TMC647055inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase CAS# 1204416-97-6 |
- Melphalan
Catalog No.:BCC2403
CAS No.:148-82-3
- GRI 977143
Catalog No.:BCC2401
CAS No.:325850-81-5
- Mdivi 1
Catalog No.:BCC2402
CAS No.:338967-87-6
- DAPK Substrate Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2400
CAS No.:386769-53-5
- Cesium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2399
CAS No.:7647-17-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1204416-97-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44556044 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C32H38N4O6S | M.Wt | 606.73 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
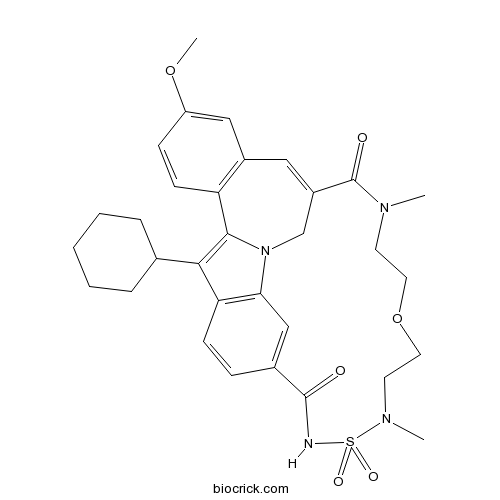
| SMILES | CN1CCOCCN(S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)C2=CC3=C(C=C2)C(=C4N3CC(=CC5=C4C=CC(=C5)OC)C1=O)C6CCCCC6)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UOBYJVFBFSLCTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C32H38N4O6S/c1-34-13-15-42-16-14-35(2)43(39,40)33-31(37)22-9-11-27-28(19-22)36-20-24(32(34)38)17-23-18-25(41-3)10-12-26(23)30(36)29(27)21-7-5-4-6-8-21/h9-12,17-19,21H,4-8,13-16,20H2,1-3H3,(H,33,37) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

TMC647055 Dilution Calculator

TMC647055 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6482 mL | 8.2409 mL | 16.4818 mL | 32.9636 mL | 41.2045 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3296 mL | 1.6482 mL | 3.2964 mL | 6.5927 mL | 8.2409 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1648 mL | 0.8241 mL | 1.6482 mL | 3.2964 mL | 4.1204 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.033 mL | 0.1648 mL | 0.3296 mL | 0.6593 mL | 0.8241 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0165 mL | 0.0824 mL | 0.1648 mL | 0.3296 mL | 0.412 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
TMC647055 is a potent and selective non-nucleoside inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase with EC50 value of 82 nM [1].
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase is a RNA-dependant RNA-polymerase that is responsible for viral replication and plays an important role in HCV life cycle. HCV is a major cause of chronic liver disease and acute hepatitis, ultimately leading to liver failure, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma [1].
TMC647055 is a selective and cell-permeating HCV NS5B inhibitor. In RNA polymerase primer-dependent transcription assay, TMC647055 inhibited HCV NS5B polymerase with IC50 value of 34 nM. In the Huh7-Luc cell line, TMC647055 inhibited the replication of genotype 1b replicon with EC50 values of 77 and 139 nM measured with luciferase readout and qRT-PCR readout, respectively. TMC647055 exhibited high-affinity interaction with NS5B across all genotypes (except for genotype 2b) with median KD value < 35 nM. In Huh7-Luc replicon cells, TMC647055 (750 nM) reduced 30 cell colonies formation. Also, TMC647055 (1.5 μM and 3.75 μM) reduced HCV replicon RNA [2] [3].
References:
[1]. Vendeville S, Lin TI, Hu L, et al. Finger loop inhibitors of the HCV NS5b polymerase. Part II. Optimization of tetracyclic indole-based macrocycle leading to the discovery of TMC647055. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2012, 22(13): 4437-4443.
[2]. Devogelaere B, Berke JM, Vijgen L, et al. TMC647055, a potent nonnucleoside hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor with cross-genotypic coverage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2012, 56(9): 4676-4684.
[3]. Cummings MD, Lin TI, Hu L, et al. Discovery and early development of TMC647055, a non-nucleoside inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase. J Med Chem, 2014, 57(5): 1880-1892.
- Icotinib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1639
CAS No.:1204313-51-8
- AZD1208
Catalog No.:BCC2079
CAS No.:1204144-28-4
- Biapenem
Catalog No.:BCC1071
CAS No.:120410-24-4
- Jionoside B1
Catalog No.:BCN2858
CAS No.:120406-37-3
- AS 1949490
Catalog No.:BCC7762
CAS No.:1203680-76-5
- Cyclotraxin B
Catalog No.:BCC6357
CAS No.:1203586-72-4
- DASA-58
Catalog No.:BCC6522
CAS No.:1203494-49-8
- Citroside A
Catalog No.:BCN7294
CAS No.:120330-44-1
- CX-6258
Catalog No.:BCC1504
CAS No.:1202916-90-2
- Dorzolamide
Catalog No.:BCC4287
CAS No.:120279-96-1
- 4-Hydroxysapriparaquinone
Catalog No.:BCN4806
CAS No.:120278-25-3
- Salvinolone
Catalog No.:BCN3215
CAS No.:120278-22-0
- Verlukast
Catalog No.:BCC2035
CAS No.:120443-16-5
- Jionoside A1
Catalog No.:BCN2922
CAS No.:120444-60-2
- (±)-Vesamicol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6737
CAS No.:120447-62-3
- ER 27319 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC5914
CAS No.:1204480-26-1
- Lophanthoidin B
Catalog No.:BCN6091
CAS No.:120462-42-2
- Lophanthoidin E
Catalog No.:BCN6092
CAS No.:120462-45-5
- Lophanthoidin F
Catalog No.:BCN6093
CAS No.:120462-46-6
- Ganoderenic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN2446
CAS No.:120462-47-7
- Ganoderenic acid H
Catalog No.:BCN2447
CAS No.:120462-48-8
- Pinanediol talabostat boronate
Catalog No.:BCC1640
CAS No.:1204669-37-3
- Epacadostat
Catalog No.:BCC6531
CAS No.:1204669-58-8
- SRT3109
Catalog No.:BCC1965
CAS No.:1204707-71-0
Molecular modeling study on the drug resistance mechanism of NS5B polymerase to TMC647055.[Pubmed:26836778]
Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;94(2):147-58.
NS5B polymerase plays an important role in viral replication machinery. TMC647055 (TMC) is a novel and potent non-nucleoside inhibitor of the HCV NS5B polymerase. However, mutations that result in drug resistance to TMC have been reported. In this study, we used molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, binding free energy calculations, and free energy decomposition to investigate the drug resistance mechanism of HCV to TMC resulting from L392I, P495T, P495S, and P495L mutations in NS5B polymerase. From the calculated results we determined that the decrease in the binding affinity between TMC and NS5B(L392I) polymerase is mainly caused by the extra methyl group at the CB atom of Ile. The polarity of the side-chain of residue 495 has no distinct influence on residue 495 binding with TMC, whereas the smaller size of the side-chain of residue 495 causes a substantial decrease in the van der Walls interaction between TMC and residue 495. Moreover, the longer length of the side-chain of residue 495 has a significant effect on the electrostatic interaction between TMC and Arg-503. Finally, we performed the same calculations and detailed analysis on other 3 mutations (L392V, P495V, and P495I). The results further confirmed our conclusions. The computational results not only reveal the drug resistance mechanism between TMC647055 and NS5B polymerase, but also provide valuable information for the rational design of more potent non-nucleoside inhibitors targeting HCV NS5B polymerase.
Efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of simeprevir and TMC647055/ritonavir with or without ribavirin and JNJ-56914845 in HCV genotype 1 infection.[Pubmed:28187751]
BMC Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb 10;17(1):26.
BACKGROUND: A Phase 2a, open-label study (NCT01724086) was conducted to assess the efficacy and safety of a once-daily, 2-direct-acting-antiviral-agent (2-DAA) combination of simeprevir + TMC647055/ritonavir +/- ribavirin and of the 3-DAA combination of simeprevir + TMC647055/ritonavir + JNJ-56914845 in chronic hepatitis C virus genotype (GT)1-infected treatment-naive and prior-relapse patients. METHODS: The study comprised four 12-week treatment panels: Panel 1 (n = 10; GT1a) and Panel 2-Arm 1 (n = 12; GT1b): simeprevir 75 mg once daily + TMC647055 450 mg once daily/ritonavir 30 mg once daily + ribavirin 1000-1200 mg/day; Panel 2-Arm 2 (n = 9; GT1b): simeprevir 75 mg + TMC647055 450 mg/ritonavir 30 mg without ribavirin; Panel 3: simeprevir 75 mg + TMC647055 600 mg/ritonavir 50 mg with (Arm 1: GT1a; n = 7) or without (Arm 2: GT1b; n = 8) ribavirin; Panel 4: simeprevir 75 mg + TMC647055 450 mg/ritonavir 30 mg + JNJ-56914845 30 mg once daily (Arm 1: n = 22; GT1a/GT1b) or 60 mg once daily (Arm 2: n = 22; GT1a/GT1b). Primary endpoint was sustained virologic response 12 weeks after end of treatment (12 weeks of combination treatment; SVR12). RESULTS: In Panel 1 and Panel 2-Arm 1, 5/10 and 6/12 (50%) GT1a/GT1b + ribavirin patients achieved SVR12, versus 3/9 (33%) GT1b without ribavirin patients in Panel 2-Arm 2. In Panel 3-Arm 1 and Panel 3-Arm 2, 6/7 (86%) GT1a + ribavirin and 4/8 (50%) GT1b without ribavirin patients, respectively, achieved SVR12. In Panel 4, 10/14 (71%) and 14/15 (93%) GT1a patients in Arms 1 and 2 achieved SVR12 compared with 8/8 and 7/7 (100%) GT1b patients in each arm, respectively. No deaths, serious adverse events (AEs), Grade 4 AEs or AEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred. CONCLUSIONS: The 2- and 3-DAA combinations were well tolerated. High SVR rates of 93% and 100% in GT1a- and GT1b-infected patients, respectively, were achieved in this study by combining simeprevir with JNJ-56914845 60 mg and TMC647055/ritonavir. TRIAL REGISTRATION: NCT01724086 (date of registration: September 26, 2012).
Discovery and early development of TMC647055, a non-nucleoside inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase.[Pubmed:24144360]
J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 13;57(5):1880-92.
Structure-based macrocyclization of a 6-carboxylic acid indole chemotype has yielded potent and selective finger-loop inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5B polymerase. Lead optimization in conjunction with in vivo evaluation in rats identified several compounds showing (i) nanomolar potency in HCV replicon cells, (ii) limited toxicity and off-target activities, and (iii) encouraging preclinical pharmacokinetic profiles characterized by high liver distribution. This effort culminated in the identification of TMC647055 (10a), a nonzwitterionic 17-membered-ring macrocycle characterized by high affinity, long polymerase residence time, and broad genotypic coverage. In vitro results of the combination of 10a with the HCV protease inhibitor TMC435 (simeprevir) supported an evaluation of this combination in patients with regard to virus suppression and resistance emergence. In a phase 1b trial with HCV genotype 1-infected patients, 10a was considered to be safe and well-tolerated and demonstrated potent antiviral activity, which was further enhanced in a combination study with TMC435.
TMC647055, a potent nonnucleoside hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor with cross-genotypic coverage.[Pubmed:22710121]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Sep;56(9):4676-84.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a major global health burden and is associated with an increased risk of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. There remains an unmet medical need for efficacious and safe direct antivirals with complementary modes of action for combination in treatment regimens to deliver a high cure rate with a short duration of treatment for HCV patients. Here we report the in vitro inhibitory activity, mode of action, binding kinetics, and resistance profile of TMC647055, a novel and potent nonnucleoside inhibitor of the HCV NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. In vitro combination studies with an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor demonstrated potent suppression of HCV RNA replication, confirming the potential for combination of these two classes in the treatment of chronic HCV infection. TMC647055 is a potent nonnucleoside NS5B polymerase inhibitor of HCV replication with a promising in vitro biochemical, kinetic, and virological profile that is currently undergoing clinical evaluation.


