Salvianolic acid DCAS# 142998-47-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 142998-47-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 75412558 | Appearance | Yellowish powder |
| Formula | C20H18O10 | M.Wt | 418.4 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol and water | ||
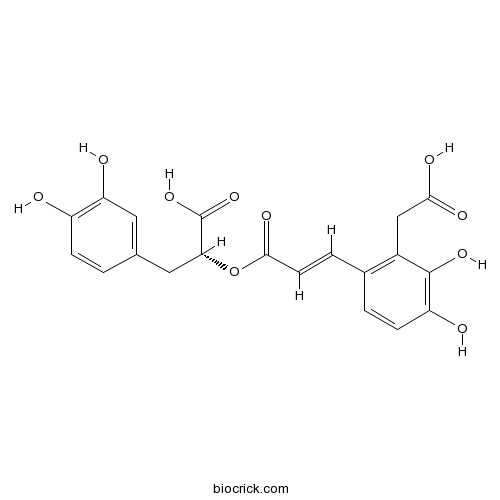
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[(E)-3-[2-(carboxymethyl)-3,4-dihydroxyphenyl]prop-2-enoyl]oxy-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1CC(C(=O)O)OC(=O)C=CC2=C(C(=C(C=C2)O)O)CC(=O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KFCMFABBVSIHTB-WUTVXBCWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H18O10/c21-13-4-1-10(7-15(13)23)8-16(20(28)29)30-18(26)6-3-11-2-5-14(22)19(27)12(11)9-17(24)25/h1-7,16,21-23,27H,8-9H2,(H,24,25)(H,28,29)/b6-3+/t16-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Salvianolic acid and notoginseng triterpenes can promote EA-hy926 and expression of protein, have protective effects on angiogenesis in EA-hy926 cells in vitro. |

Salvianolic acid D Dilution Calculator

Salvianolic acid D Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3901 mL | 11.9503 mL | 23.9006 mL | 47.8011 mL | 59.7514 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.478 mL | 2.3901 mL | 4.7801 mL | 9.5602 mL | 11.9503 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.239 mL | 1.195 mL | 2.3901 mL | 4.7801 mL | 5.9751 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0478 mL | 0.239 mL | 0.478 mL | 0.956 mL | 1.195 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0239 mL | 0.1195 mL | 0.239 mL | 0.478 mL | 0.5975 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Salvianolic acid E
Catalog No.:BCN8194
CAS No.:142998-46-7
- Fmoc-D-Ala(3-pyridyl)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3324
CAS No.:142994-45-4
- Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3177
CAS No.:142994-19-2
- UNC2025
Catalog No.:BCC8062
CAS No.:1429881-91-3
- HPOB
Catalog No.:BCC5574
CAS No.:1429651-50-2
- Triptoquinone A
Catalog No.:BCN6781
CAS No.:142950-86-5
- Triptoquinone B
Catalog No.:BCN6238
CAS No.:142937-50-6
- Mutant IDH1 inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC4144
CAS No.:1429180-08-4
- OXF BD 02
Catalog No.:BCC5598
CAS No.:1429129-68-9
- Petunidin chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3018
CAS No.:1429-30-7
- 8alpha-Methacryloyloxy-13-ethoxyvernojalcanolide
Catalog No.:BCN7445
CAS No.:142891-14-3
- 1-O-Ethylpiptocarphin F
Catalog No.:BCN6448
CAS No.:142891-12-1
- Lauric acid
Catalog No.:BCN2635
CAS No.:143-07-7
- Protoveratrine A
Catalog No.:BCN5346
CAS No.:143-57-7
- Vinblastine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2292
CAS No.:143-67-9
- ML216
Catalog No.:BCC8061
CAS No.:1430213-30-1
- 1alpha-Hydroxy VD4
Catalog No.:BCC1300
CAS No.:143032-85-3
- Ethyl 3,4-dicaffeoylquinate
Catalog No.:BCN8004
CAS No.:143051-73-4
- Phytic acid sodium salt hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN1283
CAS No.:14306-25-3
- BQ-3020
Catalog No.:BCC5728
CAS No.:143113-45-5
- Neotuberostemonine
Catalog No.:BCN6239
CAS No.:143120-46-1
- GSK-LSD1 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5647
CAS No.:1431368-48-7
- BMX-IN-1
Catalog No.:BCC1434
CAS No.:1431525-23-3
- H-D-Ala-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3199
CAS No.:14316-06-4
Multiple on-line screening and identification methods for hydroxyl radical scavengers in Yudanshen.[Pubmed:29730337]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jul 15;156:278-283.
Yudanshen, the genuine medicinal materials of Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza), is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) used to treat cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Although its pharmacological and antioxidative activities have been well-documented, there is little research on the hydroxyl radical (OH) scavenging capacity of Yudanshen. In this study, we established multiple on-line high-performance liquid chromatography- chemiluminescence detector-diode-quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-CL-DAD-Q-TOF/MS) methods to rapidly screen and identify the OH scavengers in Yudanshen simultaneously. The chromatographic and potency fingerprints revealed seventeen peaks that showed the inhibition of OH. Fourteen of them were identified as danshensu, protocatechuic aldehyde, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, salvianolic acid F, salvianolic acid H/L, salvianolic acid G, Salvianolic acid D, salvianolic acid E, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid B, isosalvianolic acid B, salvianolic acid A, and salvianolic acid C. This study explores the OH scavenging activities of Yudanshen, and provides novel and powerful multiple on-line methods in the field of TCM for rapid screening and identification of OH scavengers.
A fast and accurate method for the identification of peroxidase inhibitors from Radix Salvia Miltiorrhizae by on-flow biochemical assay coupled with LC/Q-TOF-MS: comparison with ultrafiltration-based affinity selection.[Pubmed:29725726]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Jul;410(18):4311-4322.
Development of fast and accurate methods to discover lead compounds for drug candidates is highly important. In this study, a reliable and effective post-column on-flow biochemical assay (POBA) was established to screen potent peroxidase inhibitors from complex chemical mixtures (e.g., natural product extracts). Multiple factors such as flow rate, organic phase, detection wavelength, and reaction coil were carefully investigated. To better understand the features of POBA, another emerging technology of ultrafiltration LC-MS was used for comparison. The result showed that POBA had advantages in saving time, avoiding false positives, and improving the accuracy. To illustrate the practicality of the method, Radix Salvia Miltiorrhizae, a traditional herb for cardiovascular disease treatment, was applied as the research objective. Finally, six compounds including tanshinol, protocatechuic aldehyde, Salvianolic acid D, rosmarinic acid, lithospermic acid, and salvianolic acid B were determined as novel peroxidase inhibitors. Their bioactivities were validated by microplate-based assay, molecular docking, and pharmacophore modeling. This study demonstrates a great potential of POBA in the efficient and accurate discovery of drug candidates. Graphical abstract Compared with a classical method of ultrafiltration LC-MS, the newly developed method of on-flow bioassay shows advantages in saving time, avoiding false positives and improving the accuracy.
A quality marker study on salvianolic acids for injection.[Pubmed:29544864]
Phytomedicine. 2018 May 15;44:138-147.
BACKGROUND: The quality of Chinese medicine (CM) has being an active and challenging research area for CM. Prof. Chang-Xiao Liu et al first proposed the concept of quality marker (Q-Marker) for the quality evaluation and control on CM. This article describe the exploratory studies of Q-Marker in salvianolic acids for injection (SAI) based on this new concept. PURPOSE: This study was designed to screen Q-Marker of SAI and establish its quality control method based on the concept of CM Q-Marker. METHODS: Based on the concept of CM Q-Marker, the SAI was investigated for the identification of chemical components and their sources. The pharmacological effects on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion induced injury in rats were also investigated. Furthermore, the target cell extracts and pharmacokinetic studies were conducted to screen Q-Markers. Finally, the fingerprints and determination based on Q-Markers were established to assess the quality of SAI more effectively. RESULTS: Overall, 20 constituents in SAI were identified. It was found that salvianolic acid B (SA-B), rosmarinic acid (RA), lithospermic acid (LA), Salvianolic acid D (SA-D) and salvianolic acid Y (SA-Y) are major chemical components of SAI. Based on chemical components identifications, analysis of their sources, target cell extracts and pharmacokinetic studies, four phenolic acids, namely SA-B, RA, LA and SA-D, were screened and determined as effective Q-Markers of SAI. CONCLUSION: This study demonstrated that the described method is a powerful approach for detecting Q-Markers, which can be used as control index for the quality assessment of CM.
Screening and analysis of potentially active components in Shenxiong glucose injection using UHPLC coupled with photodiode array detection and MS/MS.[Pubmed:29430840]
J Sep Sci. 2018 May;41(10):2130-2138.
Shenxiong glucose injection, a pharmaceutical preparation containing a water extract of the roots of Salvia miltiorrhizae and ligustrazine hydrochloride, is widely used in clinical to treat cardiovascular diseases in China. The chemical components of the water extract have been reported and the cardioprotective effects of the injection have been evaluated. However, the chemical constituents of the injection and their correlations with its pharmacological effects have not been established. In this study, 13 chemical constituents of the injection have been identified or characterized by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection and electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Besides, the potentially active compounds of this preparation that directly act on cardiac cells have been screened by cell extraction and ultra high performance liquid chromatography targeted multiple reaction monitoring. As a result, eight potentially active compounds, danshensu (1), ligustrazine hydrochloride (4), salvianolic acid I/H (7), lithospermic acid (8), Salvianolic acid D (9), rosmarinic acid (10), salvianolic acid B (12), and salvianolic acid C (13), were obtained and structurally characterized from the 11 target compounds used for screening. The liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography with multiple reaction monitoring tandem mass spectrometry combination method has demonstrated its potency for the screening, detection, and structural identification of bioactive compounds in a complex matrix.


