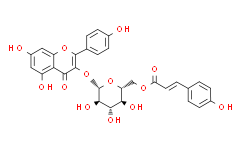
TribulosideCAS# 22153-44-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 22153-44-2 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H26O13 | M.Wt | 594.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Tribuloside Dilution Calculator

Tribuloside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.682 mL | 8.4101 mL | 16.8203 mL | 33.6406 mL | 42.0507 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3364 mL | 1.682 mL | 3.3641 mL | 6.7281 mL | 8.4101 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1682 mL | 0.841 mL | 1.682 mL | 3.3641 mL | 4.2051 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0336 mL | 0.1682 mL | 0.3364 mL | 0.6728 mL | 0.841 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0168 mL | 0.0841 mL | 0.1682 mL | 0.3364 mL | 0.4205 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (25R)-26-O-β-D-Glucopyranosyl-22-hydroxy-5β-furost-3β,26-diol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-galactopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX0820
CAS No.:897386-27-5
- Coreoside B
Catalog No.:BCX0819
CAS No.:1580464-83-0
- Xylohexaose
Catalog No.:BCX0818
CAS No.:49694-21-5
- Hirudonucleodisulfide A
Catalog No.:BCX0817
CAS No.:1072789-37-7
- Xylopentaose
Catalog No.:BCX0816
CAS No.:49694-20-4
- Kuwanon U
Catalog No.:BCX0815
CAS No.:123702-95-4
- Nepetalacton
Catalog No.:BCX0814
CAS No.:21651-62-7
- Xylotetraose
Catalog No.:BCX0813
CAS No.:22416-58-6
- 16-Hydroxyhexadecanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0812
CAS No.:506-13-8
- Monascorubrin
Catalog No.:BCX0811
CAS No.:13283-90-4
- Acetyl Dopamine Dimer I
Catalog No.:BCX0810
CAS No.:315188-82-0
- guan-fu base I
Catalog No.:BCX0809
CAS No.:110225-59-7
- 6''- methyl glycyrrhizinate
Catalog No.:BCX0822
CAS No.:1186016-30-7
- Picfeltarraegenin I
Catalog No.:BCX0823
CAS No.:82145-63-9
- Licorice glycoside C2
Catalog No.:BCX0824
CAS No.:202657-55-4
- Heptasaccharide
Catalog No.:BCX0825
CAS No.:121591-98-8
- 6',6''- dimethyl glycyrrhizinate
Catalog No.:BCX0826
CAS No.:114006-81-4
- Platycoside F
Catalog No.:BCX0827
CAS No.:314756-03-1
- Quercetin 3-O-β-D-Glucuronide 6''-Methyl Ester
Catalog No.:BCX0828
CAS No.:79543-28-5
- 4′′,5′′-dehydroisopsoralidin
Catalog No.:BCX0829
CAS No.:65639-51-2
- Paeonoside
Catalog No.:BCX0830
CAS No.:20309-70-0
- Artemisitene
Catalog No.:BCX0831
CAS No.:101020-89-7
- 6''-O-Acetyldaidzin
Catalog No.:BCX0832
CAS No.:71385-83-6
- Aquilarone B
Catalog No.:BCX0833
CAS No.:1404479-45-3
Tribuloside acts on the PDE/cAMP/PKA pathway to enhance melanogenesis, melanocyte dendricity and melanosome transport.[Pubmed:38158096]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 6;323:117673.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Tribuloside, a natural flavonoid extracted from Chinese medicine Tribulus terrestris L., has shown potent efficacy in treating various diseases. In China, the fruits of Tribulus terrestris L. have long been utilized for relieving headache, dizziness, itchiness, and vitiligo. Water-based extract derived from Tribulus terrestris L. can enhance melanogenesis in mouse hair follicle melanocytes by elevating the expression of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH) and melanocortin-1 recepter (MC-1R). Nevertheless, there is a lack of information regarding the impact of Tribuloside on pigmentation in both laboratory settings and living organisms. AIM OF THE STUDY: The present research aimed to examine the impact of Tribuloside on pigmentation, and delve into the underlying mechanism. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Following the administration of Tribuloside in human epidermal melanocytes (HEMCs), we utilized microplate reader, Masson-Fontana ammoniacal silver stain, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to measure melanin contents, dendrite lengths, melanosome counts; L-DOPA oxidation assay to indicate tyrosinase activity, Western blotting to evaluate the expression of melanogenic and associated phosphodiesterase (PDE)/cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)/cyclic-AMP dependent protein kinase A (PKA) pathway proteins. A PDE-Glo assay to verify the inhibitory effect of Tribuloside on PDE was also conducted. Additionally, we examined the impact of Tribuloside on the pigmentation in both zebrafish model and human skin samples. RESULTS: Tribuloside had a notable impact on the production of melanin in melanocytes, zebrafish, and human skin samples. These functions might be attributed to the inhibitory effect of Tribuloside on PDE, which could increase the intracellular level of cAMP to stimulate the phosphorylation of cAMP-response element binding (CREB). Once activated, it induced microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) expression and increased the expression of tyrosinase, Rab27a and cell division cycle protein 42 (Cdc42), ultimately facilitating melanogenesis, melanocyte dendricity, and melanin transport. CONCLUSION: Tribuloside acts on the PDE/cAMP/PKA pathway to enhance melanogenesis, melanocyte dendricity, and melanosome transport; meanwhile, Tribuloside does not have any toxic effects on cells and may be introduced into clinical prescriptions to promote pigmentation.
Enzyme immobilized on magnetic fluorescent bifunctional nanoparticles for alpha-glucosidase inhibitors virtual screening from Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb extracts accompanied with molecular modeling.[Pubmed:37847969]
J Chromatogr A. 2023 Nov 22;1711:464433.
Agrimonia pilosa Ledeb (APL) is a significant source of inhibitors for alpha-glucosidase, which is an essential target enzyme for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, cancer and acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ligand fishing is a suitable approach for the highly selective screening of bioactive substances in complex mixtures. Yet it is unable to conduct biomedical imaging screening, which is crucial for real-time identification. In this case, a bioanalytical platform combining magnetic fluorescent ligand fishing and in-situ imaging technique was established for the screening and identification of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs) from APL crude extract, utilizing alpha-glucosidase coated CuInS(2)/ZnS-Fe(3)O(4)@SiO(2) (AG-CIZSFS) nanocomposites as extracting material and fluorescent tracer. The AG-CIZSFS nanocomposites prepared through solvothermal and crosslinking methods displayed fast magnetic separation, excellent fluorescence performance and high enzyme activity. The tolerance of immobilized enzyme to temperature and pH was stronger than that of free enzyme. Prior to proof-of-concept with APL crude extract, a number essential parameters (glutaraldehyde concentration, immobilized time, enzyme amount, reaction solution pH, incubation temperature, incubation time, percentage of methanol in eluen, elution times and eluent volume) were optimized using an artificial test mixture. The fished ligands were identified by UPLC-MS/MS and their biological activities were preliminarily evaluated by real-time cellular morphological imaging of human colon carcinoma (HCT-116) cells based on confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Their alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activities were further verified and studied by classical pNPG method and molecular docking. The isolated compounds exhibited significant alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activities with a IC(50) value of 11.57 microg.mL(-1). Six potential AGIs including Tribuloside, ivorengenin A, tormentic acid, 1beta, 2beta, 3beta, 19alpha-Tetra hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid, corosolic acid and pomolic acid were ultimately screened out and identified from APL crude extracts. The proposed approach, which combined highly specific screening with in-situ visual imaging, provided a powerful platform for discovering bioactive components from multi-component and multi-target traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).
Integrated LC-MS/MS and network pharmacology approach for predictingactive ingredients and pharmacological mechanisms of Tribulus terrestris L. against cardiac diseases.[Pubmed:37042962]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023;41(21):11930-11945.
Tribulus terrestris L. (Gokshura) is a medicinal herb used for treating cardiac diseases and several other diseases. However, the active ingredients and the possible mechanism of action for treating cardiac diseases remain unclear. Hence, the study was designed to identify the active ingredients and to explore the potential mechanism of action of Tribulus terrestris L. for treating cardiac diseases by an integrated approach of metabolomics and network pharmacology. We performed HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS analysis to identify putative compounds and network pharmacology approach for predictive key targets and pathways. Using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation, we identified the active ingredients in Tribulus terrestris L. that can act as putative lead compounds to treat cardiac diseases. A total of 55 putative compounds were identified using methanolic extract of Tribulus terrestris L. using HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS analysis. Network pharmacology analysis predicted 32 human protein targets from 25 secondary metabolites, which have shown direct interaction with cardiac diseases. Based on the degrees of interaction, the hub targets such as TACR1, F2, F2R, ADRA1B, CHRM5, ADRA1A, ADRA1D, HTR2B, and AVPR1A were identified. In silico molecular docking and simulation resulted in the identification of active ingredients such as Kaempferol 3-rutinoside 7-glucuronide, Keioside, rutin, moupinamide, aurantiamide, quercetin-3-o-alpha-rhamnoside, Tribuloside, and 3'',6''- Di-O-p-coumaroyltrifolin against hub protein targets. Hence, these compounds could be potential lead compounds for treating cardiac diseases. A further assessment of its efficacy can be made based on in vivo and in vitro studies for better understanding and strong assertion.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Determination of Therapeutic and Safety Effects of Zygophyllum coccineum Extract in Induced Inflammation in Rats.[Pubmed:35898689]
Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 18;2022:7513155.
BACKGROUND: Z. coccineum is a facultative plant with many medicinal applications. This study examined the anti-inflammatory activity of Zygophyllum coccineum (Z. coccineum) in an arthritis animal model. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Seventy-Six Wistar Albino rats of either sex randomly divided into six groups (12/each). The inflammation model was done using Complete Freund's Adjuvant in albino rats. The anti-inflammatory activities of the extract were estimated at different dose levels (15.6, 31, and 60 mg/kg) as well as upon using methotrexate (MTX) as a standard drug (0.3 mg/kg). Paw volume and arthritis index scores have been tested in all examined animals' treatments. Histological examination of joints was also performed. Flow cytometric studies were done to isolated osteoclasts. Cytokines assay as well as biochemical testing was done in the examined samples. Results. In vitro studies reported an IC(50) of 15.6 mug/ml for Z. coccineum extract in lipoxygenase inhibition assay (L.O.X.). Moreover, it could be noticed that isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, Tribuloside, and 7-acetoxy-4-methyl coumarin were the most common compounds in Z. coccineum extract separated using L.C.-ESI-TOF-M.S. (liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization ion-trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry). Microscopic examinations of synovial tissue and hind limb muscles revealed the effect of different doses of Z. coccineum extract on restoring chondrocytes and muscles structures. Osteoclast size and apoptotic rate examinations revealed the protective effect of Z. coccineum extract on osteoclast. The results upon induction of animals and upon treatment using of MTX significantly increased apoptotic rate of osteoclast compared to control, while using of 15.6 mug/ml. for Z. coccineum extract lead to recover regular apoptotic rate demonstrating the protective effect of the extract. Z. coccineum extract regulated the secretion of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Biochemical tests indicated the safety of Z. coccineum extract on kidney and liver functions. Conclusion. Z. coccineum extract has efficient and safe anti-inflammatory potential in an induced rat model.
Searching and designing potential inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro from natural sources using atomistic and deep-learning calculations.[Pubmed:35493244]
RSC Adv. 2021 Nov 29;11(61):38495-38504.
The spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) worldwide has caused the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. A hundred million people were infected, resulting in several millions of death worldwide. In order to prevent viral replication, scientists have been aiming to prevent the biological activity of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (3CL pro or Mpro). In this work, we demonstrate that using a reasonable combination of deep-learning calculations and atomistic simulations could lead to a new approach for developing SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitors. Initially, the binding affinities of the natural compounds to SARS-CoV-2 Mpro were estimated via atomistic simulations. The compound tomatine, thevetine, and Tribuloside could bind to SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with nanomolar/high-nanomolar affinities. Secondly, the deep-learning (DL) calculations were performed to chemically alter the top-lead natural compounds to improve ligand-binding affinity. The obtained results were then validated by free energy calculations using atomistic simulations. The outcome of the research will probably boost COVID-19 therapy.
Rescuing the Host Immune System by Targeting the Immune Evasion Complex ORF8-IRF3 in SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Natural Products Using Molecular Modeling Approaches.[Pubmed:35010372]
Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 23;19(1):112.
The perennial emergence of SARS-CoV-2 and its new variants causing upper respiratory complexities since December 2019 has aggravated the pandemic situation around the world. SARS-CoV-2 encodes several proteins among which ORF8 is a novel factor that is unique to SARS-CoV-2 only and is reported to help the virus in disease severity and immune evasion. ORF8-IRF3 complex induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, thus helps in the evasion of immune response. Consequently, targeting the ORF8-IRF3 complex is considered as a prime target for the discovery of novel drugs against SARS-CoV-2. In this regard, computational methods are of great interest to fast track the identification and development of novel drugs. Virtual screening of South African Natural Compounds Database (SANCDB), followed by docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation analysis, were performed to determine novel natural compounds. Computational molecular search and rescoring of the SANCDB database followed by induced-fit docking (IFD) protocol identified Quercetin 3-O-(6''-galloyl)-beta-D-galactopyranoside (SANC00850), Tribuloside (SANC01050), and Rutin (SANC00867) are the best scoring compounds. Structural-dynamic properties assessment revealed that these three compounds have stable dynamics, compactness, and a higher number of hydrogen bonds. For validation, we used MM/GBSA, in silico bioactivity estimation and dissociation constant (K(D)) approaches, which revealed that these compounds are the more potent inhibitors of the ORF8-IRF3 complex and would rescue the host immune system potentially. These compounds need further in vitro and in vivo validations to be used as therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2 to rescue the host immune system during COVID-19 infection.
The interaction of the bioflavonoids with five SARS-CoV-2 proteins targets: An in silico study.[Pubmed:34020130]
Comput Biol Med. 2021 Jul;134:104464.
Flavonoids have been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, antibacterial and antiviral efficacy. Therefore, in this study, we choose 85 flavonoid compounds and screened them to determine their in-silico interaction with protein targets crucial for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The five important targets chosen were the main protease (Mpro), Spike receptor binding domain (Spike-RBD), RNA - dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp or Nsp12), non-structural protein 15 (Nsp15) of SARS-CoV-2 and the host angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) spike-RBD binding domain. The compounds were initially docked at the selected sites and further evaluated for binding free energy, using the molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface area (MMGBSA) method. The three compounds with the best binding scores were subjected to molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The compound, Tribuloside, had a high average binding free energy of -86.99 and -88.98 kcal/mol for Mpro and Nsp12, respectively. The compound, legalon, had an average binding free energy of -59.02 kcal/mol at the ACE2 spike-RBD binding site. The compound, isosilybin, had an average free binding energy of -63.06 kcal/mol for the Spike-RBD protein. Overall, our results suggest that Tribuloside, legalon and isosilybin should be evaluated in future studies to determine their efficacy to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infectivity.
Isolation, structural elucidation and cytotoxicity evaluation of a new pentahydroxy-pimarane diterpenoid along with other chemical constituents from Aerva lanata.[Pubmed:25348942]
Nat Prod Res. 2015 Feb;29(3):253-61.
Aervalanata possesses various useful medicinal and pharmaceutical activities. Phytochemical investigation of the plant has now led to the isolation of a new 2alpha,3alpha,15,16,19-pentahydroxy pimar-8(14)-ene diterpenoid (1) together with 12 other known compounds identified as beta-sitosterol (2), beta-sitosterol-3-O-beta-D-glucoside (3), canthin-6-one (4), 10-hydroxycanthin-6-one (aervine, 5), 10-methoxycanthin-6-one (methylaervine, 6), beta-carboline-1-propionic acid (7), 1-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(2S,3R,8E)-2-[(2'R)-2-hydroxylpalmitoylamino]-8-octadecene-1,3-diol (8), 1-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-(2S,3S,4R,8Z)-2-[(2'R)-2'-hydroxytetracosanoylamino]-8(Z)-octadene-1,3,4-triol (9), (2S,3S,4R,10E)-2-[(2'R)-2'-hydroxytetracosanoylamino]-10-octadecene-1,3,4-triol (10), 6'-O-(4''-hydroxy-trans-cinnamoyl)-kaempferol-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (Tribuloside, 11), 3-cinnamoylTribuloside (12) and sulfonoquinovosyldiacylglyceride (13). Among these, six compounds (8-13) are reported for the first time from this plant. Cytotoxicity evaluation of the compounds against five cancer cell lines (CHO, HepG2, HeLa, A-431 and MCF-7) shows promising IC50 values for compounds 4, 6 and 12.
A new cinnamoylglycoflavonoid, antimycobacterial and antioxidant constituents from Heritiera littoralis leaf extracts.[Pubmed:24443810]
Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(6):351-8.
A new cinnamolyglycoflavonoid 3-cinnamoylTribuloside (1), its precursor Tribuloside and two known flavonoid glycosides afzelin and astilbin were isolated from Heritiera littoralis Dryand (Sterculiaceae) ethanolic leaf extract. The dichloromethane leaf extract afforded two known pentacyclic triterpenoids, 3beta-taraxerol and friedelin. Extracts and compounds isolated therefrom, with the exception of 3beta-taraxerol, exhibited antimycobacterial activity against the non-pathogenic Mycobacterium species Mycobacterium madagascariense and Mycobacterium indicus pranii, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) 5.0 mg/mL for the crude extracts and MICs in the range of 1.6-0.8 mg/mL for the pure compounds. The extracts together with 3-cinnamoylTribuloside (1), Tribuloside and astilbin exhibited 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity. The compounds that showed dual activities could be further evaluated under clinical settings for co-administration with standard anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Simultaneous determination of seven flavonoids in Potentilla multifida by HPLC.[Pubmed:17504571]
J Chromatogr Sci. 2007 Apr;45(4):216-9.
A reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic method is described for the simultaneous determination of seven flavonoids in Potentilla multifida: hyperin, quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, luteolin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide, apigenin-7-O-beta-D-glucuronide, quercetin, Tribuloside, and apigenin. The method involves the use of a Hypersil octadecylsilyl silica (ODS) analytical column (125A, 5 microm, 4.6 x 250 mm) at 25 degrees C with the mixture of acetonitrile and aqueous H(3)PO(4) as the mobile phase and detection at 254 nm. The recovery of the method is 95.4-104.8%, and linearity (r > 0.9998) is obtained for all the flavonoids. The results indicate that the flavonoid content of P. multifida varied significantly from locality to locality.


