PG 01037 dihydrochlorideD3 receptor selective antagonist CAS# 675599-62-9 |
- RVX-208
Catalog No.:BCC4475
CAS No.:1044870-39-4
- I-BET-762
Catalog No.:BCC4474
CAS No.:1260907-17-2
- Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC1132
CAS No.:1268524-70-4
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- CPI-203
Catalog No.:BCC4099
CAS No.:1446144-04-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 675599-62-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 90488894 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H28Cl4N4O | M.Wt | 554.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 20 mM in water with gentle warming and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
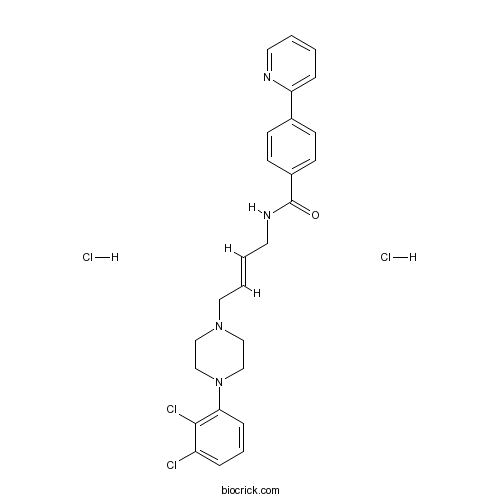
| Chemical Name | N-[(E)-4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]but-2-enyl]-4-pyridin-2-ylbenzamide;dihydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCN1CC=CCNC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC=CC=N3)C4=C(C(=CC=C4)Cl)Cl.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DACFFMAXBWGOKQ-CZEFNJPISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H26Cl2N4O.2ClH/c27-22-6-5-8-24(25(22)28)32-18-16-31(17-19-32)15-4-3-14-30-26(33)21-11-9-20(10-12-21)23-7-1-2-13-29-23;;/h1-13H,14-19H2,(H,30,33);2*1H/b4-3+;; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dopamine D3 receptor antagonist; 133-fold selective for D3 over D2 receptors in vitro (Ki values are 0.70, 93.3 and 375 nM for D3, D2 and D4 receptors respectively). Attenuates abnormal involuntary movements associated with L-DOPA in rat models of Parkinson's disease. Inhibits the effects of methamphetamine; attenuates drug-induced behaviors in vivo. |

PG 01037 dihydrochloride Dilution Calculator

PG 01037 dihydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8039 mL | 9.0197 mL | 18.0395 mL | 36.0789 mL | 45.0987 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3608 mL | 1.8039 mL | 3.6079 mL | 7.2158 mL | 9.0197 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1804 mL | 0.902 mL | 1.8039 mL | 3.6079 mL | 4.5099 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0361 mL | 0.1804 mL | 0.3608 mL | 0.7216 mL | 0.902 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.018 mL | 0.0902 mL | 0.1804 mL | 0.3608 mL | 0.451 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Nutlin-3a chiral
Catalog No.:BCC1812
CAS No.:675576-98-4
- Nutlin-3b
Catalog No.:BCC1156
CAS No.:675576-97-3
- 8'-Epicleomiscosin A
Catalog No.:BCC3917
CAS No.:
- Polygodial
Catalog No.:BCC7597
CAS No.:6754-20-7
- Dehydrotumulosic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3740
CAS No.:6754-16-1
- Helenalin
Catalog No.:BCN8073
CAS No.:6754-13-8
- Alpha-caryophyllene
Catalog No.:BCN3877
CAS No.:6753-98-6
- Thapsigargin
Catalog No.:BCC6952
CAS No.:67526-95-8
- 4-Methoxy-5-(3-morpholinopropoxy)-2-nitrobenzonitrile
Catalog No.:BCC8710
CAS No.:675126-26-8
- Spathulenol
Catalog No.:BCN4227
CAS No.:6750-60-3
- Arnidiol
Catalog No.:BCN3810
CAS No.:6750-30-7
- Eupatolide
Catalog No.:BCN7345
CAS No.:6750-25-0
- Lariciresinol dimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN4228
CAS No.:67560-68-3
- Maoyecrystal E
Catalog No.:BCN3283
CAS No.:675603-39-1
- Baicalein 7-O-beta-D-ethylglucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN7981
CAS No.:675624-38-1
- Diosbulbin G
Catalog No.:BCN4229
CAS No.:67567-15-1
- Hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4230
CAS No.:67600-94-6
- 5,7,2'-Trihydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCC9241
CAS No.:120980-68-9
- Clerodermic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN4231
CAS No.:67650-47-9
- Methylenetanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3156
CAS No.:67656-29-5
- 9-Hydroxycamptothecin
Catalog No.:BCC8276
CAS No.:67656-30-8
- 1-Azakenpaullone
Catalog No.:BCC5332
CAS No.:676596-65-9
- Syringylpropane
Catalog No.:BCN3540
CAS No.:6766-82-1
- De-O-methylacetovanillochromene
Catalog No.:BCN4232
CAS No.:67667-62-3
Evaluation of the D3 dopamine receptor selective antagonist PG01037 on L-dopa-dependent abnormal involuntary movements in rats.[Pubmed:19371585]
Neuropharmacology. 2009 May-Jun;56(6-7):944-55.
The D3 dopamine receptor selective antagonist PG01037 has been evaluated for the ability to attenuate L-dopa-associated abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs) in unilaterally lesioned male Sprague-Dawley rats, which is a model of L-dopa-dependent dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson's Disease. The intrinsic activity of PG01037 was determined using a) a forskolin-dependent adenylyl cyclase inhibition assay with transfected HEK 293 cells expressing either the human D2Long or D3 dopamine receptor subtype and b) an assay for agonist-associated mitogenesis. For the initial experiments, the 5-HT1A receptor selective partial agonist buspirone was used as a positive control to verify our ability to quantitate changes in total AIMs and AIMs minus locomotor scores. Subcutaneous (s.c.) administration of PG01037 was found to have minimal effect on AIMs score. However, it was observed that the in vivo efficacy of PG01037 increased when administered by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection 15 min after L-dopa/benserazide administration, as compared to a 60 min, 30 min or 0 min pretreatment. It was also found that i.p. administration of PG01037 could inhibit involuntary movements after they had achieved maximum intensity. PG01037 was found to attenuate AIM scores in these animals in a dose dependent manner with IC(50) value equal to a) 7.4 mg/kg following L-dopa/benserazide administration (8 mg/kg each, i.p.) and b) 18.4 mg/kg following the administration of apomorphine (0.05 mg/kg, s.c.). However, PG01037 did not effectively inhibit SKF 81297-dependent abnormal involuntary movements. Rotarod studies indicate that PG01037 at a dose of 10 mg/kg did not adversely affect motor coordination of the unilaterally lesioned rats. Evaluation of lesioned rats using a cylinder test behavioral paradigm indicated that PG01037 did not dramatically attenuate the beneficial effects of L-dopa. These studies suggest that D3 dopamine receptor selective antagonists are potential pharmacotherapeutic candidates for the treatment of L-dopa-associated dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson's Disease.
Heterocyclic analogues of N-(4-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)arylcarboxamides with functionalized linking chains as novel dopamine D3 receptor ligands: potential substance abuse therapeutic agents.[Pubmed:17672446]
J Med Chem. 2007 Aug 23;50(17):4135-46.
Dopamine D3 receptor antagonists and partial agonists have been shown to modulate drug-seeking effects induced by cocaine and other abused substances. Compound 6 [PG01037, (N-(4-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)-trans-but-2-enyl)-4-pyridine-2-ylben zamide)] and related analogues are currently being evaluated in animal models of drug addiction. In these studies, a discrepancy between in vitro binding affinity, in vivo occupancy, and behavioral potency has been observed. The purpose of this study was to examine (1) modifications of the 2-pyridylphenyl moiety of 6 and (2) hydroxyl, acetyl, and cyclopropyl substitutions on the butylamide linking chain systematically coupled with 2-fluorenylamide or 2-pyridylphenylamide and 2-methoxy- or 2,3-dichloro-substituted phenylpiperazines to measure the impact on binding affinity, D2/D3 selectivity, lipophilicity, and function. In general, these modifications were well tolerated at the human dopamine D3 (hD3) receptor (Ki = 1-5 nM) as measured in competition binding assays. Several analogues showed >100-fold selectivity for dopamine D3 over D2 and D4 receptors. In addition, while all the derivatives with an olefinic linker were antagonists, in quinpirole-stimulated mitogenesis at hD3 receptors, several of the hydroxybutyl-linked analogues (16, 17, 21) showed partial agonist activity. Finally, several structural modifications reduced lipophilicities while retaining the desired binding profile.
Novel heterocyclic trans olefin analogues of N-{4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butyl}arylcarboxamides as selective probes with high affinity for the dopamine D3 receptor.[Pubmed:15689168]
J Med Chem. 2005 Feb 10;48(3):839-48.
Dopamine D3 receptor subtypes have been hypothesized to play a pivotal role in modulating the reinforcing and drug-seeking effects induced by cocaine. However, definitive pharmacological investigations have been hampered by the lack of highly D3 receptor selective compounds that can be used in vivo. To address this problem, the potent and D3-receptor-selective antagonist NGB 2904 (1, 9H-fluorene-2-carboxylic acid {4-[(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-butyl}-amide, Ki (hD3) = 2.0 nM, Ki (hD2L) = 112 nM, D2/D3 selectivity ratio of 56) was chosen as a lead structure for chemical modification in an attempt to reduce its high lipophilicity (c log D = 6.94) while optimizing D3 receptor binding affinity and D2/D3 selectivity. A series of >30 novel analogues were synthesized, and their binding affinities were evaluated in competition binding assays in HEK 293 cells transfected with either D2(L), D3, or D4 human dopamine receptors using the high affinity, selective D2-like receptor antagonist (125)I-IABN. Structural diversity in the aryl amide end of the molecule was found to have a major influence on (sub)nanomolar D3 receptor affinity and D2/D3 selectivity, which was optimized using a more rigid trans-butenyl linker between the aryl amide and the piperazine. Several analogues demonstrated superior D3 receptor binding affinities and selectivities as compared to the parent ligand. Compound 29 (N-{4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]-trans-but-2-enyl}-4-pyridine-2-yl-b enzamide) displayed the most promising pharmacological profile (Ki (hD3) = 0.7 nM, Ki (hD2L) = 93.3 nM, D2/D3 selectivity ratio of 133). In addition, this ligand inhibited quinpirole stimulation of mitogenesis at human dopamine D3 receptors transfected into Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, with an EC50 value of 3.0 nM. Compound 29 was a nearly 5 times more potent antagonist at the D3 receptor than 1 (EC50 = 14.4 nM). Moreover, a decrease in c log D value of approximately 2 orders of magnitude was determined for this novel D3-receptor-preferring ligand, compared to 1. In summary, chemical modification of 1 has resulted in compounds with high affinity and selectivity for D3 receptors. The most promising candidate, compound 29, is currently being evaluated in animal models of cocaine abuse and will provide an important tool with which to elucidate the role of D3 receptors in drug reinforcement in vivo.


