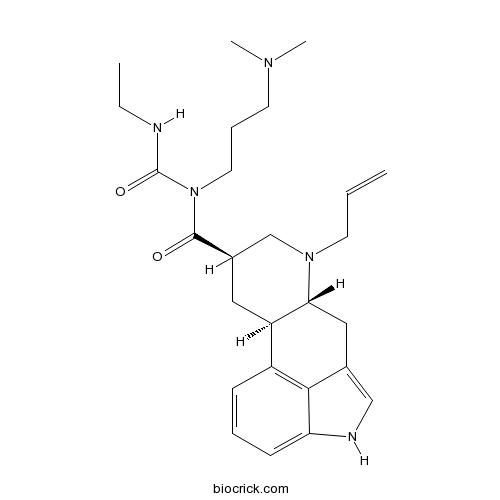
Cabergolinelong-lasting inhibitory activity on PRL secretion CAS# 81409-90-7 |
- Leupeptin, Microbial
Catalog No.:BCC1217
CAS No.:103476-89-7
- Calpain Inhibitor II, ALLM
Catalog No.:BCC1234
CAS No.:136632-32-1
- CA-074 Me
Catalog No.:BCC3649
CAS No.:147859-80-1
- Cathepsin Inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4896
CAS No.:225120-65-0
- L 006235
Catalog No.:BCC2361
CAS No.:294623-49-7
- E-64-c
Catalog No.:BCC3588
CAS No.:76684-89-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 81409-90-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 54746 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H37N5O2 | M.Wt | 451.6 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | FCE-21336 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 33 mg/mL (73.07 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (6aR,9R,10aR)-N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-7-prop-2-enyl-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CCNC(=O)N(CCCN(C)C)C(=O)C1CC2C(CC3=CNC4=CC=CC2=C34)N(C1)CC=C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KORNTPPJEAJQIU-KJXAQDMKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H37N5O2/c1-5-11-30-17-19(25(32)31(26(33)27-6-2)13-8-12-29(3)4)14-21-20-9-7-10-22-24(20)18(16-28-22)15-23(21)30/h5,7,9-10,16,19,21,23,28H,1,6,8,11-15,17H2,2-4H3,(H,27,33)/t19-,21-,23-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective D2-like dopamine receptor agonist (Ki values are 0.7, 1.5, 9.0 and 165 nM for D2, D3, D4 and D5 receptors respectively) that also displays high affinity for several serotonin receptor subtypes (Ki = 1.2 - 20.0 nM for 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B). Inhibits secretion of prolactin and growth hormone and reverses levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinsonian monkeys. |

Cabergoline Dilution Calculator

Cabergoline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2143 mL | 11.0717 mL | 22.1435 mL | 44.287 mL | 55.3587 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4429 mL | 2.2143 mL | 4.4287 mL | 8.8574 mL | 11.0717 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2214 mL | 1.1072 mL | 2.2143 mL | 4.4287 mL | 5.5359 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0443 mL | 0.2214 mL | 0.4429 mL | 0.8857 mL | 1.1072 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0221 mL | 0.1107 mL | 0.2214 mL | 0.4429 mL | 0.5536 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 0.1 nM
Unlike other pituitary hormones, prolactin (PRL) secretion is predominantly inhibited by dopamine secreted by the hypothalamus. Cabergoline is an ergoline derivative with potent, selective and long-lasting inhibitory activity on PRL secretion acting on dopamine receptors present in pituitary lactotrophes.
In vitro: Receptor binding studies have demonstrated that cabergoline has high in vitro selectivity and affinity for the subtype D2 of the dopamine receptor. In rat anterior pituitary cells, the concentration of cabergoline required to inhibit PRL secretory activity by 50% were 0.1 nmol/l [1].
In vivo: In various animal models, cabergoline markedly reduced plasma PRL levels in vivo after single or multiple doses, and the PRL-lowering effects appeared 2 - 8 h after administration lasting for 72 h or longer. In addition, a single dose of cabergoline 0.6 mg/kg to rats, inhibited the serum levels of PRL for 6 days significantly [1].
Clinical trial: Cabergoline at doses of 0.125 - 1 mg twice a week caused a dose-dependent suppression of PRL secretion in women with hyperprolactinaemia. cabergoline was shown to be more effective than bromocriptine in inducing a complete biochemical response and clinical efficacy and was better tolerated than bromocriptine in the majority of patients [1].
Reference:
[1] Annamaria Colao, Gaetano Lombardi & Lucio Annunziato. Cabergoline. Exp. Opin. Pharmacother. (2000) 1(3):555-574
- EHNA hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6996
CAS No.:81408-49-3
- Alfuzosin
Catalog No.:BCC4080
CAS No.:81403-80-7
- Alfuzosin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2494
CAS No.:81403-68-1
- Acetylvalerenolic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8112
CAS No.:81397-67-3
- Fmoc-His(Boc)-OH.CHA
Catalog No.:BCC2595
CAS No.:81379-52-4
- Seglitide
Catalog No.:BCC7191
CAS No.:81377-02-8
- Momordicoside G
Catalog No.:BCN4349
CAS No.:81371-54-2
- Momordicoside K
Catalog No.:BCN3272
CAS No.:81348-84-7
- Momordicoside L
Catalog No.:BCN3274
CAS No.:81348-83-6
- Momordicoside F1
Catalog No.:BCN3273
CAS No.:81348-81-4
- Cyclo(Tyr-Hpro)
Catalog No.:BCN2424
CAS No.:813461-21-1
- Schisandrin C epoxide
Catalog No.:BCN3744
CAS No.:81345-36-0
- Sanggenone D
Catalog No.:BCN1194
CAS No.:81422-93-7
- 8-Acetoxypinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN2161
CAS No.:81426-14-4
- 8-Hydroxypinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3389
CAS No.:81426-17-7
- (-)-Pinoresinol
Catalog No.:BCN3254
CAS No.:81446-29-9
- Taxagifine
Catalog No.:BCN6949
CAS No.:81489-69-2
- 1-Hydroxypinoresinol 1-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7019
CAS No.:81495-71-8
- alpha-Dihydroartemisinin
Catalog No.:BCN2627
CAS No.:81496-81-3
- Nafamostat
Catalog No.:BCC4187
CAS No.:81525-10-2
- Forsythoside B
Catalog No.:BCN1205
CAS No.:81525-13-5
- 2-Pentadecenedioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3666
CAS No.:81588-35-4
- Neuromedin C (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC5832
CAS No.:81608-30-2
- Withaperuvin C
Catalog No.:BCN6727
CAS No.:81644-34-0
Long-term cardiac (valvulopathy) safety of cabergoline in prolactinoma.[Pubmed:28217516]
Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jan-Feb;21(1):154-159.
BACKGROUND: Clinical relevance of association of Cabergoline use for hyperprolactinemia and cardiac valvulopathy remains unclear. OBJECTIVE: The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence of valvular heart abnormalities in patients taking Cabergoline for the treatment of prolactinoma and to explore any associations with the cumulative dose of drug used. DESIGN: A cross-sectional echocardiographic study was performed in patients who were receiving Cabergoline therapy for prolactinoma. RESULTS: Hundred (61 females, 39 males) prolactinoma cases (81 macroprolactinoma and 19 microprolactinoma) were included in the study. The mean age at presentation was 33.9 +/- 9.0 years (range: 16-58 years). The mean duration of treatment was 53.11 +/- 43.15 months (range: 12-155 months). The mean cumulative dose was 308.6 +/- 290.2 mg (range: 26-1196 mg; interquartile range: 104-416 mg). Mild mitral regurgitation was present in one patient (cumulative Cabergoline dose 104 mg). Mild tricuspid regurgitation was present in another two patients (cumulative Cabergoline dose 52 mg and 104 mg). Aortic and pulmonary valve functioning was normal in all the cases. There were no cases of significant valvular regurgitation (moderate to severe, Grade 3-4). None of the patients had morphological abnormalities such as thickening, calcification, and restricted mobility of any of the cardiac valves. CONCLUSION: Cabergoline appears to be safe in patients with prolactinoma up to the cumulative dose of ~300 mg. The screening for valvulopathy should be restricted to those with higher cumulative Cabergoline exposure.
A review of the receptor-binding and pharmacokinetic properties of dopamine agonists.[Pubmed:16982285]
Clin Ther. 2006 Aug;28(8):1065-1078.
BACKGROUND: Dopamine agonists (DAs), which can be categorized as ergot derived and non-ergot derived, are used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. OBJECTIVES: This review describes the pharmacologic and pharmacokinetic properties of selected DAs and relates these characteristics to clinical outcomes, with an emphasis on adverse events. METHODS: Relevant articles were identified through a search of MEDLINE (to May 2006) using the terms dopamine agonists (or each individual drug name) and pbarmacokinetics, metabolism, drug-drug interaction, interactions, CYP450, fibrosis, valvular heart disease, tremor, clinical trials, reviews, and meta-analyses. Abstracts from recent sessions of the International Congress of Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disorders were also examined. Clinical studies with <20 patients overall or <10 patients per treatment group in the final analysis were excluded. All DAs that were graded at least possibly useful with respect to at least 3 of 4 items connected to the treatment/prevention of motor symptoms/complications in the most recent evidence-based medical review update were included. This resulted in a focus on the ergot-derived DAs bromocriptine, Cabergoline, and pergolide, and the non-ergot-derived DAs pramipexole and ropinirole. RESULTS: Bromocriptine, Cabergoline, pergolide, and ropinirole, but not pramipexole, have the potential for drug-drug interactions mediated by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system. The occurrence of dyskinesia may be linked to stimulation of the dopamine D(1) receptor, for which Cabergoline and pergolide have a similar and relatively high affinity; bromocriptine, pramipexole, and ropinirole have been associated with a lower risk of dyskinesias. The valvular heart disease (VHD) and pulmonary and retroperitoneal fibrosis seen with long-term use appear to represent a class effect of the ergot-derived DAs that may be related to stimulation of serotonin 5-HT(2B) (and possibly 5-HT(2A)) receptors. The incidence of valvular regurgitation was 31% to 47% with ergot-derived DAs, 10% with non-ergot-derived DAs, and 13% with controls. CONCLUSIONS: As reflected in the results of the clinical trials included in this review, dyskinesia associated with DA therapy may be linked to stimulation of the D(1) receptor. Fibrosis (including VHD) seemed to be a class effect of the ergot-derived DAs. Each of the DAs except pramipexole has the potential to interact with other drugs via the CYP enzyme system.
Effect of cabergoline, a dopamine agonist, on estrogen-induced rat pituitary tumors: in vitro culture studies.[Pubmed:7670571]
Endocr J. 1995 Jun;42(3):413-20.
Cabergoline (CG) is a dopamine agonist that inhibits secretion of prolactin (PRL) and growth hormone. The purpose of this study was to investigate the PRL-lowering effect and antitumor effect of CG on estradiol-induced rat pituitary tumors in vitro and to elucidate these mechanisms. We compared the effects of CG with those of bromocriptine (BC) in terms of the inhibition of hormone secretion as well as antitumor effects on rat pituitary tumors. Primary cultures of dissociated pituitary tumor cells were used in these studies. A significant inhibition of prolactin (PRL) secretion was observed for both drugs within 12 h after treatment, and the inhibitory effects of CG and BC were antagonized by sulpiride or haloperidol. Inhibitory effect on PRL secretion after 12-h BC or CG pretreatment was more pronounced with CG than BC treatment at all time points. PRL secretion in group pretreated with CG was significantly suppressed at 72 h when compared to that of vehicle. Inhibition of de novo PRL synthesis was better demonstrated in the CG group. These findings suggest that CG has a higher affinity for the D2 receptor of pituitary cells as compared to BC and may preferentially inhibit PRL secretion rather than PRL production. An antitumor effect of CG has been confirmed at a lower dosage than that of BC.


