SB7424575-HT6 receptor antagonist,highly selective and high affinity CAS# 607742-69-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 607742-69-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11256720 | Appearance | Powder |
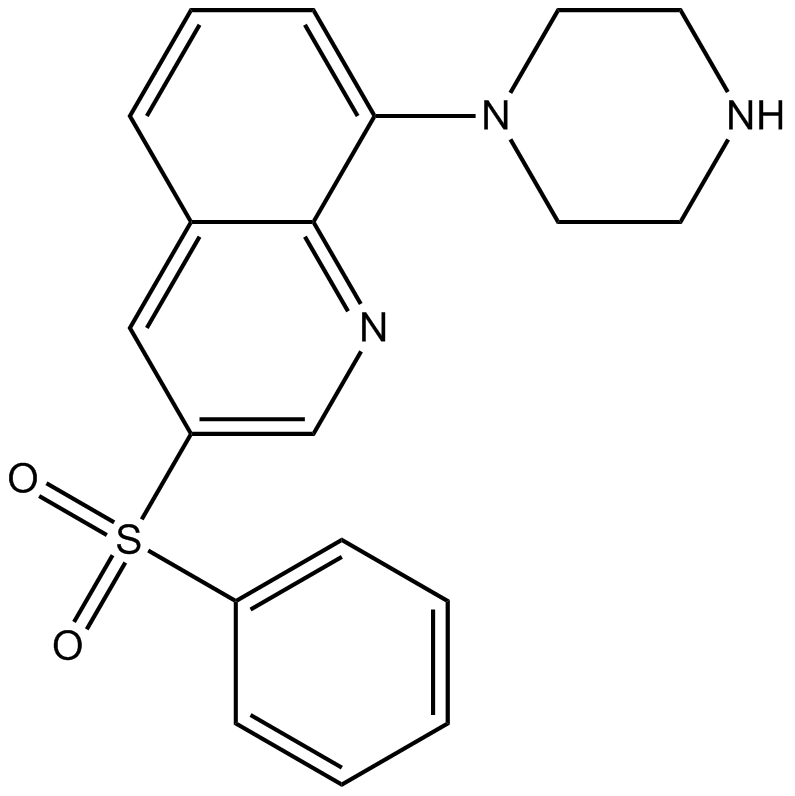
| Formula | C19H19N3O2S | M.Wt | 353.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (141.47 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-(benzenesulfonyl)-8-piperazin-1-ylquinoline | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCN1)C2=CC=CC3=CC(=CN=C32)S(=O)(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JJZFWROHYSMCMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H19N3O2S/c23-25(24,16-6-2-1-3-7-16)17-13-15-5-4-8-18(19(15)21-14-17)22-11-9-20-10-12-22/h1-8,13-14,20H,9-12H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | SB742457 is a highly selective antagonist of 5-HT6 receptor with a pKi value of 9.63. | |||||
| Targets | 5-HT6 | |||||
| IC50 | 9.63(pKi) | |||||

SB742457 Dilution Calculator

SB742457 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8293 mL | 14.1467 mL | 28.2933 mL | 56.5867 mL | 70.7334 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5659 mL | 2.8293 mL | 5.6587 mL | 11.3173 mL | 14.1467 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2829 mL | 1.4147 mL | 2.8293 mL | 5.6587 mL | 7.0733 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0566 mL | 0.2829 mL | 0.5659 mL | 1.1317 mL | 1.4147 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0283 mL | 0.1415 mL | 0.2829 mL | 0.5659 mL | 0.7073 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SB742457 is a selective antagonist of 5-HT6 receptor with a pKi value of 9.63 [1].
SB742457 has been found to be a highly selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with high affinity to human 5-HT6 receptor. The pKi value of SB742457 is 9.63. In addition, because of the orally bioavailable, SB742457 has been reported to promote brain penetration in rat over previously developed compounds. Besides, subchronic daily oral pre-dosing of SB742457 (1.5mg/kg) has been noted to significantly induce by the cholinergic antagonist scopolamine (0.5mg/kg) in a novel object recognition paradigm. Apart from these, acute oral treatment of SB742457 has been found to induce significant increases levels of glutamate and acetylcholine in extracellular in the medial prefrontal cortex of freely moving rats [1].
References:
[1] Aaron T.T. Chuang, Andrew Foley, Perdita L. Pugh, David Sunter, Xin Tong, Ciaran Regan, Lee A. Dawson, Andrew D. Medhurst, Neil Upton.5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB-742457 as a novel cognitive enhancing agent for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association Volume 2, Issue 3, Supplement, Pages?S631–S632, July 2006
- A 77-01
Catalog No.:BCC1318
CAS No.:607737-87-1
- Ethyl 4-methoxysalicylate
Catalog No.:BCN3499
CAS No.:35031-00-6
- Meloside A
Catalog No.:BCN2278
CAS No.:60767-80-8
- ent-Kauran-17,19-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4122
CAS No.:60761-79-7
- 2-Hydroxy-1,8-cineole
Catalog No.:BCN4121
CAS No.:60761-00-4
- Canthin-6-one N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2992
CAS No.:60755-87-5
- AZ 10606120 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6005
CAS No.:607378-18-7
- SB 772077B dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6116
CAS No.:607373-46-6
- Physoperuvine
Catalog No.:BCN1402
CAS No.:60723-27-5
- Myristicin
Catalog No.:BCN2730
CAS No.:607-91-0
- Sesamin
Catalog No.:BCN4123
CAS No.:607-80-7
- FC 131
Catalog No.:BCC7917
CAS No.:606968-52-9
- Quercetin 3-O-beta-D-glucose-7-O-beta-D-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN7821
CAS No.:60778-02-1
- Berbamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2400
CAS No.:6078-17-7
- Norbraylin
Catalog No.:BCN4124
CAS No.:60796-64-7
- 5,7,8-Trimethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN4125
CAS No.:60796-65-8
- Dulcitol
Catalog No.:BCN8153
CAS No.:608-66-2
- Sinomenine HCl
Catalog No.:BCN6318
CAS No.:6080-33-7
- Lithium Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC3804
CAS No.:6080-58-6
- 4-Methoxy-1-methoxycarbonyl-beta-carboline
Catalog No.:BCN1401
CAS No.:60807-25-2
- Apremilast (CC-10004)
Catalog No.:BCC2273
CAS No.:608141-41-9
- Esculentoside B
Catalog No.:BCN5011
CAS No.:60820-94-2
- Crotaverrine
Catalog No.:BCN2142
CAS No.:60827-69-2
- Ligularidine
Catalog No.:BCN2141
CAS No.:60872-63-1
Age-related declines in delayed non-match-to-sample performance (DNMS) are reversed by the novel 5HT6 receptor antagonist SB742457.[Pubmed:22766392]
Neuropharmacology. 2012 Oct;63(5):890-7.
Alterations in synaptic plasticity and neurocognitive function with age have been well documented in the literature. These changes are accompanied by modifications of neurotransmitter systems in the central nervous system (CNS). The serotonergic system in particular plays an important role in attention, alertness and cognition. Disturbances in serotonergic function have been implicated in differing neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders including depression, psychosis aggression and dementia. The serotonin receptor subtype 5HT6 is distributed within CNS regions relevant to learning and memory, including the striatum, cortex and hippocampus. We examined here the effects of acute and chronic administration of the 5HT6 receptor antagonist SB742457 on performance in a delayed non-matching-to-sample task (DNMS), which was used to identify neurocognitive differences between middle-aged (MA, 13 months) and young adult (YG, 3 months) rats. We found that MA rats have significantly lower performance in the DNMS task compared to YG rats. Acute administration of SB742457 (3 mg/kg/po) significantly improved performance of the MA rats. Chronic administration of SB742457 (3 mg/kg) reversed the age-related deficit of the MA to match their performance to that of YG rats. Furthermore, these improvements were observed for 1 week post-SB742457 treatment cessation. The acute and chronic effects of this treatment suggest that there is both an immediate effect on neurotransmitter action and potentially a longer-term modification of synaptic plasticity. Together these data indicate a role for modulation of the serotonergic system in the development of cognition-enhancing agents.
Human Kinetic Modeling of the 5HT6 PET Radioligand 11C-GSK215083 and Its Utility for Determining Occupancy at Both 5HT6 and 5HT2A Receptors by SB742457 as a Potential Therapeutic Mechanism of Action in Alzheimer Disease.[Pubmed:26383152]
J Nucl Med. 2015 Dec;56(12):1901-9.
UNLABELLED: Antagonism of 5-hydroxytrypamine-6 (5HT6) receptors is associated with procognitive effects in preclinical species, suggesting a therapeutic potential for this mechanism in Alzheimer disease (AD) and other cognitive diseases. In a phase 2 dose study, SB742457, a novel 5HT6 antagonist, showed increasing procognitive effects in patients with AD as the dose increased, with a procognitive signal in AD patients at a dose of 35 mg/d superior to the other doses tested (5 and 15 mg/d). METHODS: In this article, we describe the quantification and pharmacologic selectivity of a new 5HT6 PET ligand ((11)C-GSK215083) in healthy volunteers and its use to measure occupancies achieved at various doses of SB742457. RESULTS: Kinetic analysis of (11)C-GSK215083 uptake in the human brain demonstrated the multilinear model, MA2, to represent the method of choice when a blood input was available and the full tissue reference method when no input was available. Pharmacologic dissection of the in vivo (11)C-GSK215083-specific binding showed the ligand bound mostly the 5HT6 in the striatum (blocked by SB742457 but not by the selective 5-hydroxytryptamine-2A (5HT2A) antagonist ketanserin) and the 5HT2A in the frontal cortex (blocked by both ketanserin and SB742457). Repeated administration of SB742457 (3, 15, and 35 mg/d) saturated the 5HT6 receptors at all doses. In the cortex, 5HT2A receptor occupancy was 24% +/- 6% (3 mg/d), 35% +/- 4% (15 mg/d), and 58% +/- 19% (35 mg/d; mean +/- SD), suggesting a progressive engagement of 5HT2A as the dose increased. CONCLUSION: Collectively, these data support the use of (11)C-GSK215083 as a 5HT6 clinical imaging tool and suggest that blocking both the 5HT6 and the 5HT2A receptors may be required for the optimal therapeutic action of SB742457 in AD.
Central nervous system effects of the interaction between risperidone (single dose) and the 5-HT6 antagonist SB742457 (repeated doses) in healthy men.[Pubmed:21223356]
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011 Jun;71(6):907-16.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ABOUT THIS SUBJECT: * Several lines of evidence suggest a possible role of 5-HT(6) receptor antagonists in dementia or cognitive dysfunction of schizophrenia. SB-742457 is a potent 5-HT(6) antagonist and has shown efficacy in different animal models of cognitive impairment. It is currently in development as a cognitive enhancer. Risperidone, commonly used to control agitation and psychotic features in both schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease, is a D(2)/5-HT(2A ) antagonist with low affinity for 5-HT(6) receptors and limited effects on cognitive parameters. WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS: * As the combination of risperidone and SB-742457 may constitute a reasonable combination in cognitively impaired patients, pharmacodynamic interaction effects were investigated in this study. The only significant drug-drug interaction was a small increase of electroencephalogram (EEG) alpha and beta bands, which might suggest mild arousing activity of SB-742457 on the central nervous system-depressant effects of risperidone. The clinical relevance of these findings in patients remains to be established. Additionally, this study provided an extensive multidimensional pharmacodynamic profile of risperidone in healthy volunteers, showing that this antipsychotic suppresses motor performance (eye-hand coordination, finger tapping and postural stability), alertness, memory and neurophysiological functions (saccadic eye movements and EEG power spectrum). AIM: Several lines of evidence suggest a possible role of 5-HT(6 ) receptor antagonists in cognitive dysfunction of schizophrenia. Atypical antipsychotics, such as risperidone, are currently used in these disorders. Therefore, the pharmacological interactions between the 5-HT(6) antagonist SB-742457 and risperidone were investigated in the light of possible co-medication. METHODS: A randomized, double-blind, two-way crossover design was used to study the interaction between multiple doses SB-742457 50 mg and a single dose risperidone 2 mg in 18 healthy subjects. RESULTS: Treatment was well tolerated. The most common adverse event was somnolence in 83% during the combination vs. 50% of subjects after risperidone, 32% after placebo and 11% after SB-742457. Combination treatment produced a statistically significant increase in the maximum plasma concentration of risperidone and had no effect on SB-742457 pharmacokinetics. Risperidone decreased saccadic peak velocity, finger tapping, adaptive tracking, subjective alertness, delayed word recognition and body sway and increased electroencephalogram (EEG) theta power and prolactin. The only pharmacodynamic interaction of risperidone and SB-742457 was an increase of absolute EEG alpha (ratio = 1.25, 95% CI = 1.11, 1.40, P= 0.0004) and beta power (ratio = 1.14, 95% CI = 1.03, 1.27, P= 0.016). No significant effects of SB-742457 alone were found. CONCLUSION: The pharmacokinetic interactions between SB-742457 and risperidone detected in this study were not clinically relevant. The increase in EEG alpha and beta power is incompatible with enhanced risperidone activity, but could point to mild arousing effects of the combination. Most pharmacodynamic changes of risperidone are consistent with previously reported data. The potential cognitive effects of SB-742457 remain to be established.


