1-O-AcetylbritannilactoneCAS# 33627-41-7 |
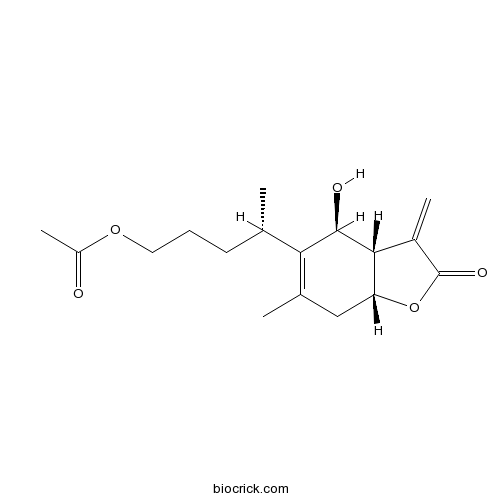
- 1-O-Acetyl britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCN2365
CAS No.:681457-46-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 33627-41-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 75528891 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H24O5 | M.Wt | 308.36 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Inulicin | ||
| Solubility | Ethanol : 50 mg/mL (162.14 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | [(4S)-4-[(3aS,4S,7aR)-4-hydroxy-6-methyl-3-methylidene-2-oxo-3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl]pentyl] acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(C2C(C1)OC(=O)C2=C)O)C(C)CCCOC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QKUFZFLZBUSEHN-CZLJMHDISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H24O5/c1-9(6-5-7-21-12(4)18)14-10(2)8-13-15(16(14)19)11(3)17(20)22-13/h9,13,15-16,19H,3,5-8H2,1-2,4H3/t9-,13+,15+,16+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone has anticancer activity, it combined with gemcitabine elicits a potent apoptosis of lung cancer cell and hence it has the potential to be developed as a chemotherapeutic agent. 2. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone may serve as a novel therapeutic intervention for various cardiovascular diseases, including chronic ischemia, by regulating VEGF signaling and modulating angiogenesis. 3. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone suppresses angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth possibly via regulating the VEGFR-Src-FAK signaling. 4. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone exhibits anti-melanogenic activity by suppression of tyrosinase expression via ERK and Akt signaling, it may act as potent natural skin-lightening agents. 5. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone is a potent inhibitor of LPS-stimulated VSMC inflammatory responses through blockade of NF-kappaB activity and inhibition of inflammatory gene COX-2 expression. |
| Targets | VEGFR | Src | FAK | ERK | Akt | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | p38MAPK | cAMP | p65 | NF-kB | Tyrosinase | COX | PGE |

1-O-Acetylbritannilactone Dilution Calculator

1-O-Acetylbritannilactone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.243 mL | 16.2148 mL | 32.4296 mL | 64.8593 mL | 81.0741 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6486 mL | 3.243 mL | 6.4859 mL | 12.9719 mL | 16.2148 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3243 mL | 1.6215 mL | 3.243 mL | 6.4859 mL | 8.1074 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0649 mL | 0.3243 mL | 0.6486 mL | 1.2972 mL | 1.6215 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0324 mL | 0.1621 mL | 0.3243 mL | 0.6486 mL | 0.8107 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
1-O-Acetylbritannilactone is an active compound isolated from Inula Britannica L. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone inhibits VEGF-mediated activation of Src and FAK. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone inhibits LPS-induced PGE2 production and COX-2 expression, and NF-κB activation and translocation.
In Vitro:1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (ABL) inhibits angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth through regulating VEGF-Src-FAK signaling. 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone dose-dependently inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced proliferation, migration, and capillary structure formation of cultured human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs). Treatment of A549 NSCLC cells with 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone results in cell growth inhibition and Src-FAK in-activation. The potential effect of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone is tested ton Src and FAK phosphorylation in A549 lung cancer cells. Significant high levels of Src and FAK phosphorylations are noticed a in A549 cells, which are both inhibited by treatment of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (5 μM and 10 μM). Src and FAK are both important for cancer cell proliferation. Thus, A549 cell growth, tested by MTT assay and clonogenicity assay,is remarkably inhibited by corresponding 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone treatment. The anti-A549 cell growth activity of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone is again dose-dependent[1].1-O-acetylbritannilactone (ABL) isolated from Inula britannica-F., inhibits inflammatory responses in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (5, 10, 20 μM) has several concentration dependent effects, including inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced PGE2 production and COX-2 expression, and blockade of NF-κB activation and translocation. In addition, 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone directly inhibits the binding of active NF-κB to specific DNA cis-element[2].
In Vivo:Administration of a single dose of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (12 mg/kg/day) remarkably suppresses growth of A549 xenografts in nude mice. In vivo microvessels formation and Src activation are also significantly inhibited in 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone -treated xenograft tumors. To investigate the potential activity of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone in vivo, a nude mice xenograft model is applied. A single dose of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (12 mg/kg/day, i.p.) dramatically inhibits the growth of A549 xenografts in nude mice. Further, the weights of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone-treated tumors are remarkably lighter than that of vehicle-treated tumors. Notably, 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone administration does not affect mice body weights[1].
References:
[1]. Zhengfu H, et al. 1-o-acetylbritannilactone (ABL) inhibits angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth through regulating VEGF-Src-FAK signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 21;464(2):422-7.
[2]. Liu YP, et al. Acetylbritannilactone suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular smooth muscle cell inflammatory response. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Dec 22;577(1-3):28-34.
- Britannin
Catalog No.:BCN2366
CAS No.:33627-28-0
- Desoxyrhapontigenin
Catalog No.:BCN6479
CAS No.:33626-08-3
- Britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCN3509
CAS No.:33620-72-3
- Ispinesib (SB-715992)
Catalog No.:BCC2509
CAS No.:336113-53-2
- Myricanol
Catalog No.:BCN5258
CAS No.:33606-81-4
- Polpunonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7136
CAS No.:33600-93-0
- (-)-Bilobalide
Catalog No.:BCN1279
CAS No.:33570-04-6
- Cyclo(Phe-Leu)
Catalog No.:BCN2418
CAS No.:3354-31-2
- Raddeanoside 20
Catalog No.:BCN2796
CAS No.:335354-79-5
- iMAC2
Catalog No.:BCC2396
CAS No.:335166-36-4
- Bax channel blocker
Catalog No.:BCC2392
CAS No.:335165-68-9
- 6'-Iodoresiniferatoxin
Catalog No.:BCC7114
CAS No.:335151-55-8
- (S)-(+)-Ketamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7930
CAS No.:33643-47-9
- H-Thr-Obzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2674
CAS No.:33645-24-8
- Secnidazole
Catalog No.:BCC4971
CAS No.:3366-95-8
- Hypophyllanthin
Catalog No.:BCN5259
CAS No.:33676-00-5
- 19,20-(E)-Vallesamine
Catalog No.:BCN5260
CAS No.:3368-87-4
- Pachypodol
Catalog No.:BCN5261
CAS No.:33708-72-4
- (-)-Gallocatechin
Catalog No.:BCN5927
CAS No.:3371-27-5
- Voacamine
Catalog No.:BCN8433
CAS No.:3371-85-5
- 4,4'-Di-O-methylellagic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3709
CAS No.:3374-77-4
- Cannabivarin
Catalog No.:BCN7587
CAS No.:33745-21-0
- Abieta-8,11,13-triene-7,15,18-triol
Catalog No.:BCN5262
CAS No.:337527-10-3
- Androstanolone heptanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8827
CAS No.:33776-88-4
Acetylbritannilactone suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular smooth muscle cell inflammatory response.[Pubmed:17915214]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Dec 22;577(1-3):28-34.
To investigate the mechanism of action by which a new anti-inflammatory active compound, 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (ABL) isolated from Inula britannica-F., inhibits inflammatory responses in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Enzyme immunoassay was used to measure the levels of prostandin E(2) (PGE(2)) production. Immunocytochemistry staining and Western blot analysis were performed to detect the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) p65 and the expression of IkappaB-alpha, pIkappaB-alpha and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) were used to detect DNA-binding activity of NF-kappaB in VSMCs. ABL (5, 10, 20 micrommol/l) had several concentration-dependent effects, including inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced PGE(2) production and COX-2 expression, and blockade of NF-kappaB activation and translocation. These effects were owing to reductions in IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation and degradation induced by LPS. In addition, ABL directly inhibited the binding of active NF-kappaB to specific DNA cis-element. These results indicate that ABL is a potent inhibitor of LPS-stimulated VSMC inflammatory responses through blockade of NF-kappaB activity and inhibition of inflammatory gene COX-2 expression.
The combination use of 1-O-acetylbritannilactone (ABL) and gemcitabine inhibits cell growth and induces cell apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells.[Pubmed:27209702]
Pharmazie. 2016 Apr;71(4):213-7.
1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (ABL), a natural chemical component obtained from Chinese traditional medicine, Inula britannica, has been demonstrated to have anticancer activities. In the present study, we evaluated the anti-proliferative and the pro-apoptotic abilities of ABL alone or in combination with gemcitabine in human NSCLC cell line. A549 cells were treated, in vitro, with ABL, gemcitabine, and the combination of ABL and gemcitabine for 72 h. Our results showed ABL and gemcitabine inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis of A549 cells. These effects after the combination of ABL and gemcitabine were superior to those of each alone. Furthermore, signal transduction analysis revealed NF-kappaB expression was significantly decreased by ABL and the combination treatment. IkappaBalpha and Bax levels were up regulated whereas Bcl-2 was substantially downregulated after all treatments. Our findings suggest that ABL combined with gemcitabine elicits a potent apoptosis of lung cancer cell and hence ABL has the potential to be developed as a chemotherapeutic agent.
Hypo-pigmenting effect of sesquiterpenes from Inula britannica in B16 melanoma cells.[Pubmed:24346861]
Arch Pharm Res. 2014 May;37(5):567-74.
During the course of screens to identify anti-melanogenic agents from natural resources, we found that the methanol extract of the dried flower of Inula britannica L. inhibited melanin synthesis in cultured melanoma cells stimulated with 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX). A bioassay-guided isolation of the chloroform fraction of the I. britannica using an in vitro melanogenesis inhibition assay led to the isolation of sesquiterpenes, 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (1), britannilactone (2) and neobritannilactone B (3). Compounds 1 and 2 significantly reduced melanin production in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 values of 13.3 and 15.5 muM, respectively, whereas compound 3 was found to be cytotoxic. Compound 1 also inhibited the tyrosinase activity only in cell based-systems. Western blot analysis indicated that compound 1 inhibited melanogenesis by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt signaling and also inhibiting cAMP related binding protein, which regulates its downstream pathway, including tyrosinase, tyrosinase related protein-1 and TRP-2. These results demonstrated that compound 1, a major sesquiterpene from the flowers of I. britannica, exhibited anti-melanogenic activity by suppression of tyrosinase expression via ERK and Akt signaling. Taken together, our results suggest that these compounds may act as potent natural skin-lightening agents.
1-o-acetylbritannilactone (ABL) inhibits angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth through regulating VEGF-Src-FAK signaling.[Pubmed:26102035]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 21;464(2):422-7.
The search for safe, effective and affordable therapeutics against non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and other lung cancers is important. Here we explored the potential effect of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (ABL), a novel extract from Inula britannica-F, on angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth. We demonstrated that ABL dose-dependently inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced proliferation, migration, and capillary structure formation of cultured human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs). In vivo, ABL administration suppressed VEGF-induced new vasculature formation in Matrigel plugs. For the mechanism investigations, we found that ABL largely inhibited VEGF-mediated activation of Src kinase and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in HUVECs. Furthermore, treatment of A549 NSCLC cells with ABL resulted in cell growth inhibition and Src-FAK in-activation. Significantly, administration of a single dose of ABL (12 mg/kg/day) remarkably suppressed growth of A549 xenografts in nude mice. In vivo microvessels formation and Src activation were also significantly inhibited in ABL-treated xenograft tumors. Taken together, our findings suggest that ABL suppresses angiogenesis and lung cancer cell growth possibly via regulating the VEGFR-Src-FAK signaling.
Acetylbritannilactone Modulates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling and Regulates Angiogenesis in Endothelial Cells.[Pubmed:26863518]
PLoS One. 2016 Feb 10;11(2):e0148968.
The present study was conducted to determine the effects of 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (ABL), a compound extracted from Inula britannica L., on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling and angiogenesis in endothelial cells (ECs). We showed that ABL promotes VEGF-induced cell proliferation, growth, migration, and tube formation in cultured human ECs. Furthermore, the modulatory effect of ABL on VEGF-induced Akt, MAPK p42/44, and p38 phosphorylation, as well as on upstream VEGFR-2 phosphorylation, were associated with VEGF-dependent Matrigel angiogenesis in vivo. In addition, animals treated with ABL (26 mg/kg/day) recovered blood flow significantly earlier than control animals, suggesting that ABL affects ischemia-mediated angiogenesis and arteriogenesis in vivo. Finally, we demonstrated that ABL strongly reduced the levels of VEGFR-2 on the cell surface, enhanced VEGFR-2 endocytosis, which consistent with inhibited VE-cadherin, a negative regulator of VEGF signaling associated with VEGFR-2 complex formation, but did not alter VE-cadherin or VEGFR-2 expression in ECs. Our results suggest that ABL may serve as a novel therapeutic intervention for various cardiovascular diseases, including chronic ischemia, by regulating VEGF signaling and modulating angiogenesis.


