inhibits FGF2-induced EC proliferation with an IC50 of 31±1.6 nM, migration with an IC50 of 15.2±4.5 nM, and lamellipodia formation in a dose dependent manner. SSR128129E inhibits responses mediated by FGFR1-4. For instance, SSR128129E blocks EC migration in response to FGF1, a ligand of FGFR1 and FGFR4, and capillary tube formation in response to FGF19, a ligand of FGFR4. Proliferation and migration of the murine pancreatic Panc02 tumor cell line in response to FGF7 are also blocked by SSR128129E, showing that SSR128129E inhibits FGFR subtypes of other species as well. SSR128129E blocks different FGFR subtypes in various cell lines with nanomolar potency[1].In Vivo:Oral delivery of SSR128129E (30 mg/kg/day, from day 3) inhibits growth of orthotopic Panc02 tumors by 44% and delays growth of Lewis lung carcinoma. oral SSR128129E (30 mg/kg/day, from day 5) reduces tumor size and weight by 53% and 40%, respectively. SSR128129E inhibits the growth of subcutaneous CT26 colon tumors by 34% and of the multidrug resistant MCF7/ADR breast cancer xenograft model by 40%. SSR128129E reduces tumor invasiveness and metastasis of Panc02 tumor cells to peritoneal lymph nodes[1]. References: | |||||

SSR128129E Dilution Calculator

SSR128129E Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8876 mL | 14.4379 mL | 28.8759 mL | 57.7517 mL | 72.1897 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5775 mL | 2.8876 mL | 5.7752 mL | 11.5503 mL | 14.4379 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2888 mL | 1.4438 mL | 2.8876 mL | 5.7752 mL | 7.219 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0578 mL | 0.2888 mL | 0.5775 mL | 1.155 mL | 1.4438 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0289 mL | 0.1444 mL | 0.2888 mL | 0.5775 mL | 0.7219 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SSR128129E is an allosteric inhibitor of FGFR1 with IC50 value of 1.9 μM [1].
The fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) are receptor tyrosine kinases for fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and play an important role in cancer and inflammation. FGF2 plays an important role in angiogenesis [1] [2].
SSR128129E is an orally-active and allosteric FGFR1 inhibitor. In human umbilical venous endothelial cells (HUVECs), SSR128129E inhibited FGF2-induced endothelial cells (ECs) proliferation and migration with IC50 values of 31 and 15.2 nM respectively and also inhibited lamellipodia formation. SSR128129E inhibited responses mediated by FGFR1-4. In FGFR2-expressing HEK293 cells, SSR128129E inhibited phosphorylation of FRS2 and ERK1/2 induced by FGF2 [1].
In arthritis mice, SSR128129E inhibited bone and joint damage and reduced angiogenesis in the inflamed joints. In orthotopic Panc02 tumor model, SSR128129E (30 mg/kg) inhibited tumor growth by 44%. In murine 4T1 breast tumors, SSR128129E (30 mg/kg) reduced tumor weight and size by 40% and 53%, respectively [1]. In atherosclerosis-prone apolipoprotein E (apoE)-deficient mice, SSR128129E (50 mg/kg) reduced neointimal proliferation and reduced FGFR2 mRNA levels and lesion size in the aortic sinus [2].
References:
[1]. Bono F, De Smet F, Herbert C, et al. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and growth by a small-molecule multi-FGF receptor blocker with allosteric properties. Cancer Cell, 2013, 23(4): 477-488.
[2]. Dol-Gleizes F, Delesque-Touchard N, Marès AM, et al. A new synthetic FGF receptor antagonist inhibits arteriosclerosis in a mouse vein graft model and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. PLoS One, 2013, 8(11): e80027.
- EX-527 R-enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC5595
CAS No.:848193-69-1
- EX-527 S-enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC5594
CAS No.:848193-68-0
- Alvelestat
Catalog No.:BCC4058
CAS No.:848141-11-7
- HKI 357
Catalog No.:BCC6046
CAS No.:848133-17-5
- 3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4393
CAS No.:84812-00-0
- threo-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN1331
CAS No.:848031-94-7
- 5-Epilithospermoside
Catalog No.:BCN4392
CAS No.:84799-31-5
- Lck Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1689
CAS No.:847950-09-8
- RO4929097
Catalog No.:BCC2089
CAS No.:847925-91-1
- Lenalidomide hemihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4198
CAS No.:847871-99-2
- S 32212 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6208
CAS No.:847871-78-7
- Tasumatrol L
Catalog No.:BCN6955
CAS No.:847835-17-0
- AS 602801
Catalog No.:BCC1369
CAS No.:848344-36-5
- NCH 51
Catalog No.:BCC2422
CAS No.:848354-66-5
- Vasicinolone
Catalog No.:BCN4394
CAS No.:84847-50-7
- A 582941
Catalog No.:BCC7920
CAS No.:848591-90-2
- P11
Catalog No.:BCC6275
CAS No.:848644-86-0
- Stigmasta-4,25-dien-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN4395
CAS No.:848669-08-9
- Stigmasta-4,22,25-trien-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN4396
CAS No.:848669-09-0
- BIIB021
Catalog No.:BCC2124
CAS No.:848695-25-0
- Gnetin D
Catalog No.:BCN3380
CAS No.:84870-53-1
- p-Hydroxyphenethyl trans-ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN3995
CAS No.:84873-15-4
- Pulsatilla camphor
Catalog No.:BCN8184
CAS No.:90921-11-2
- Betulinic acid 3β-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1->2)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)]-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCC8303
CAS No.:848784-87-2
Tumor vasculature is regulated by FGF/FGFR signaling-mediated angiogenesis and bone marrow-derived cell recruitment: this mechanism is inhibited by SSR128129E, the first allosteric antagonist of FGFRs.[Pubmed:24760775]
J Cell Physiol. 2015 Jan;230(1):43-51.
Tumor angiogenesis is accompanied by vasculogenesis, which is involved in the differentiation and mobilization of human bone marrow cells. In order to further characterize the role of vasculogenesis in the tumor growth process, the effects of FGF2 on the differentiation of human bone marrow AC133(+) cells (BM-AC133(+)) into vascular precursors were studied in vitro. FGF2, like VEGFA, induced progenitor cell differentiation into cell types with endothelial cell characteristics. SSR128129E, a newly discovered specific FGFR antagonist acting by allosteric interaction with FGFR, abrogated FGF2-induced endothelial cell differentiation, showing that FGFR signaling is essential during this process. To assess the involvement of the FGF/FRGR signaling in vivo, the pre-clinical model of Lewis lung carcinoma (LL2) in mice was used. Subcutaneous injection of LL2 cells into mice induced an increase of circulating EPCs from peripheral blood associated with tumor growth and an increase of intra-tumoral vascular index. Treatment with the FGFR antagonist SSR128129E strongly decreased LL2 tumor growth as well as the intra-tumoral vascular index (41% and 50% decrease vs. vehicle-treated mice respectively, P < 0.01). Interestingly, SSR128129E treatment significantly decreased the number of circulating EPCs from the peripheral blood (53% inhibition vs. vehicle-treated mice, P < 0.01). These results demonstrate for the first time that the blockade of the FGF/FGFR pathway by SSR128129E reduces EPC recruitment during angiogenesis-dependent tumor growth. In this context, circulating EPCs could be a reliable surrogate marker for tumor growth and angiogenic activity.
Preclinical evidence that SSR128129E--a novel small-molecule multi-fibroblast growth factor receptor blocker--radiosensitises human glioblastoma.[Pubmed:24953334]
Eur J Cancer. 2014 Sep;50(13):2351-9.
Resistance of glioblastoma to radiotherapy is mainly due to tumour cell radioresistance, which is partially controlled by growth factors such as fibroblast growth factor (FGF). Because we have previously demonstrated the role of FGF-2 in tumour cell radioresistance, we investigate here whether inhibiting FGF-2 pathways by targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) may represent a new strategy to optimise the efficiency of radiotherapy in glioblastoma. Treating radioresistant U87 and SF763 glioblastoma cells with the FGFR inhibitor, SSR12819E, radiosensitises these cells while the survival after irradiation of the more radiosensitive U251 and SF767 cells was not affected. SSR128129E administration to U87 cells increases the radiation-induced mitotic cell death. It also decreased cell membrane availability of the FGFR-1 mainly expressed in these cells, increased this receptor's ubiquitylation, inhibited radiation-induced RhoB activation and modulated the level of hypoxia inducible factor, HIF-1alpha, a master regulator of hypoxia, thus suggesting a role of FGFR in the regulation of hypoxia pathways. Moreover, treating orthotopically U87 xenografted mice with SSR128129E before two subsequent local 2.5Gy irradiations significantly increased the animals neurological sign free survival (NSFS) compared to the other groups of treatment. These results strongly suggest that targeting FGFR with the FGFR blocker SSR128129E might represent an interesting strategy to improve the efficiency of radiotherapy in glioblastoma.


