Dabrafenib (GSK2118436)Inhibitor of BRAF(V600) mutants CAS# 1195765-45-7 |
- Bivalirudin Trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC1421
CAS No.:128270-60-0
- Edoxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1543
CAS No.:480449-70-5
- 5-R-Rivaroxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1313
CAS No.:865479-71-6
- Dabigatran etexilate mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1511
CAS No.:872728-81-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1195765-45-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44462760 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H20F3N5O2S2 | M.Wt | 519.56 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | GSK2118436A; GSK2118436 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 33 mg/mL (63.52 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
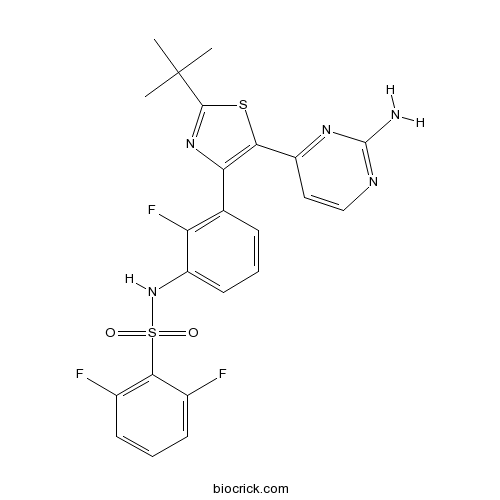
| Chemical Name | N-[3-[5-(2-aminopyrimidin-4-yl)-2-tert-butyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]-2-fluorophenyl]-2,6-difluorobenzenesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=NC(=C(S1)C2=NC(=NC=C2)N)C3=C(C(=CC=C3)NS(=O)(=O)C4=C(C=CC=C4F)F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BFSMGDJOXZAERB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H20F3N5O2S2/c1-23(2,3)21-30-18(19(34-21)16-10-11-28-22(27)29-16)12-6-4-9-15(17(12)26)31-35(32,33)20-13(24)7-5-8-14(20)25/h4-11,31H,1-3H3,(H2,27,28,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dabrafenib (GSK2118436) is a inhibitor of mutant BRAFV600 specific with an IC50 value of 0.8 nM. | |||||
| Targets | B-Raf (V600E) | B-Raf | C-Raf | |||
| IC50 | 0.8 nM | 3.2 nM | 5.0 nM | |||

Dabrafenib (GSK2118436) Dilution Calculator

Dabrafenib (GSK2118436) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9247 mL | 9.6235 mL | 19.2471 mL | 38.4941 mL | 48.1176 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3849 mL | 1.9247 mL | 3.8494 mL | 7.6988 mL | 9.6235 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1925 mL | 0.9624 mL | 1.9247 mL | 3.8494 mL | 4.8118 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0385 mL | 0.1925 mL | 0.3849 mL | 0.7699 mL | 0.9624 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0192 mL | 0.0962 mL | 0.1925 mL | 0.3849 mL | 0.4812 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Dabrafenib is a specific inhibitor of BRAF V600 mutants with IC50 values of 0.5nM, 0.6nM and 1.9nM against V600E, V600K and V600D, respectively [1].
BRAF plays a central role in regulating MAPK signaling pathway which regulates cell growth, division and differentiation. The V600E mutation of BRAF increases the kinase activity and is involved in metastatic melanomas. Dabrafenib is an ATP-competitive and reversible inhibitor of BRAF mutants. It potently inhibits BRAFV600E, BRAFV600K and BRAFV600D with IC50 values of 0.5nM, 0.6nM and 1.9nM, respectively. Dabrafenib is currently approved by FDA and is widely used in cancer patients harboring BRAF mutations. It is reported that treatment of dabrafenib shrinks the overall size of brain metastases in patients. It also has an impressive 60% response rate for melanomas outside of the brain. Dabrafenib provides a significant survival benefit in patients with metastatic melanoma [1, 2].
References:
[1] Hong S, Hong S. Overcoming metastatic melanoma with BRAF inhibitors. Archives of pharmacal research, 2011, 34(5): 699-701.
[2] Hong D S, Vence L, Falchook G, et al. BRAF (V600) inhibitor GSK2118436 targeted inhibition of mutant BRAF in cancer patients does not impair overall immune competency. Clinical Cancer Research, 2012, 18(8): 2326-2335.
- 11-Hydroxygelsenicine
Catalog No.:BCN4761
CAS No.:1195760-68-9
- N,N-Dimethylsphingosine
Catalog No.:BCC7959
CAS No.:119567-63-4
- Othonnine
Catalog No.:BCN2061
CAS No.:119565-25-2
- Ceanothic acid acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6083
CAS No.:119533-63-0
- Ethyllucidone
Catalog No.:BCN6082
CAS No.:1195233-59-0
- Meropenem trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4226
CAS No.:119478-56-7
- Fruquintinib(HMPL-013)
Catalog No.:BCC6415
CAS No.:1194506-26-7
- Eliprodil
Catalog No.:BCC7280
CAS No.:119431-25-3
- Loureirin B
Catalog No.:BCN5021
CAS No.:119425-90-0
- Loureirin A
Catalog No.:BCN3671
CAS No.:119425-89-7
- Galanin (1-30) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC6961
CAS No.:119418-04-1
- Licoricesaponin E2
Catalog No.:BCN7894
CAS No.:119417-96-8
- Dabrafenib Mesylate (GSK-2118436)
Catalog No.:BCC1513
CAS No.:1195768-06-9
- 7-Ethyl-10-Hydroxy-Camptothecin
Catalog No.:BCN8386
CAS No.:119577-28-5
- 2-Hydroxyquinoxaline
Catalog No.:BCC8577
CAS No.:1196-57-2
- GSK2190915 sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5588
CAS No.:1196070-26-4
- PF-3845
Catalog No.:BCC2326
CAS No.:1196109-52-0
- Olprinone Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1821
CAS No.:119615-63-3
- Sulfo-NHS-Biotin
Catalog No.:BCC3576
CAS No.:119616-38-5
- Arecaidine but-2-ynyl ester tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC6627
CAS No.:119630-77-2
- Naloxone benzoylhydrazone
Catalog No.:BCC5757
CAS No.:119630-94-3
- Moguisteine
Catalog No.:BCC4925
CAS No.:119637-67-1
- Yucalexin P-17
Catalog No.:BCN6595
CAS No.:119642-82-9
- Amadacycline methanesulfonate
Catalog No.:BCC1356
CAS No.:1196800-40-4
Tumor genetic analyses of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436).[Pubmed:23833299]
Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 1;19(17):4868-78.
PURPOSE: Dabrafenib is a selective inhibitor of V600-mutant BRAF kinase, which recently showed improved progression-free survival (PFS) as compared with dacarbazine, in metastatic melanoma patients. This study examined potential genetic markers associated with response and PFS in the phase I study of dabrafenib. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Baseline (pretreatment or archival) melanoma samples were evaluated in 41 patients using a custom genotyping melanoma-specific assay, sequencing of PTEN, and copy number analysis using multiplex ligation amplification and array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Nine patients had on-treatment and/or progression samples available. RESULTS: All baseline patient samples had BRAF(V600E/K) confirmed. Baseline PTEN loss/mutation was not associated with best overall response to dabrafenib, but it showed a trend for shorter median PFS [18.3 (95% confidence interval, CI, 9.1-24.3) vs. 32.1 weeks (95% CI, 24.1-33), P=0.059]. Higher copy number of CCND1 (P=0.009) and lower copy number of CDKN2A (P=0.012) at baseline were significantly associated with decreased PFS. Although no melanomas had high-level amplification of BRAF, the two patients with progressive disease as their best response had BRAF copy gain in their tumors. CONCLUSIONS: Copy number changes in CDKN2A, CCND1, and mutation/copy number changes in PTEN correlated with the duration of PFS in patients treated with dabrafenib. The results suggest that these markers should be considered in the design and interpretation of future trials with selective BRAF inhibitors in advanced melanoma patients.
Dose selection, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436).[Pubmed:24958809]
Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 1;20(17):4449-58.
PURPOSE: Dabrafenib is a selective, potent ATP-competitive inhibitor of the BRAFV600-mutant kinase that has demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials. We report the rationale for dose selection in the first-in-human study of dabrafenib, including pharmacokinetics, tissue pharmacodynamics, 2[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) pharmacodynamics, and dose-response relationship. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Dabrafenib was administered orally once, twice (BID), or three times daily (TID). Selected dose cohorts were expanded to collect adequate data on safety, pharmacokinetics, or pharmacodynamics. A recommended phase II dose (RP2D) was chosen based on safety, pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and response data. RESULTS: One hundred and eighty-four patients were enrolled and treated with doses ranging from 12 mg once daily to 300 mg BID in 10 cohorts. Pharmacokinetic assessment of dabrafenib demonstrated a less-than-dose-proportional increase in exposure after repeat dosing above 150 mg BID. Similar to parent drug concentrations, exposure for all metabolites demonstrated less-than-dose-proportional increases. Predicted target inhibition of pERK (>80%) was achieved at 150 mg BID, with a similar magnitude of inhibition at higher doses in BRAFV600 mutation melanoma biopsy samples. Although there was large variability between patients, FDG uptake decreased with higher daily doses in patients with BRAFV600 mutation-positive melanoma. A favorable activity and tolerability profile was demonstrated at 150 mg BID. There was no improvement with TID dosing compared with BID dosing, based on FDG-PET and tumor response analyses in patients with melanoma. CONCLUSION: The RP2D of dabrafenib was determined to be 150 mg BID after considering multiple factors, including pharmacokinetics, tissue pharmacodynamics, FDG-PET pharmacodynamics, and the dose-response relationship. A maximum tolerated dose for dabrafenib was not determined.
Phase II trial (BREAK-2) of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436) in patients with metastatic melanoma.[Pubmed:23918947]
J Clin Oncol. 2013 Sep 10;31(26):3205-11.
PURPOSE: Dabrafenib (GSK2118436) is a potent inhibitor of mutated BRAF kinase. Our multicenter, single-arm, phase II study assessed the safety and clinical activity of dabrafenib in BRAF(V600E/K) mutation-positive metastatic melanoma (mut(+) MM). PATIENTS AND METHODS: Histologically confirmed patients with stage IV BRAF(V600E/K) mut(+) MM received oral dabrafenib 150 mg twice daily until disease progression, death, or unacceptable adverse events (AEs). The primary end point was investigator-assessed overall response rate in BRAF(V600E) mut(+) MM patients. Secondary end points included progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Exploratory objectives included the comparison of BRAF mutation status between tumor-specific circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and tumor tissue, and the evaluation of cfDNA as a predictor of clinical outcome. RESULTS: Seventy-six patients with BRAF(V600E) and 16 patients with BRAF(V600K) mut(+) MM were enrolled onto the study. In the BRAF(V600E) group, 45 patients (59%) had a confirmed response (95% CI, 48.2 to 70.3), including five patients (7%) with complete responses. Two patients (13%) with BRAF(V600K) mut(+) MM had a confirmed partial response (95% CI, 0 to 28.7). In the BRAF(V600E) and BRAF(V600K) groups, median PFS was 6.3 months and 4.5 months, and median OS was 13.1 months and 12.9 months, respectively. The most common AEs were arthralgia (33%), hyperkeratosis (27%), and pyrexia (24%). Overall, 25 patients (27%) experienced a serious AE and nine patients (10%) had squamous cell carcinoma. Baseline cfDNA levels predicted response rate and PFS in BRAF(V600E) mut(+) MM patients. CONCLUSION: Dabrafenib was well tolerated and clinically active in patients with BRAF(V600E/K) mut(+) MM. cfDNA may be a useful prognostic and response marker in future studies.


