Apoptosis InhibitorAssociate with caspase-3 inhibition CAS# 54135-60-3 |
- Z-DEVD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1137
CAS No.:210344-95-9
- Caspase-3/7 Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC1140
CAS No.:220509-74-0
- AZ 10417808
Catalog No.:BCC2356
CAS No.:331645-84-2
- Ivachtin
Catalog No.:BCC2357
CAS No.:745046-84-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 54135-60-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2748618 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H16O4 | M.Wt | 236.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >9.1mg/mL in DMSO | ||
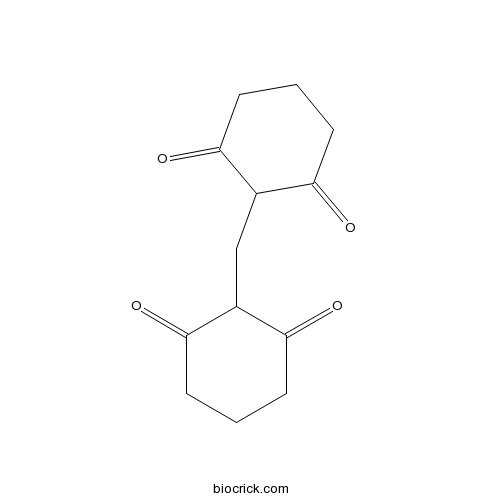
| Chemical Name | 2-[(2,6-dioxocyclohexyl)methyl]cyclohexane-1,3-dione | ||
| SMILES | C1CC(=O)C(C(=O)C1)CC2C(=O)CCCC2=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ILUMEPMGPCKGHH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H16O4/c14-10-3-1-4-11(15)8(10)7-9-12(16)5-2-6-13(9)17/h8-9H,1-7H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Apoptosis Inhibitor is a cell-permeable inhibitor of apoptosis induction. | |||||
| Targets | Caspase | |||||

Apoptosis Inhibitor Dilution Calculator

Apoptosis Inhibitor Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.2319 mL | 21.1595 mL | 42.3191 mL | 84.6382 mL | 105.7977 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8464 mL | 4.2319 mL | 8.4638 mL | 16.9276 mL | 21.1595 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4232 mL | 2.116 mL | 4.2319 mL | 8.4638 mL | 10.5798 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0846 mL | 0.4232 mL | 0.8464 mL | 1.6928 mL | 2.116 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0423 mL | 0.2116 mL | 0.4232 mL | 0.8464 mL | 1.058 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
M50054, 2,2'-methylenebis (1,3-cyclohexanedione), is a novel inhibitor of apoptosis. [1]
In human Fas-expressing WC8 cells, M50054 inhibited apoptosis by soluble human Fas ligand in vitro cell death assay. M50054 inhibited the apoptotic U937 cell death which is a human monocytic leukemic cell line, induced by anticancer agents such as etoposide. M50054 inhibited apoptotic characters such as DNA phosphatidylserine and fragmentation exposure in these cells. These anti-apoptotic effects were dependent on inhibition of caspase-3 activation. Additionally, M50054 significantly inhibited anti-Fas-antibody-induced elevation of plasma aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase. Alopecia (hair loss) symptoms were also significantly improved with topical treatment with M50054. M50054 inhibits apoptosis induced by a variety of stimuli via inhibition of caspase-3 activation, and may thus be effective for hepatitis and chemotherapy-induced alopecia. [1]
Reference:
Tsuda T, Ohmori Y, Muramatsu H et al. Inhibitory effect of M50054, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis, on anti-Fas-antibody-induced hepatitis and chemotherapy-induced alopecia.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Dec 14;433(1):37-45.
- 9-Benzylcarbazole-3-carboxaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8800
CAS No.:54117-37-2
- 15-Hydroxydehydroabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5720
CAS No.:54113-95-0
- Muscone
Catalog No.:BCN6275
CAS No.:541-91-3
- Isovaleramide
Catalog No.:BCC4668
CAS No.:541-46-8
- Decamethonium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC4568
CAS No.:541-22-0
- L-Carnitine inner salt
Catalog No.:BCN1229
CAS No.:541-15-1
- 2-(1-Hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-4-methoxy-7H-furo[3,2-g][1]benzopyran-7-one
Catalog No.:BCN1422
CAS No.:54087-32-0
- Isoastilbin
Catalog No.:BCN5719
CAS No.:54081-48-0
- Palosuran
Catalog No.:BCC4311
CAS No.:540769-28-6
- Tofacitinib (CP-690550) Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC2189
CAS No.:540737-29-9
- Etonogestrel
Catalog No.:BCC5230
CAS No.:54048-10-1
- Albendazole Oxide
Catalog No.:BCC4757
CAS No.:54029-12-8
- Neoisoastilbin
Catalog No.:BCN6532
CAS No.:54141-72-9
- Flecainide acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1578
CAS No.:54143-56-5
- Vicriviroc Malate
Catalog No.:BCC1230
CAS No.:541503-81-5
- Apilimod
Catalog No.:BCC5286
CAS No.:541550-19-0
- 1-Monopalmitin
Catalog No.:BCN7749
CAS No.:542-44-9
- Cimaterol
Catalog No.:BCC6647
CAS No.:54239-37-1
- 3-Benzoylpyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8623
CAS No.:5424-19-1
- Stachyose trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8361
CAS No.:54261-98-2
- (+)-Fluprostenol
Catalog No.:BCC7947
CAS No.:54276-17-4
- 2',4'-Dihydroxy-3',6'-dimethoxydihydrochalcone
Catalog No.:BCN1421
CAS No.:54299-52-4
- Ac-Gly-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2943
CAS No.:543-24-8
- Amsacrine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4310
CAS No.:54301-15-4
Mouse Lung Fibroblast Resistance to Fas-Mediated Apoptosis Is Dependent on the Baculoviral Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein 4 and the Cellular FLICE-Inhibitory Protein.[Pubmed:28352235]
Front Physiol. 2017 Mar 14;8:128.
A characteristic feature of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is accumulation of apoptotic resistant fibroblasts/myofibroblasts in the fibroblastic foci. As caveolin (Cav)-null mice develop pulmonary fibrosis (PF), we hypothesized that the participating fibroblasts display an apoptosis-resistant phenotype. To test this hypothesis and identify the molecular mechanisms involved we isolated lung fibroblasts from Cav-null mice and examined the expression of several inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs), of c-FLIP, of Bcl-2 proteins and of the death receptor CD95/Fas. We found significant increase in XIAP and c-FLIP constitutive protein expression with no alteration of Bcl-2 and lower levels of CD95/Fas. The isolated fibroblasts were then treated with the CD95/Fas ligand (FasL) to induce apoptosis. While the morphological and biochemical alterations induced by FasL were similar in wild-type (wt) and Cav-null mouse lung fibroblasts, the time course and the extent of the alterations were greater in the Cav-null fibroblasts. Several salient features of Cav-null fibroblasts response such as loss of membrane potential, fragmentation of the mitochondrial continuum concurrent with caspase-8 activation, and subsequent Bid cleavage, prior to caspase-3 activation were detected. Furthermore, M30 antigen formation, phosphatidylserine expression and DNA fragmentation were caspase-3 dependent. SiRNA-mediated silencing of XIAP and c-FLIP, individually or combined, enhanced the sensitivity of lung fibroblasts to FasL-induced apoptosis. Pharmacological inhibition of Bcl-2 had no effect. Together our findings support a mechanism in which CD95/Fas engagement activates caspase-8, inducing mitochondrial apoptosis through Bid cleavage. XIAP and c-FLIP fine tune this process in a cell-type specific manner.
Overexpression of the X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protects Against Retinal Degeneration in a Feline Model of Retinal Detachment.[Pubmed:28335619]
Hum Gene Ther. 2017 Jun;28(6):482-492.
Retinal detachment is an acute disorder in humans that is caused by trauma or disease, and it can often lead to permanent visual deficits that result from the death of photoreceptors in the retina. The final pathway for photoreceptor cell death is apoptosis and necroptosis. The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) has been shown to block both of these cell death pathways. This study tested the effects of XIAP on photoreceptor survival in a feline model of retinal detachment. The study was performed in 12 cats, divided into two experimental groups. Six animals received a subretinal injection of adeno-associated virus (AAV) carrying XIAP, and six animals received AAV carrying green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a control. Three weeks after viral delivery, retinas were detached by injecting C3F8 gas into the subretinal space. Optical coherence tomography revealed that the retinal detachments resolved within 3-6 weeks as the gas was slowly resorbed. Analysis of histological sections through the plane of the detachment showed significant preservation of the photoreceptor layer in AAV-XIAP-treated animals compared to AAV-GFP-treated animals at 9 weeks after the detachment. XIAP-treated detached retinas were similar to intact controls. These studies support the potential for XIAP therapy in the treatment of human retinal detachment.
MPT0B002, a novel microtubule inhibitor, downregulates T315I mutant Bcr-Abl and induces apoptosis of imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells.[Pubmed:28349229]
Invest New Drugs. 2017 Aug;35(4):427-435.
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a hematopoietic malignancy caused by the constitutive activation of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase. The Bcr-Abl inhibitor imatinib and other second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as dasatinib and nilotinib have remarkable efficacy in CML treatment. However, gene mutation-mediated drug resistance remains a critical problem. Among point mutations, the Bcr-Abl T315I mutation confers resistance to these Bcr-Abl inhibitors. Previously, we have synthesized the compound (1-methyl-1H-indol-5-yl)-(3,4,5-trimethoxy-phenyl)-methanone (MPT0B002) as a novel microtubule inhibitor. In this study, we evaluated its effects on the proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of K562 CML cells and BaF3 cells expressing either wild-type Bcr-Abl (BaF3/p210) or T315I-mutated Bcr-Abl (BaF3/T315I). MPT0B002 inhibited cell viability in a dose-dependent manner in these cells but did not affect the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. It disrupted tubulin polymerization and arrested cell cycle at the G2/M phase. Treatment with MPT0B002 induced apoptosis, and this induction was associated with increased levels of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP. Furthermore, MPT0B002 can downregulate both Bcr-Abl and Bcr-Abl-T315I mRNA expressions and protein levels and the downstream signaling pathways. Taken together, our findings suggest that MPT0B002 may be considered a promising compound to downregulate not only wild type Bcr-Abl but also the T315I mutant to overcome Bcr-Abl-T315I mutation-mediated resistance in CML cells.
Apoptosis inhibitor 5 is an endogenous inhibitor of caspase-2.[Pubmed:28336776]
EMBO Rep. 2017 May;18(5):733-744.
Caspases are key enzymes responsible for mediating apoptotic cell death. Across species, caspase-2 is the most conserved caspase and stands out due to unique features. Apart from cell death, caspase-2 also regulates autophagy, genomic stability and ageing. Caspase-2 requires dimerization for its activation which is primarily accomplished by recruitment to high molecular weight protein complexes in cells. Here, we demonstrate that Apoptosis Inhibitor 5 (API5/AAC11) is an endogenous and direct inhibitor of caspase-2. API5 protein directly binds to the caspase recruitment domain (CARD) of caspase-2 and impedes dimerization and activation of caspase-2. Interestingly, recombinant API5 directly inhibits full length but not processed caspase-2. Depletion of endogenous API5 leads to an increase in caspase-2 dimerization and activation. Consistently, loss of API5 sensitizes cells to caspase-2-dependent apoptotic cell death. These results establish API5/AAC-11 as a direct inhibitor of caspase-2 and shed further light onto mechanisms driving the activation of this poorly understood caspase.


