AMT hydrochloridePotent, selective iNOS inhibitor CAS# 21463-31-0 |
- Arctiin
Catalog No.:BCN1090
CAS No.:20362-31-6
- Daunorubicin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5083
CAS No.:23541-50-6
- Etoposide
Catalog No.:BCC1151
CAS No.:33419-42-0
- Flumequine
Catalog No.:BCC5090
CAS No.:42835-25-6
- Amonafide
Catalog No.:BCC1249
CAS No.:69408-81-7
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 21463-31-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6603722 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C5H10N2S | M.Wt | 130.2 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in water | ||
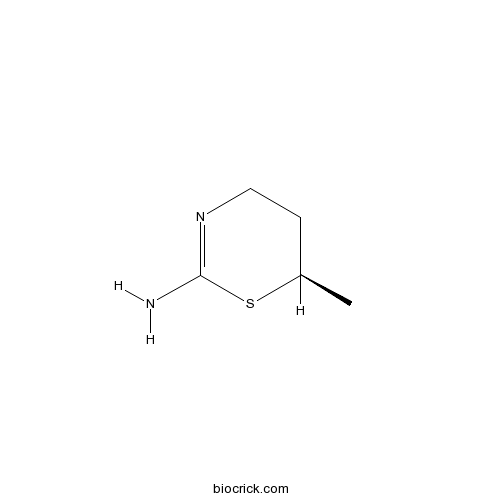
| Chemical Name | (6R)-6-methyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-1,3-thiazin-2-amine | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCN=C(S1)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BATVOUKHGLKDGQ-SCSAIBSYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H10N2S/c1-4-2-3-7-5(6)8-4/h4H,2-3H2,1H3,(H2,6,7)/t4-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective and reversible inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 3.6 nM; approximately 30 and 40 times selective over nNOS and eNOS respectively). |

AMT hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

AMT hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.6805 mL | 38.4025 mL | 76.8049 mL | 153.6098 mL | 192.0123 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.5361 mL | 7.6805 mL | 15.361 mL | 30.722 mL | 38.4025 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.768 mL | 3.8402 mL | 7.6805 mL | 15.361 mL | 19.2012 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1536 mL | 0.768 mL | 1.5361 mL | 3.0722 mL | 3.8402 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0768 mL | 0.384 mL | 0.768 mL | 1.5361 mL | 1.9201 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (+)-Syringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7496
CAS No.:21453-69-0
- 1400W dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7057
CAS No.:214358-33-5
- 16alpha-Hydroxybauerenol
Catalog No.:BCN7724
CAS No.:214351-30-1
- Rosamultic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3516
CAS No.:214285-76-4
- Demethylsuberosin
Catalog No.:BCN6508
CAS No.:21422-04-8
- 5,7-dimethoxy-2,2-dimethylchromene
Catalog No.:BCN8030
CAS No.:21421-66-9
- N-Benzylphthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC9096
CAS No.:2142-01-0
- Picrotin
Catalog No.:BCC8233
CAS No.:21416-53-5
- 1-Decarboxy-3-oxo-ceanothic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4924
CAS No.:214150-74-0
- 26-Deoxycimicifugoside
Catalog No.:BCN2906
CAS No.:214146-75-5
- Glucoraphanin
Catalog No.:BCN3817
CAS No.:21414-41-5
- Magnoflorine
Catalog No.:BCN4923
CAS No.:2141-09-5
- 2-Deacetyltaxachitriene A
Catalog No.:BCN7415
CAS No.:214769-96-7
- H-Arg(NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2864
CAS No.:2149-70-4
- Agrimonolide
Catalog No.:BCN4925
CAS No.:21499-24-1
- Bruceine D
Catalog No.:BCN2894
CAS No.:21499-66-1
- 7,3',4'-Trihydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4674
CAS No.:2150-11-0
- Protocatechuic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3542
CAS No.:2150-43-8
- Methyl 2,6-dihydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN3563
CAS No.:2150-45-0
- BMS 493
Catalog No.:BCC7697
CAS No.:215030-90-3
- Pemoline
Catalog No.:BCC5967
CAS No.:2152-34-3
- Betamethasone Valerate
Catalog No.:BCC3736
CAS No.:2152-44-5
- BMS 753
Catalog No.:BCC6031
CAS No.:215307-86-1
- Senampeline F
Catalog No.:BCN7804
CAS No.:71075-43-9
The nanocrystalline coordination polymer of AMT-Ag for an effective detection of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride in pharmaceutical formulation and biological fluid.[Pubmed:27236138]
Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Nov 15;85:529-535.
The present report highlights a cost effective and portable AMT-Ag nanocrystalline coordination polymer (NCCP) based electrochemical sensor for an efficient sensing of biologically active drug molecule ciprofloxacin hydrochloride (CFX). The AMT-Ag NCCP, is synthesized using an easily accessible organic ligand 2-amino-5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole (AMT) with silver nitrate. In the infinite polymer array of AMT-Ag, silver (I) centers are bridged by tecton AMT through the exocyclic thiol and amino linkage. A successful ultratrace detection of CFX has been achieved due to the prominent electron channeling through the pores of polymeric nano-crystallites. The efficient charge transfer arises at the interface of electrolyte and AMT-Ag nano-crystals anchored electrode through hydrophobic interaction and pi-pi electron coupling. The voltammogram reveals the critical redox features of CFX and provides a clear representation about the steps involved in the AMT-Ag assisted oxidation of CFX. This specific signature further applied in the voltammetric assay of CFX in pharmaceutical formulation (eye drops) and biological fluid (urine) by a significantly high sensitivity (0.002microA/microM and 0.007microA/microM) and detection limit (22nM and 60nM) respectively without any interference. Therefore, the developed AMT-Ag NCCP could serve as a highly valuable platform for the fabrication of high-performance electrochemical sensors for the detection of biologically important drug molecules.
Nitric oxide signaling in stretch-induced apoptosis of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.[Pubmed:16877524]
FASEB J. 2006 Sep;20(11):1883-5.
Pressure overload associated with hypertension is an important pathological factor leading to heart remodeling and ultimately heart failure partially due to cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Here we show that endogenous NO signaling plays a critical role in mechanical stretch-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Mechanical stretch induced elevated expression of both eNOS and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and increased synthesis of NO. A sustained increase in iNOS expression was also found in hearts of hypertensive rats in vivo. Blockade of NO signaling by inhibitors of NOS (L-NAME and AMT) or downstream guanylyl cyclase (ODQ) strongly inhibited stretch-induced apoptosis, mitochondria depolarization, and cytochrome c release, suggesting that NO is required in stretch-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. The expression of iNOS, but not eNOS, was blocked by L-NAME and ODQ, indicating that the iNOS induction is NO dependent. The initial elevation of NO is likely due to Ca(2+)-dependent activation of eNOS because elimination of intracellular calcium by EGTA-AM inhibited both iNOS induction and NO elevation. Other calcium signaling inhibitors (nifedipine, ryanodine, thapsigargin, and ionic gadolinium) also attenuated the initial NO elevation. These data indicate that mechanical signals initiate Ca(2+)-dependent NO synthesis, which is further amplified by activation of NO-induced iNOS expression, to regulate cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Inhibition of sarcoplasmic reticular function by chronic interleukin-6 exposure via iNOS in adult ventricular myocytes.[Pubmed:15845578]
J Physiol. 2005 Jul 15;566(Pt 2):327-40.
Interleukin (IL)-6 has been shown to decrease cardiac contractility via a nitric oxide synthase (NOS)-dependent pathway during acute exposure. We previously reported that IL-6 decreases contractility and increases inducible NOS (iNOS) in adult rat ventricular myocytes (ARVM) after 2 h exposure. The goal of this study was to investigate the cellular mechanism underlying this chronic IL-6-induced negative inotropy and the role of iNOS. Pretreatment for 2 h with 10 ng ml-1 IL-6 decreased the kinetics of cell shortening (CS) and contractile responsiveness to Ca2+o ([Ca2+]o from(0) to 2 mM) in ARVM. We first examined whether IL-6 reduced Ca2+ influx via L-type Ca2+ -channel current (ICa,L). Whole-cell ICa,L in ARVM was measured under conditions similar to those used for CS measurements, and it was found to be unaltered by IL-6. The sarcoplasmic reticular (SR) function was then assessed by examining postrest potentiation (PRP) and caffeine responsiveness of CS. Results showed that treatment with IL-6 for 2 h significantly decreased PRP, which was concomitant with a decrease in the phosphorylation of phospholamban. Following removal of IL-6, PRP and responsiveness to 10 mM caffeine were also reduced. Meanwhile, the IL-6-induced increase in nitric oxide (NO) production after 2 h (but not 1 h) was abolished by NG-monomethyl-l-arginine (l-NMMA) and 2-amino-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-4H-1,3-thiazine (AMT; a selective inhibitor of iNOS). Furthermore, IL-6-elicited suppressions of PRP and responsiveness to caffeine and Ca2+o were abolished by L-NMMA and AMT. Thus, these results suggest that activation of iNOS mediates IL-6-induced inhibition of SR function in ARVM during chronic exposure.
Novel potent and selective inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase.[Pubmed:7536889]
Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Apr;47(4):831-4.
We have identified two novel potent and selective inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase, S-ethylisothiourea and 2-amino-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-4H-1,3-thiazine. Ki values of 14.7 nM for S-ethylisothiourea and 4.2 nM for 2-amino-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-4H-1,3-thiazine were obtained with partially purified preparations of inducible nitric oxide synthase. These compounds demonstrate about 1000-fold greater potency than prototypical inhibitors, and the inhibitions are 10-40-fold more selective for murine inducible nitric oxide synthase, compared with the rat neuronal and bovine endothelial isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. These compounds also potently inhibit the nitric oxide synthase activity in intact J774 mouse macrophages. The inhibition is competitive with the substrate L-arginine and reversible in both enzymatic and intact cell assays. These potent and selective inhibitors of inducible nitric oxide synthase may have potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.


