Dolastatin 10Antitumor agent CAS# 110417-88-4 |
- Repaglinide
Catalog No.:BCC2504
CAS No.:135062-02-1
- Dronedarone
Catalog No.:BCN2176
CAS No.:141626-36-0
- NS309
Catalog No.:BCC1809
CAS No.:18711-16-5
- TRAM-34
Catalog No.:BCC1122
CAS No.:289905-88-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 110417-88-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 100208 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C42H68N6O6S | M.Wt | 785.09 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | DLS 10; NSC 376128 | ||
| Solubility | >78.5mg/ml in EtOH | ||
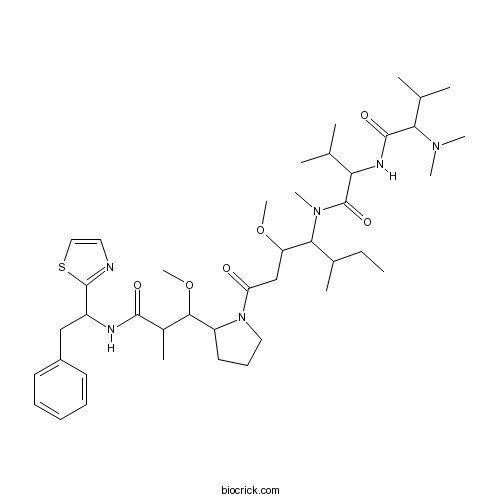
| Chemical Name | 2-[[2-(dimethylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-N-[3-methoxy-1-[2-[1-methoxy-2-methyl-3-oxo-3-[[2-phenyl-1-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)ethyl]amino]propyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-5-methyl-1-oxoheptan-4-yl]-N,3-dimethylbutanamide | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(CC(=O)N1CCCC1C(C(C)C(=O)NC(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C3=NC=CS3)OC)OC)N(C)C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)N(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OFDNQWIFNXBECV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C42H68N6O6S/c1-13-28(6)37(47(10)42(52)35(26(2)3)45-40(51)36(27(4)5)46(8)9)33(53-11)25-34(49)48-22-17-20-32(48)38(54-12)29(7)39(50)44-31(41-43-21-23-55-41)24-30-18-15-14-16-19-30/h14-16,18-19,21,23,26-29,31-33,35-38H,13,17,20,22,24-25H2,1-12H3,(H,44,50)(H,45,51) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dolastatin 10 is a potent antimitotic peptide, isolated from the marine mollusk Dolabela auricularia, that inhibits tubulin polymerization.In Vitro:Dolastatin 10 is a unique pentapeptide that isolated from the sea hare Dolabella auricularia. These in vitro data are quite comparable to those of Dolastatin 10 and Auristatin PE, each of which has GI50 References: | |||||

Dolastatin 10 Dilution Calculator

Dolastatin 10 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2737 mL | 6.3687 mL | 12.7374 mL | 25.4748 mL | 31.8435 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2547 mL | 1.2737 mL | 2.5475 mL | 5.095 mL | 6.3687 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1274 mL | 0.6369 mL | 1.2737 mL | 2.5475 mL | 3.1843 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1274 mL | 0.2547 mL | 0.5095 mL | 0.6369 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0127 mL | 0.0637 mL | 0.1274 mL | 0.2547 mL | 0.3184 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Dolastatin 10 is an antitumor agent [1].
Dolastatin 10 is a potent antimitotic polypeptide isolated from a marine animal and is developed as a potential antitumor agent. Dolastatin 10 is found to have activity to inhibit tubulin polymerization with IC50 value of 1.2μM. Besides that, it potently inhibits vincristine binding to tubulin with a Ki value of 1.4μM in a noncompetitive manner. Dolastatin 10 also shows moderate effect on enhancing the binding of colchicines to tubulin. In addition, Dolastatin 10 has the inhibitory activity in tubulin-dependent GTP binding [1].
In the cellular assay, Dolastatin 10 shows activity against some human leukaemia, lymphoma and solid tumour cell lines (such as OVCAR-3 and NSCLC) with IC50 values ranging from 0.1nM to 10nM. It is currently tested in the clinical trials [2].
References:
[1] Bai R L, Pettit G R, Hamel E. Binding of dolastatin 10 to tubulin at a distinct site for peptide antimitotic agents near the exchangeable nucleotide and vinca alkaloid sites. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1990, 265(28): 17141-17149.
[2] Schwartsmann G. Marine organisms and other novel natural sources of new cancer drugs. Annals of Oncology, 2000, 11(suppl 3): 235-243.
- Gelsemiol
Catalog No.:BCN5992
CAS No.:110414-77-2
- Higenamine HCl
Catalog No.:BCN2831
CAS No.:11041-94-4
- Meclizine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC9017
CAS No.:1104-22-9
- 2,3-Dihydroheveaflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4019
CAS No.:110382-42-8
- 3-O-Methyltagitinin F
Catalog No.:BCN5991
CAS No.:110382-37-1
- Ch 55
Catalog No.:BCC7241
CAS No.:110368-33-7
- S 32826
Catalog No.:BCC7678
CAS No.:1103672-43-0
- Bavisant dihydrochloride hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1404
CAS No.:1103522-80-0
- CGS 19755
Catalog No.:BCC6986
CAS No.:110347-85-8
- FD-838
Catalog No.:BCN6396
CAS No.:110341-78-1
- α-Bungarotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC7264
CAS No.:11032-79-4
- Santalol
Catalog No.:BCN8352
CAS No.:11031-45-1
- ML-7 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1770
CAS No.:110448-33-4
- BYK 204165
Catalog No.:BCC2449
CAS No.:1104546-89-5
- Crotastriatine
Catalog No.:BCN2101
CAS No.:11051-94-8
- 6,11-Di-O-acetylalbrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7273
CAS No.:110538-20-0
- Scutebarbatine F
Catalog No.:BCN5377
CAS No.:910099-78-4
- Albrassitriol
Catalog No.:BCN7274
CAS No.:110557-39-6
- Salermide
Catalog No.:BCC7867
CAS No.:1105698-15-4
- Laminin (925-933)
Catalog No.:BCC1015
CAS No.:110590-60-8
- human Insulin expressed in yeast
Catalog No.:BCC7689
CAS No.:11061-68-0
- Epimedin A
Catalog No.:BCN1038
CAS No.:110623-72-8
- Epimedin B
Catalog No.:BCN1039
CAS No.:110623-73-9
- Epimedin C
Catalog No.:BCN1040
CAS No.:110642-44-9
Discovery of cytotoxic dolastatin 10 analogues with N-terminal modifications.[Pubmed:25431858]
J Med Chem. 2014 Dec 26;57(24):10527-43.
Auristatins, synthetic analogues of the antineoplastic natural product Dolastatin 10, are ultrapotent cytotoxic microtubule inhibitors that are clinically used as payloads in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). The design and synthesis of several new auristatin analogues with N-terminal modifications that include amino acids with alpha,alpha-disubstituted carbon atoms are described, including the discovery of our lead auristatin, PF-06380101. This modification of the peptide structure is unprecedented and led to analogues with excellent potencies in tumor cell proliferation assays and differential ADME properties when compared to other synthetic auristatin analogues that are used in the preparation of ADCs. In addition, auristatin cocrystal structures with tubulin are being presented that allow for the detailed examination of their binding modes. A surprising finding is that all analyzed analogues have a cis-configuration at the Val-Dil amide bond in their functionally relevant tubulin bound state, whereas in solution this bond is exclusively in the trans-configuration. This remarkable observation shines light onto the preferred binding mode of auristatins and serves as a valuable tool for structure-based drug design.
Antineoplastic agents. 592. Highly effective cancer cell growth inhibitory structural modifications of dolastatin 10.[Pubmed:21534541]
J Nat Prod. 2011 May 27;74(5):962-8.
The dolastatin series of unique peptides, originally discovered as constituents of the sea hare Dolabella auricularia, is of increasing importance in providing biological leads, especially to new and useful anticancer drugs. Dolastatin 10 and three analogues, minor structural modifications designated auristatins, are currently in human cancer clinical trials. The present study was undertaken to explore delivery to the cancer sites by way of phosphate or quinoline modifications. The initial objectives, auristatin TP as sodium phosphate 3b (GI50 10(-2)-10(-4) mug/mL), auristatin 2-AQ (4, GI50 10(-2)-10(-3) mug/mL), and auristatin 6-AQ (5, GI50 10(-4) mug/mL), exhibited superior cancer cell growth inhibitory properties.
A synthetic dolastatin 10 analogue suppresses microtubule dynamics, inhibits cell proliferation, and induces apoptotic cell death.[Pubmed:23445405]
J Med Chem. 2013 Mar 28;56(6):2235-45.
We have synthesized eight analogues (D1-D8) of Dolastatin 10 containing several unique amino acid subunits. Of these agents, D5 was found to be most effective in inhibiting both HeLa cell proliferation and microtubule assembly in vitro. At low nanomolar concentrations, D5 inhibited the proliferation of several types of cancer cells in culture. D5 bound to tubulin with a dissociation constant of 29.4 +/- 6 muM. D5 depolymerized microtubules in cultured cells and produced mulitpolar spindles. At its half-maximal inhibitory concentration (15 nM), D5 strongly suppressed the dynamics of individual microtubules in live MCF-7 cells. D5 increased the accumulation of checkpoint proteins BubR1 and Mad2 at the kinetochoric region and caused G2/M block in these cells. The blocked cells underwent apoptosis with the activation of Jun N-terminal kinase. The results suggested that D5 exerts its antiproliferative action by dampening microtubule dynamics.
Potentiation of the activity of cisplatin in a human colon tumour xenograft model by auristatin PYE, a structural modification of dolastatin 10.[Pubmed:21472238]
Mol Med Rep. 2010 Mar-Apr;3(2):309-13.
Dolastatin 10, a marine natural product peptide, is now known to act as a vascular disrupting agent (VDA). These VDA properties were not known when other aspects of its promising pre-clinical profile led to initial unsuccessful clinical trials. Auristatin PYE, a synthetic analogue of Dolastatin 10, has demonstrated improved activity in preliminary in vivo studies. However, as with other VDAs, tumour eradication was incomplete due to the maintenance of functional vasculature supporting the viable tumour at the periphery of the tumour xenograft, meaning that once the VDA effect subsides, the tumour regrows. One possible strategy for removing this peripheral tumour involves combining VDA therapy with another anticancer drug with a different mechanism of action. Here, we evaluated the effect of combining auristatin PYE with cisplatin in an HCT-116 human colon adenocarcinoma xenograft model. The effects on the growth of subcutaneously implanted HCT-116 xenografts in mice following intraperitoneal administration of a single dose of 4 mgkg-1 cisplatin and intravenous administration of 1 mgkg-1 auristatin PYE were evaluated compared to the effect of each agent administered alone. The effects on the functional tumour vasculature were also assessed. Statistically significant potentiation (p<0.01) was noted with a 465% growth delay for the combination group compared to the control, and 142 and 310% growth delays for the cisplatin and auristatin PYE groups, respectively. Shut down of tumour vasculature in the combination group was similar to that observed with auristatin PYE on its own. Auristatin PYE demonstrated synergistic antitumour effects when combined with cisplatin, suggesting that a combination chemotherapy regimen would be the most effective strategy when applying this new anticancer drug.


