6-HydroxyluteolinCAS# 18003-33-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18003-33-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281642.0 | Appearance | Powder |
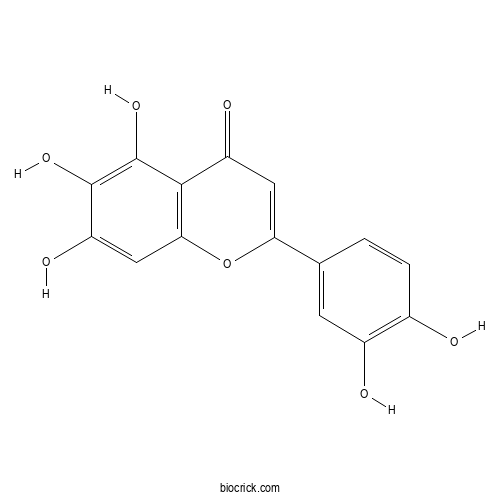
| Formula | C15H10O7 | M.Wt | 302.24 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,6,7-trihydroxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1C2=CC(=O)C3=C(O2)C=C(C(=C3O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VYAKIUWQLHRZGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H10O7/c16-7-2-1-6(3-8(7)17)11-4-9(18)13-12(22-11)5-10(19)14(20)15(13)21/h1-5,16-17,19-21H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

6-Hydroxyluteolin Dilution Calculator

6-Hydroxyluteolin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3086 mL | 16.5431 mL | 33.0863 mL | 66.1726 mL | 82.7157 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6617 mL | 3.3086 mL | 6.6173 mL | 13.2345 mL | 16.5431 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3309 mL | 1.6543 mL | 3.3086 mL | 6.6173 mL | 8.2716 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0662 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6617 mL | 1.3235 mL | 1.6543 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1654 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6617 mL | 0.8272 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sinomenine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCX1271
CAS No.:1000026-77-6
- Protoanemonin
Catalog No.:BCX1270
CAS No.:108-28-1
- Demethyldaphnoretin-7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1269
CAS No.:438578-91-7
- Scheffoleoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1268
CAS No.:160669-23-8
- 3-epi-Bufalin
Catalog No.:BCX1267
CAS No.:465-20-3
- Araloside C
Catalog No.:BCX1266
CAS No.:55446-15-6
- Dihydrolanosterol
Catalog No.:BCX1265
CAS No.:911660-54-3
- Tarasaponin IV
Catalog No.:BCX1264
CAS No.:156980-31-3
- Fallacinol
Catalog No.:BCX1263
CAS No.:569-05-1
- Isoasiaticoside
Catalog No.:BCX1262
CAS No.:948827-09-6
- Tenacissoside A
Catalog No.:BCX1261
CAS No.:107352-30-7
- cis-Pellitorine
Catalog No.:BCX1260
CAS No.:639086-18-3
- Phenoxodiol
Catalog No.:BCX1273
CAS No.:81267-65-4
- 2'-O-Methylphloretin
Catalog No.:BCX1274
CAS No.:111316-17-7
- 2',4,4',6'-Tetramethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCX1275
CAS No.:94103-36-3
- Hispidol
Catalog No.:BCX1276
CAS No.:5786-54-9
- N-Acetylcytisine
Catalog No.:BCX1277
CAS No.:6018-52-6
- Palvanil
Catalog No.:BCX1278
CAS No.:69693-13-6
- Micromarin F
Catalog No.:BCX1279
CAS No.:73292-93-0
- 3,5,7-Trimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1280
CAS No.:26964-29-4
- Ethyl rosmarinate
Catalog No.:BCX1281
CAS No.:174591-47-0
- 1-(2,6-Dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-propen-1-one
Catalog No.:BCX1282
CAS No.:85679-87-4
- 5-Hydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1283
CAS No.:70786-48-0
- Morusignin L
Catalog No.:BCX1284
CAS No.:149733-95-9
Computational identification of potential inhibitors targeting cdk1 in colorectal cancer.[Pubmed:38099190]
Front Chem. 2023 Nov 30;11:1264808.
Introduction: Despite improved treatment options, colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a huge public health concern with a significant impact on affected individuals. Cell cycle dysregulation and overexpression of certain regulators and checkpoint activators are important recurring events in the progression of cancer. Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), a key regulator of the cell cycle component central to the uncontrolled proliferation of malignant cells, has been reportedly implicated in CRC. This study aimed to identify CDK1 inhibitors with potential for clinical drug research in CRC. Methods: Ten thousand (10,000) naturally occurring compounds were evaluated for their inhibitory efficacies against CDK1 through molecular docking studies. The stability of the lead compounds in complex with CDK1 was evaluated using molecular dynamics simulation for one thousand (1,000) nanoseconds. The top-scoring candidates' ADME characteristics and drug-likeness were profiled using SwissADME. Results: Four hit compounds, namely, spiraeoside, robinetin, 6-Hydroxyluteolin, and quercetagetin were identified from molecular docking analysis to possess the least binding scores. Molecular dynamics simulation revealed that robinetin and 6-Hydroxyluteolin complexes were stable within the binding pocket of the CDK1 protein. Discussion: The findings from this study provide insight into novel candidates with specific inhibitory CDK1 activities that can be further investigated through animal testing, clinical trials, and drug development research for CRC treatment.
Phytochemical Profiling, Antioxidant and Cognitive-Enhancing Effect of Helichrysum italicum ssp. italicum (Roth) G. Don (Asteraceae).[Pubmed:37570911]
Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 25;12(15):2755.
This study aimed at the evaluation of the antioxidant and cognitive-enhancing effect of methanol-aqueous extract from Helichrysum italicum ssp. italicum aerial parts. Significant radical scavenging activity (110.33 +/- 3.47 and 234.70 +/- 5.21 mg TE/g for DPPH and ABTS) and reducing power (354.23 +/- 17.51 and 210.24 +/- 8.68 mg TE/g for CUPRAC and FRAP) were observed. The extract showed average acetylcholinesterase and low butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory potential. H. italicum extract (200 mg/kg/po) administered in combination with galantamine (3 mg/kg/po) for 12 days significantly improved the memory and learning process compared with galantamine alone in the passive avoidance test. The effect was comparable to that of Ginkgo biloba extract (100 mg/kg/po). In deep secondary metabolite annotation of the extract by UHPLC-HRMS, more than 90 hydroxybenzoic and hydroxicinnamic acid-glycosides, phenylethanoid glycosides, a series of acylquinic and caffeoylhexaric acids, methoxylated derivatives of scutellarein, quercetagetin and 6-Hydroxyluteolin, and prenylated phloroglucinol-alpha-pyrones were reported for the first time in H. italicum. Fragmentation patterns of four subclasses of heterodimer-pyrones were proposed. In-depth profiling of the pyrones revealed 23 compounds undescribed in the literature. Pyrones and acylphloroglucinols together with acylquinic acids could account for memory improvement. The presented research advanced our knowledge of H. italicum, highlighting the species as a rich source of secondary metabolites with cognitive-enhancing potential.
Exploring antidiabetic potential of a polyherbal formulation Madhurakshak Activ: An in vitro and in silico study.[Pubmed:37380135]
Fitoterapia. 2023 Sep;169:105598.
Madhurakshak Activ (MA), a commercial polyherbal antidiabetic preparation is known to manage diabetes mellitus (DM) by reducing blood glucose levels. However, lacks systematic mechanistic evaluation for their molecular and cellular mode of actions. In the present study, hydro-alcoholic and aqueous extract of MA were evaluated for their effects on glucose adsorption, diffusion, amylolysis kinetics and transport across the yeast cells using in vitro techniques. Bioactive compounds identified from MA by LC-MS/MS were assessed for their binding potential against DPP-IV and PPARgamma via an in silico approach. Our results revealed that the adsorption of glucose increased dose dependently (5 mM -100 mM). Both extracts exhibited linear glucose uptake into the yeast cells (5 mM - 25 mM), whereas glucose diffusion was directly proportional to time (30-180 min). Pharmacokinetic analysis revealed drug-like properties and low toxicity levels for all the selected compounds. Among the tested compounds, 6-Hydroxyluteolin (-8.9 against DPP-IV and PPARgamma) and glycyrrhetaldehyde (DPP-IV -9.7 and PPARgamma -8.5) have exhibited higher binding affinity compared to the positive control. Therefore, the above compounds were further considered for molecular dynamics simulation which showed stability of the docked complexes. Hence, studied mode of actions might produce a concerted role of MA in increasing the rate of glucose absorption and uptake followed by the in silico studies which suggest that the compounds identified from MA may inhibit DPP-IV and PPARgamma phosphorylation.
Identification and Comparison of Bioactive Components of Two Dryopteris sp. Extract Using LC-QTOF-MS.[Pubmed:36501275]
Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 25;11(23):3233.
Dryopteris sp. is known for its various pharmacological effects and is used as a traditional medicine in Asia. The present study investigated the chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of Dryopteris sp. distributed in Korea. The chemical compounds in the ethanolic extracts of Dryopteris lacera and Dryopteris bissetiana were investigated by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight-mass spectrometry analysis and identified by exploring the UNIFI traditional medicine library. Flavonoids such as juglanin, 6-Hydroxyluteolin 7-O-laminaribioside, peltatoside, kaempferitrin, hyperoside, and astragalin were identified in both D. lacera and D. bissetiana. Neochlorogenic acid was identified as a caffeoylquinic acid in D. bissetiana. Both extracts of D. lacera and D. bissetiana exhibited antibacterial activity against Gram-positive pathogens, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus mutans. The minimum inhibitory concentration of D. bissetiana against S. aureus was less than 625 ppm. The antibacterial activity was attributed to the identified phenolic compounds, juglanin, 6-Hydroxyluteolin 7-O-laminaribioside, kaempferitrin, astragalin, and neochlorogenic acid. Therefore, D. lacera and D. bissetiana can be used as Gram-positive selective antibiotics for further investigation.
Limoniastrum monopetalum-Mediated Nanoparticles and Biomedicines: In Silico Study and Molecular Prediction of Biomolecules.[Pubmed:36432115]
Molecules. 2022 Nov 18;27(22):8014.
An in silico approach applying computer-simulated models helps enhance biomedicines by sightseeing the pharmacology of potential therapeutics. Currently, an in silico study combined with in vitro assays investigated the antimicrobial ability of Limoniastrum monopetalum and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) fabricated by its aid. AgNPs mediated by L. monopetalum were characterized using FTIR, TEM, SEM, and DLS. L. monopetalum metabolites were detected by QTOF-LCMS and assessed using an in silico study for pharmacological properties. The antibacterial ability of an L. monopetalum extract and AgNPs was investigated. PASS Online predictions and the swissADME web server were used for antibacterial activity and potential molecular target metabolites, respectively. Spherical AgNPs with a 68.79 nm average size diameter were obtained. Twelve biomolecules (ferulic acid, trihydroxy-octadecenoic acid, catechin, pinoresinol, gallic acid, myricetin, 6-Hydroxyluteolin, 6,7-dihydroxy-5-methoxy 7-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside, methyl gallate, isorhamnetin, chlorogenic acid, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxy-beta-l-mannopyranosyl)-beta-d-glucopyranoside) were identified. The L. monopetalum extract and AgNPs displayed antibacterial effects. The computational study suggested that L. Monopetalum metabolites could hold promising antibacterial activity with minimal toxicity and an acceptable pharmaceutical profile. The in silico approach indicated that metabolites 8 and 12 have the highest antibacterial activity, and swissADME web server results suggested the CA II enzyme as a potential molecular target for both metabolites. Novel therapeutic agents could be discovered using in silico molecular target prediction combined with in vitro studies. Among L. Monopetalum metabolites, metabolite 12 could serve as a starting point for potential antibacterial treatment for several human bacterial infections.
In Vivo Antidepressant-Like Effect Assessment of Two Aloysia Species in Mice and LCMS Chemical Characterization of Ethanol Extract.[Pubmed:36431928]
Molecules. 2022 Nov 13;27(22):7828.
Medicinal plants belonging to the Verbenaceae family demonstrated antidepressant effects in preclinical studies. Depression is one of the largest contributors to the global health burden of all countries. Plants from the Aloysia genus are traditionally used for affective disorders, and some of them have proven anxiolytic and antidepressant activity. The aim of this work was to evaluate the antidepressant effect of the ethanolic extract of Aloysia gratissima var. gratissima (Agg) and Aloysia virgata var. platyphylla (Avp) in mice. A tail suspension test (TST) and forced swimming test (FST) were conducted after three doses in a period of 24 h and after 7 days of treatment. Imipramine was used as an antidepressant drug. The main results demonstrated that Agg extract reduced the immobility time in mice treated orally for 7 consecutive days when compared to the control group (reduced by about 77%, imipramine 70%). Animals treated with three doses of Avp in a 24-h period had reduced immobility time in the FST (60%), and after 7 days of treatment the reduction was greater (Avp 50, 100, and 200 about 85%; Avp 400, 96.5%; p < 0.0001, imipramine, 77%). LCMS analysis showed the presence of verbascoside, hoffmaniaketone, and hoffmaniaketone acetate in both, A. virgata var. platyphylla and A. gratissima var gratissima. The flavonoids nepetin and 6-Hydroxyluteolin were also found in Agg. Both tested extracts demonstrated promising antidepressant-like activity in mice.
Flavonoids and phenylethanoids from the flowers and leaves of Aeschynanthus species and cultivars (Gesneriaceae).[Pubmed:36002075]
Phytochemistry. 2022 Nov;203:113367.
Forty-one flavones, each one of flavonol, chalcone and dihydroflavonol, two flavanones, and four phenylethanoids were isolated from corollas, calyces and leaves of two Aeschynanthus species, A. fulgens and A. pulcher, and six cultivars, 'Mahligai', 'Mona Lisa', SoeKa', 'Redona', 'Freshya' and 'Bravera'. Flavonoids were mainly the glucuronides and/or methylglucuronides based on hispidulin, nepetin, pectolinarigenin, 6-Hydroxyluteolin, scutellarein, apigenin and luteolin, and identified by UV spectra, HR-MS, LC-MS, acid hydrolysis, NMR, and/or HPLC and TLC comparisons with authentic samples. Of these flavonoids, twelve, i.e. hispidulin 7,4'-di-O-glucuronide, 7,4'-di-O-methylglucuronide, 7-O-methylglucuronide-4'-O-glucuronide, 7-O-glucuronide-4'-O-methylglucuronide, 7-O-glucosyl-(1 --> 2)-glucuronide and 8-C-glucoside, nepetin 7,4'-di-O-glucuronide, 7-O-glucuronide-4'-O-methylglucuronide and 7-O-methylglucuronide-4'-O-glucuronide, pectolinarigenin 7-O-glucosyl-(1 --> 2)-glucuronide and 7-O-xylosyl-(1 --> 2)-(6''-malonylglucoside), and 6-Hydroxyluteolin 7,4'-di-O-glucuronide, were previously undescribed.
High-throughput virtual screening of small-molecule inhibitors targeting immune cell checkpoints to discover new immunotherapeutics for human diseases.[Pubmed:35633442]
Mol Divers. 2023 Apr;27(2):729-751.
Immunotherapy is widely used to treat various cancers, and the drugs used are called immune checkpoint (ICP) inhibitors. Overexpression of immune cell checkpoints is reported for other human diseases such as acute infections (malaria), chronic viral infection (HIV, hepatitis B virus, TB infections), allergy, asthma, neurodegeneration, and autoimmune diseases. Some mAbs (monoclonal antibodies) are available against ICPs, but they have side effects. Small molecule seems to be safer in comparison with mAbs. Three independent small-molecule inhibitor libraries consisting of 9466 compounds were screened against seven immune cell checkpoints by applying high-throughput virtual screening approach. A total of 13 ICP inhibitors were finalized based on docking, MM-GBSA scores, and ADME properties. Six compounds were selected for MD simulation, and then, rutin hydrate (targeting all seven immune cell checkpoints), amikacin hydrate (targeting six), and 6-Hydroxyluteolin (targeting three) were found to be the best immune cell checkpoint inhibitors. These three potential inhibitors have shown the potential to activate human immune cells and thus may control the spread of human lifestyle or infectious diseases. Proposed inhibitors warrant the in vitro and in vivo validation to develop it as an immunotherapeutic.
Phenolic acids and flavonoids from Salvia plebeia and HPLC-UV profiling of four Salvia species.[Pubmed:35287319]
Heliyon. 2022 Mar 4;8(3):e09046.
We isolated and purified phenolic acids and flavonoids from the ethanolic extract of Salvia plebeia using silica gel and a Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography. Spectroscopy revealed the isolated compounds were caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid, hispidulin, luteolin, jaceosidin, nepitrin, homoplantaginin, 6-Hydroxyluteolin 7-O-glucoside, 6-methoxynaringenin 7-O-glucoside, naasanone, and cosmosiin. Quantitative analyses, using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with UV (HPLC-UV), revealed that the major flavonoid from S. plebeia was 6-Hydroxyluteolin 7-O-glucoside (100.63 mg/g) and the most abundant phenolic acid was rosmarinic acid (47.73 mg/g). Furthermore, among four other Salvia species, S. officinalis contained the highest overall phenolic acid and flavonoid level but these were still lower than S. plebeia. These results can help assess the potential of phenolic acids and flavonoids as potent sources of pharmacological ingredients from different Salvia species extracts.
[A new hexenol glycoside from Buddleja officinalis].[Pubmed:34951244]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Dec;46(23):6178-6184.
The chemical constituents of the flower buds of Buddleja officinalis were investigated in this study. Eight compounds were isolated from the water extract of B. officinalis by column chromatography, and their structures were elucidated on the basis of physicochemical properties and spectral data. These compounds were identified as(Z)-hex-3-en-1-ol-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-[beta-D-xylcopyranosyl-(1-->6)]-beta-D-glucopyranoside(1), ebracteatoside B(2), jasmonic acid-11-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside(3), 6-Hydroxyluteolin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside(4), luteolin-7-O-galacturonide(5), vicenin-2(6), decaffeoylverbascoside(7), and 6-O-(E)-feruloyl-D-glucopyranoside(8). Compound 1 is a new 3-hexenol glycoside. Compounds 2, 3, and 6 were isolated from Buddleja genus for the first time, and compounds 4 and 5 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
[Study on mechanism of Valerianae Jatamansi Rhizoma et Radix against post-traumatic stress disorder based on molecular docking and network pharmacology].[Pubmed:34047082]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 May;46(10):2380-2391.
This paper aims to investigate the active components and mechanism of Valerianae Jatamansi Rhizoma et Radix against post-traumatic stress disorder(PTSD) based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. The main components and targets of Valerianae Jatamansi Rhizoma et Radix were obtained by literature mining methods, SwissTargetPrediction, BATMAN and ETCM database. PTSD-related genes were collected from DrugBank, TTD and CTD databases. The protein-protein interaction(PPI) network was constructed based on STRING, and the core targets of Valerianae Jatamansi Rhizoma et Radix in the treatment of PTSD were selected according to the topological parameters. Cytoscape 3.7.2 was used to construct the compound-target network. DAVID database was used for GO enrichment analysis and KEGG enrichment analysis. The relationship network of "compound-target-pathway" was constructed through Cytoscape 3.7.2 to analyze and obtain the key targets and their corresponding components in the network, and their results were verified by molecular docking. The results showed that a total of 47 components(such as valeraldehyde, dihydrovalerin, valerate, chlorovaltrate K, 8-hydroxypinoresinol, 6-Hydroxyluteolin, apigenin, farnesin, vanillin, luteolin, kaempferol, glycosmisic acid and pogostemon) of Valerianae Jatamansi Rhizoma et Radix may act on 94 key targets such as CNR1, MAOA, NR3 C1, MAPK14, MAPK8, HTR2 C and DRD2. Totally 29 GO terms were obtained by GO functional enrichment analysis(P<0.05), and 20 signaling pathways were obtained from KEGG pathway enrichment, mainly involving neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, serotonergic synapse, calcium signaling pathway, cAMP signaling pathway, dopaminergic synapse, retrograde endocannabinoid signaling, neurotrophin signaling pathway, gap junction, cholinergic synapse, estrogen signaling pathway, glutamatergic synapse and long-term potentiation. Molecular docking analysis showed that hydrogen bonding, pi-pi interaction and hydrophobic effecting may be the main forms of interaction. This study used the network of compound-target-pathway and molecular docking technology to screen the effective components of Valerianae Jatamansi Rhizoma et Radix against PTSD, and explore its anti-PTSD mechanism, so as to provide scientific basis for exploring the anti-PTSD drugs from traditional Chinese medicine and clarifying its mechanism of action.
Polyphenolic Compounds Extracted and Purified from Buddleja Globosa Hope (Buddlejaceae) Leaves Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Centrifugal Partition Chromatography.[Pubmed:33920316]
Molecules. 2021 Apr 10;26(8):2192.
Chemical profiling of Buddleja globosa was performed by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization (HPLC-DAD-ESI-IT/MS) and quadrupole time-of-flight high-resolution mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-QTOF/MS). The identification of 17 main phenolic compounds in B. globosa leaf extracts was achieved. Along with caffeoyl glucoside isomers, caffeoylshikimic acid and several verbascoside derivatives (beta-hydroxyverbascoside and beta-hydroxyisoverbascoside) were identified. Among flavonoid compounds, the presence of 6-Hydroxyluteolin-7-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-glucoside, luteolin 7-O-glucoside, apigenin 7-O-glucoside was confirmed. Campneoside I, forsythoside B, lipedoside A and forsythoside A were identified along with verbascoside, isoverbascoside, eukovoside and martynoside. The isolation of two bioactive phenolic compounds verbascoside and forsythoside B from Buddleja globosa (Buddlejaceae) was successfully achieved by centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC). Both compounds were obtained in one-step using optimized CPC methodology with the two-phase solvent system comprising ethyl acetate-n-butanol-ethanol-water (0.25:0.75:0.1:1, v/v). Additionally, eight Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs) were tested for the extraction of polyphenols and compared with 80% methanol. The contents of verbascoside and luteolin 7-O-glucoside after extraction with 80% methanol were 26.165 and 3.206 mg/g, respectively. Among the NADESs tested in this study, proline- citric acid (1:1) and choline chloride-1, 2- propanediol (1:2) were the most promising solvents. With these NADES, extraction yields for verbascoside and luteolin 7-O-glucoside were 51.045 and 4.387 mg/g, respectively. Taken together, the results of this study confirm that CPC enabled the fast isolation of bioactive polyphenols from B. globosa. NADESs displayed higher extraction efficiency of phenolic and therefore could be used as an ecofriendly alternative to classic organic solvents.
Flavonoids and Terpenoids with PTP-1B Inhibitory Properties from the Infusion of Salvia amarissima Ortega.[Pubmed:32752292]
Molecules. 2020 Aug 1;25(15):3530.
An infusion prepared from the aerial parts of Salvia amarissima Ortega inhibited the enzyme protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP-1B) (IC(50)~88 and 33 mug/mL, respectively). Phytochemical analysis of the infusion yielded amarisolide (1), 5,6,4'-trihydroxy-7,3'-dimethoxyflavone (2), 6-Hydroxyluteolin (3), rutin (4), rosmarinic acid (5), isoquercitrin (6), pedalitin (7) and a new neo-clerodane type diterpenoid glucoside, named amarisolide G (8a,b). Compound 8a,b is a new natural product, and 2-6 are reported for the first time for the species. All compounds were tested for their inhibitory activity against PTP-1B; their IC(50) values ranged from 62.0 to 514.2 muM. The activity was compared to that of ursolic acid (IC(50) = 29.14 muM). The most active compound was pedalitin (7). Docking analysis predicted that compound 7 has higher affinity for the allosteric site of the enzyme. Gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry analyses of the essential oils prepared from dried and fresh materials revealed that germacrene D (15) and beta-selinene (16), followed by beta-caryophyllene (13) and spathulenol (17) were their major components. An ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry method was developed and validated to quantify amarisolide (1) in the ethyl acetate soluble fraction of the infusion of S. amarissima.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activities from the Basolateral Fraction of Caco-2 Cells Exposed to a Rosmarinic Acid Enriched Extract.[Pubmed:29345918]
J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Feb 7;66(5):1167-1174.
The potential use of Origanum majorana L. as a source of bioavailable phenolic compounds, specifically rosmarinic acid (RA), has been evaluated. Phenolic bioavailability was tested using an in vitro digestion process followed by a Caco-2 cellular model of intestinal absorption. The high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detector-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-PAD-MS/MS) analysis showed the main components in the extract were 6-Hydroxyluteolin-7-O-glucoside and rosmarinic acid, followed by luteolin-O-glucoside. After digestion process, the amount of total phenolic compounds (TPC) only decreased slightly, although a remarkable reduction in RA (near 50%) was detected. Bioavailable fraction contained 7.37 +/- 1.39 mg/L digested extract of RA with small quantities of lithospermic acid and diosmin and presented an important antioxidant activity (0.89 +/- 0.09 mmol Trolox/L digested extract). Besides, this bioavailable fraction produced a significant inhibition in TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 secretion, using a human THP-1 macrophages model. Therefore, RA content in the basolateral compartment could play an important role in the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities found.


