Sinomenine N-oxideCAS# 1000026-77-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1000026-77-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 163355498.0 | Appearance | Powder |
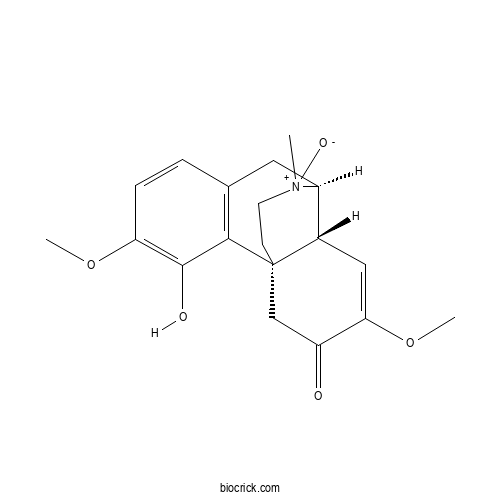
| Formula | C19H23NO5 | M.Wt | 345.39 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (1R,9S,10R)-3-hydroxy-4,12-dimethoxy-17-methyl-17-oxido-17-azoniatetracyclo[7.5.3.01,10.02,7]heptadeca-2(7),3,5,11-tetraen-13-one | ||
| SMILES | C[N+]1(CCC23CC(=O)C(=CC2C1CC4=C3C(=C(C=C4)OC)O)OC)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IQCNMIIBBLJCAC-XMPQHNGSSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H23NO5/c1-20(23)7-6-19-10-14(21)16(25-3)9-12(19)13(20)8-11-4-5-15(24-2)18(22)17(11)19/h4-5,9,12-13,22H,6-8,10H2,1-3H3/t12-,13-,19+,20?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Sinomenine N-oxide Dilution Calculator

Sinomenine N-oxide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8953 mL | 14.4764 mL | 28.9528 mL | 57.9056 mL | 72.3819 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5791 mL | 2.8953 mL | 5.7906 mL | 11.5811 mL | 14.4764 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2895 mL | 1.4476 mL | 2.8953 mL | 5.7906 mL | 7.2382 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0579 mL | 0.2895 mL | 0.5791 mL | 1.1581 mL | 1.4476 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.029 mL | 0.1448 mL | 0.2895 mL | 0.5791 mL | 0.7238 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Protoanemonin
Catalog No.:BCX1270
CAS No.:108-28-1
- Demethyldaphnoretin-7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1269
CAS No.:438578-91-7
- Scheffoleoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1268
CAS No.:160669-23-8
- 3-epi-Bufalin
Catalog No.:BCX1267
CAS No.:465-20-3
- Araloside C
Catalog No.:BCX1266
CAS No.:55446-15-6
- Dihydrolanosterol
Catalog No.:BCX1265
CAS No.:911660-54-3
- Tarasaponin IV
Catalog No.:BCX1264
CAS No.:156980-31-3
- Fallacinol
Catalog No.:BCX1263
CAS No.:569-05-1
- Isoasiaticoside
Catalog No.:BCX1262
CAS No.:948827-09-6
- Tenacissoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1261
CAS No.:107352-30-7
- cis-Pellitorine
Catalog No.:BCX1260
CAS No.:639086-18-3
- Brevicornin
Catalog No.:BCX1259
CAS No.:173792-49-9
- 6-Hydroxyluteolin
Catalog No.:BCX1272
CAS No.:18003-33-3
- Phenoxodiol
Catalog No.:BCX1273
CAS No.:81267-65-4
- 2'-O-Methylphloretin
Catalog No.:BCX1274
CAS No.:111316-17-7
- 2',4,4',6'-Tetramethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCX1275
CAS No.:94103-36-3
- Hispidol
Catalog No.:BCX1276
CAS No.:5786-54-9
- N-Acetylcytisine
Catalog No.:BCX1277
CAS No.:6018-52-6
- Palvanil
Catalog No.:BCX1278
CAS No.:69693-13-6
- Micromarin F
Catalog No.:BCX1279
CAS No.:73292-93-0
- 3,5,7-Trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1280
CAS No.:26964-29-4
- Ethyl rosmarinate
Catalog No.:BCX1281
CAS No.:174591-47-0
- 1-(2,6-Dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propen-1-one
Catalog No.:BCX1282
CAS No.:85679-87-4
- 5-Hydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1283
CAS No.:70786-48-0
Simultaneous determination of sinomenine and its metabolites desmethyl-sinomenine and sinomenine N-oxide in rat plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:38234029]
J Sep Sci. 2024 Jan;47(1):e2300790.
Sinomenine is an active ingredient extracted from herb medicine, which has been prescribed to treat rheumatoid arthritis in clinics. The present work was to develop a simple method to simultaneously determine sinomenine and its metabolites desmethyl sinomenine and Sinomenine N-oxide in rat plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Precursor-to-product transitions for detection were m/z 330.2 > 239.1 for sinomenine, m/z 316.2 > 239.1 for desmethyl-sinomenine, m/z 346.2 > 314.1 for Sinomenine N-oxide and m/z 286.2 > 153.2 for morphine (internal standard), respectively. During the validation and sample quantification, an excellent linear calibration range was observed for all the analytes with correlation coefficients more than 0.999 (r > 0.99). The extraction recovery was more than 85%. No significant matrix effect and carryover were observed. The precision was less than 6.45%, whereas accuracy ranged from -4.10% to 7.23%. The validated method has been successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic study of sinomenine, desmethyl sinomenine, and Sinomenine N-oxide in rat plasma after oral administration of sinomenine at a single dose of 5 mg/kg. The results suggested that sinomenine was rapidly metabolized into its metabolite desmethyl sinomenine and Sinomenine N-oxide.
Identification and characterization of the metabolites of sinomenine using liquid chromatography combined with benchtop Orbitrap mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.[Pubmed:38211350]
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2024 Feb 15;38(3):e9669.
RATIONALE: Sinomenine, a major bioactive compound isolated from Sinomenium acutum, has been used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other cardio-cerebrovacular diseases. However, the metabolism of this drug has not been fully investigated. The current work was carried out to investigate the in vitro metabolism of sinomenine in liver microsomes. METHODS: The metabolites were generated by incubating sinomenine (3 muM) with the liver microsomes in the presence of NADPH at 37 degrees C. The structure of the metabolites was characterized using liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). Two major metabolites synthesized and their structures were further confirmed using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. RESULTS: Under the current conditions, 12 metabolites were found and structurally identified using high resolution MS and MS(2) spectra. Among these metabolites, M1, M2, M3, M4, M5, M6, M7, M9, M11, and M12 were first reported. The metabolites M8 and M10 were synthesized and unambiguously identified as N-desmethyl-sinomenine and Sinomenine N-oxide, respectively. The phenotyping study revealed that the formation of M8 was catalyzed by CYP2C8, 2C19, 2D6, and 3A4, whereas the formation of M3, M6, and M10 were exclusively catalyzed by CYP3A4. The metabolic pathways of sinomenine include N-demethylation, O-demethylation, dehydrogenation, oxygenation, and N-oxygenation. CONCLUSIONS: N-Demethylation and N-oxygenation were the primary metabolic pathways of sinomenine. This study provides new insight into the in vitro metabolism of sinomenine, which would help prospects of sinomenine disposition and safety assessments.
New N-oxide alkaloids from the stems of Sinomenium acutum.[Pubmed:36572115]
Fitoterapia. 2023 Mar;165:105404.
Six new alkaloids (1-6) and six known alkaloids (7-12) were obtained from the stems of Sinomenium acutum. Among them, compounds 1-3 and 6 were four N-oxide alkaloids. The structures and absolute configurations of these new alkaloids were elucidated through comprehensive data of 1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS and ECD spectra. All isolated compounds were evaluated in vitro for their inhibitory activities against nitric oxide (NO) production and inhibitory effects on AChE. Among them, the Sinomenine N-oxide (9) was the most potent NO production inhibitor, with an IC(50) value of 23.04 muM.
Two new morphinane alkaloids from Sinomenium acutum.[Pubmed:21623515]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2011 Jun;13(6):523-8.
Two new morphinane alkaloids, 1-hydroxy-10-oxo-sinomenine (1) and 4,5-epoxy-14-hydroxy Sinomenine N-oxide (2), have been isolated from the stems of Sinomenium acutum. Their structures were established by various spectral analyses, especially 2D NMR experiments. The structure of 2 was confirmed by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The absolute configurations of 1 and 2 were deduced by comparison of CD spectra with the known alkaloid sinomenine (3). Compound 1 was tested for DPPH inhibition and gave IC(50) of 27.9 muM. Compound 2 was tested for neuroprotective effect and showed significant activity against beta-amyloid(25-35)-induced oxidative injury (*P < 0.05) at 10 muM in PC-12 cells.
Morphinane alkaloids with cell protective effects from Sinomenium acutum.[Pubmed:16038566]
J Nat Prod. 2005 Jul;68(7):1128-30.
One new morphinane alkaloid, Sinomenine N-oxide (1), and one new natural occurring morphinane alkaloid, N-demethylsinomenine (2), together with six known alkaloids, 7,8-didehydro-4-hydroxy-3,7-dimethoxymorphinan-6-ol (3), sinomenine (4), sinoacutine (5), N-norsinoacutine, acutumine, and acutumidine, were isolated from the stems of Sinomenium acutum. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic analysis and chemical methods. Compounds 2, 3, and 5 have protective effects against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell injury.


