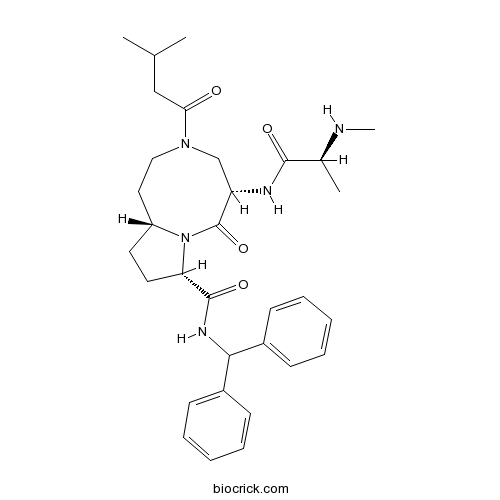
AT-406 (SM-406)IAP inhibitor CAS# 1071992-99-8 |
- Sabutoclax
Catalog No.:BCC2236
CAS No.:1228108-65-3
- ABT-199
Catalog No.:BCC3614
CAS No.:1257044-40-8
- WEHI-539
Catalog No.:BCC2055
CAS No.:1431866-33-9
- Obatoclax mesylate (GX15-070)
Catalog No.:BCC2234
CAS No.:803712-79-0
- ABT-737
Catalog No.:BCC3613
CAS No.:852808-04-9
- TW-37
Catalog No.:BCC2257
CAS No.:877877-35-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1071992-99-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25022340 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C32H43N5O4 | M.Wt | 561.71 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (178.03 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (5S,8S,10aR)-N-benzhydryl-5-[[(2S)-2-(methylamino)propanoyl]amino]-3-(3-methylbutanoyl)-6-oxo-1,2,4,5,8,9,10,10a-octahydropyrrolo[1,2-a][1,5]diazocine-8-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(=O)N1CCC2CCC(N2C(=O)C(C1)NC(=O)C(C)NC)C(=O)NC(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LSXUTRRVVSPWDZ-MKKUMYSQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C32H43N5O4/c1-21(2)19-28(38)36-18-17-25-15-16-27(37(25)32(41)26(20-36)34-30(39)22(3)33-4)31(40)35-29(23-11-7-5-8-12-23)24-13-9-6-10-14-24/h5-14,21-22,25-27,29,33H,15-20H2,1-4H3,(H,34,39)(H,35,40)/t22-,25+,26-,27-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

AT-406 (SM-406) Dilution Calculator

AT-406 (SM-406) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7803 mL | 8.9014 mL | 17.8028 mL | 35.6056 mL | 44.507 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3561 mL | 1.7803 mL | 3.5606 mL | 7.1211 mL | 8.9014 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.178 mL | 0.8901 mL | 1.7803 mL | 3.5606 mL | 4.4507 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0356 mL | 0.178 mL | 0.3561 mL | 0.7121 mL | 0.8901 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0178 mL | 0.089 mL | 0.178 mL | 0.3561 mL | 0.4451 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
K(i): The Ki of XIAP, cIAP1, and cIAP2 proteins is 66.4, 1.9, and 5.1 nM, respectively.
AT-406 is also named as SM-406. AT-406 is a potent and orally bioavailable antagonist of multiple inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). The inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), originally identified in baculoviruses, are a family of apoptosis suppressor proteins which could bind and inhibit specific enzymes (caspases) such as caspase 3, 7, and 9, but not caspase 8 [1]. Growing evidence has showed that IAPs can regulate programmed cell death, apoptosis, cell division, cell cycle progression, and signal transduction pathways [1].
In vitro: The Ki of AT-406 against XIAP, cIAP1, and cIAP2 proteins is 66.4, 1.9, and 5.1 nM, respectively [2]. In human ovarian cancer cell lines, treatment with AT-406 for 48 h could dose-dependently activate the apoptotic pathway. IC50 values of AT-406 in these ovarian cancer cells range from 0.05-0.5 μg/ml [3]. AT-406 could sensitize the response of ovarian cancer cells to carboplatin, a standard first-line chemotherapy for ovarian cancer [2].
In vivo: AT-406 exhibited good oral bioavailability in the mouse, rat, dog and non-human primates. In Rag-1 mice bearing intraperitoneally implanted OVCAR-3ip cells, AT-406 (100 mg/kg by oral gavage) significantly inhibited the progression of ovarian cancer and prolonged survival of the experimental mice both in single agent and in combination with carboplatin (40 mg/kg intraperitoneal injection) [2]. In xenograft mouse model of human breast cancer, 2-week treatment with 30?mg/kg or 100?mg/kg AT-406 effectively delayed the tumor growth [3].
Clinical trial: Oral treatment of AT-406 daily on days 1-5, initially every 14?days, later every 21?days was well tolerated at doses up to 900?mg in patients with different cancer types (Hurthle cell, melanoma, breast, rectal, hemangiopericytoma) [4].
References:
Schimmer A D. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins: translating basic knowledge into clinical practice[J]. Cancer research, 2004, 64(20): 7183-7190.
Cai Q, Sun H, Peng Y, et al. A potent and orally active antagonist (SM-406/AT-406) of multiple inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) in clinical development for cancer treatment[J]. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2011, 54(8): 2714-2726.
Zhang T, Li Y. et al. A Physiologically based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of an antagonist (SM-406/AT-406) of multiple inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) in a mouse xenograft model of human breast cancer. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2013 Sep;34(6):348-59.
Hurwitz HI1, Smith DC, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamic properties of oral DEBIO1143 (AT-406) in patients with advanced cancer: results of a first-in-man study. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;75(4):851-9.
- Deoxyflindissone
Catalog No.:BCN7268
CAS No.:107176-31-8
- MAC13243
Catalog No.:BCC1727
CAS No.:1071638-38-4
- Pyrocincholic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN5873
CAS No.:107160-24-7
- Perindopril Erbumine
Catalog No.:BCC3586
CAS No.:107133-36-8
- 8,9-Dihydroxy-10-isobutyryloxythymol
Catalog No.:BCN7974
CAS No.:107109-97-7
- Adipic dihydrazide
Catalog No.:BCC8810
CAS No.:1071-93-8
- Apo-12'-Lycopenal
Catalog No.:BCC8298
CAS No.:1071-52-9
- EIT hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6824
CAS No.:1071-37-0
- O-Phosphorylethanolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1759
CAS No.:1071-23-4
- Amyloid Beta-Peptide (12-28) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1044
CAS No.:107015-83-8
- Granisetron HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1060
CAS No.:107007-99-8
- Sarcosine
Catalog No.:BCN2744
CAS No.:107-97-1
- Epigoitrin
Catalog No.:BCN6278
CAS No.:1072-93-1
- Cevimeline
Catalog No.:BCC1470
CAS No.:107233-08-9
- 2-[(1S)-2-Formyl-1,3,3-trimethylcyclohexyl]-4-hydroxy-5-propan-2-ylbenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN3584
CAS No.:1072444-55-3
- NPPB
Catalog No.:BCC6711
CAS No.:107254-86-4
- Baogongteng C
Catalog No.:BCN1873
CAS No.:107259-50-7
- Carasinol D
Catalog No.:BCN8228
CAS No.:1072797-66-0
- MLN2238
Catalog No.:BCC2092
CAS No.:1072833-77-2
- SR-3677
Catalog No.:BCC4302
CAS No.:1072959-67-1
- Defactinib
Catalog No.:BCC5494
CAS No.:1073154-85-4
- Demethylzeylasteral
Catalog No.:BCN2282
CAS No.:107316-88-1
- LDC000067
Catalog No.:BCC5452
CAS No.:1073485-20-7
- Cleroindicin B
Catalog No.:BCN5874
CAS No.:107389-91-3
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of an antagonist (SM-406/AT-406) of multiple inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) in a mouse xenograft model of human breast cancer.[Pubmed:23813446]
Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2013 Sep;34(6):348-59.
The inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) are a class of key apoptosis regulators overexpressed or dysregulated in cancer. SM-406/AT-406 is a potent and selective small molecule mimetic of Smac that antagonizes the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). A physiologically based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (PBPK-PD) model was developed to predict the tissue concentration-time profiles of SM-406, the related onco-protein levels in tumor, and the tumor growth inhibition in a mouse model bearing human breast cancer xenograft. In the whole body physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for pharmacokinetics characterization, a well stirred (perfusion rate-limited) model was used to describe SM-406 pharmacokinetics in the lung, heart, kidney, intestine, liver and spleen, and a diffusion rate-limited (permeability limited) model was used for tumor. Pharmacodynamic (PD) models were developed to correlate the SM-406 concentration in tumor to the cIAP1 degradation, pro-caspase 8 decrease, CL-PARP accumulation and tumor growth inhibition. The PBPK-PD model well described the experimental pharmacokinetic data, the pharmacodynamic biomarker responses and tumor growth. This model may be helpful to predict tumor and plasma SM-406 concentrations in the clinic.
A potent and orally active antagonist (SM-406/AT-406) of multiple inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) in clinical development for cancer treatment.[Pubmed:21443232]
J Med Chem. 2011 Apr 28;54(8):2714-26.
We report the discovery and characterization of SM-406 (compound 2), a potent and orally bioavailable Smac mimetic and an antagonist of the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). This compound binds to XIAP, cIAP1, and cIAP2 proteins with K(i) of 66.4, 1.9, and 5.1 nM, respectively. Compound 2 effectively antagonizes XIAP BIR3 protein in a cell-free functional assay, induces rapid degradation of cellular cIAP1 protein, and inhibits cancer cell growth in various human cancer cell lines. It has good oral bioavailability in mice, rats, non-human primates, and dogs, is highly effective in induction of apoptosis in xenograft tumors, and is capable of complete inhibition of tumor growth. Compound 2 is currently in phase I clinical trials for the treatment of human cancer.


