FudosteineCAS# 13189-98-5 |
- IPA-3
Catalog No.:BCC4978
CAS No.:42521-82-4
- PF-3758309
Catalog No.:BCC1853
CAS No.:898044-15-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 13189-98-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 134669 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C6H13NO3S | M.Wt | 179.24 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (557.91 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
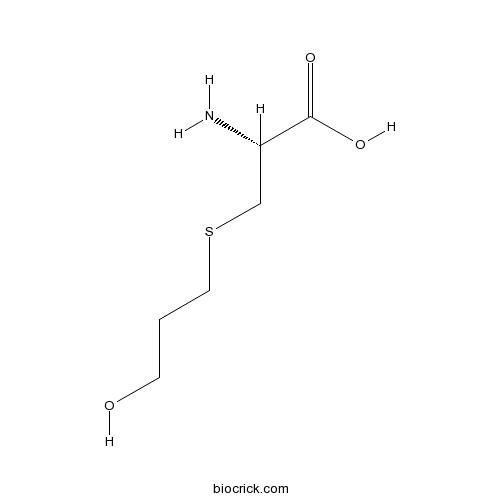
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-amino-3-(3-hydroxypropylsulfanyl)propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | N[C@@H](CSCCCO)C(O)=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KINWYTAUPKOPCQ-YFKPBYRVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C6H13NO3S/c7-5(6(9)10)4-11-3-1-2-8/h5,8H,1-4,7H2,(H,9,10)/t5-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Fudosteine is a novel mucoactive agent and a MUC5AC mucin hypersecretion inhibitor.
Target: Others
Fudosteine is a cysteine derivative that is used as an expectorant in chronic bronchial inflammatory disorders. The administration of fudosteine during the challenge with ovalbumin prevented the development of airway hyperresponsiveness and accumulation of lymphocytes in the airways. Eotaxin, IL-4, and TGF-β levels and the relative intensity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in BAL fluid were reduced by the fudosteine treatment; however, the number of eosinophils in BAL fluid and serum IgE levels did not change. The expression of TGF-β, the development of goblet cell hyperplasia, subepithelial collagenization, and basement membrane thickening were also reduced by the fudosteine treatment [1]. Fudosteine inhibits MUC5AC mucin hypersecretion by reducing MUC5AC gene expression and the effects of fudosteine are associated with the inhibition of extracellular signal-related kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in vivo and extracellular signal-related kinase in vitro [2]. References: | |||||

Fudosteine Dilution Calculator

Fudosteine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.5791 mL | 27.8956 mL | 55.7911 mL | 111.5822 mL | 139.4778 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1158 mL | 5.5791 mL | 11.1582 mL | 22.3164 mL | 27.8956 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5579 mL | 2.7896 mL | 5.5791 mL | 11.1582 mL | 13.9478 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1116 mL | 0.5579 mL | 1.1158 mL | 2.2316 mL | 2.7896 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0558 mL | 0.279 mL | 0.5579 mL | 1.1158 mL | 1.3948 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fudosteine
- 2-Hydroxyethyl Salicylate
Catalog No.:BCN3579
CAS No.:87-28-5
- (3R)-(+)-1-Benzyl-3-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)pyrrolidine
Catalog No.:BCC8389
CAS No.:131878-23-4
- Lexacalcitol
Catalog No.:BCC1704
CAS No.:131875-08-6
- (R,R)-2,6-Bis(4-isopropyl-2-oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8396
CAS No.:131864-67-0
- Aphagranin A
Catalog No.:BCN6889
CAS No.:1318173-53-3
- Cardenolide B-1
Catalog No.:BCN4714
CAS No.:1318158-89-2
- Ugaxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN6775
CAS No.:13179-11-8
- DAU 5884 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7263
CAS No.:131780-48-8
- Flavopiridol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3925
CAS No.:131740-09-5
- Urolignoside
Catalog No.:BCN6758
CAS No.:131723-83-6
- Arbidol HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3722
CAS No.:131707-23-8
- (R)-(-)-4-Benzyl-3-propionyl-2-oxazolidinone
Catalog No.:BCC8392
CAS No.:131685-53-5
- Goitrin
Catalog No.:BCN2764
CAS No.:13190-34-6
- Solanesol
Catalog No.:BCN2596
CAS No.:13190-97-1
- Paricalcitol
Catalog No.:BCC1839
CAS No.:131918-61-1
- 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-4-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-9H-Xanthen-9-one
Catalog No.:BCN1585
CAS No.:1319198-98-5
- CC0651
Catalog No.:BCC4200
CAS No.:1319207-44-7
- 3,6,19-Trihydroxy-23-oxo-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1584
CAS No.:131984-82-2
- Shizukaol A
Catalog No.:BCN6984
CAS No.:131984-98-0
- Benztropine mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4524
CAS No.:132-17-2
- Diphenylpyraline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3768
CAS No.:132-18-3
- Pheniramine Maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4700
CAS No.:132-20-7
- Benzydamine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4637
CAS No.:132-69-4
- Dihydrocucurbitacin B
Catalog No.:BCN3118
CAS No.:13201-14-4
Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass/Mass Spectrometry for the Quantification of Fudosteine in Human Serum without Precolumn Derivatization.[Pubmed:25237339]
Iran J Pharm Res. 2014 Spring;13(2):441-7.
A quantitative analysis method for Fudosteine in human serum by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI/MS/MS) was established, which shows high sensitivity and selectivity. The mobile phase composition was 75% 20 mM acetic acid and 25% acetonitril, which was pumped at a flow rate of 0.40 mL/min. The overall chromatographic run time was approximately 7 min. The autosampler was set with an injection volume of 10 muL. The calibration curve was linear in the concentration range of 0.1~15.0 microg/mL. The coefficient of determination (r) was greater than 0.9998. This method has been fully validated and shown to be specific, accurate and precise. The method was simple, rapid and the sample preparation was minimal. It was successfully applied to the analysis of healthy volunteer.
Simultaneous Determination of Genotoxic Impurities in Fudosteine Drugs by GC-MS.[Pubmed:27261527]
J Chromatogr Sci. 2016 Sep;54(8):1277-81.
A simple, sensitive and reliable gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) method has been developed, optimized and validated for the simultaneous determination of 3-chloro-1-propanol (CHP), 1,3-dichloropropane (DCP), 3-chloropropylacetate (CPA) and chloropropyl hydroxypropyl ether (CHE) contents in Fudosteine, using chlorobenzene as internal standard. Efficient chromatographic separations were achieved on an Agilent J&W DB-WAXetr, 30 m long with 0.32 mm i.d., 1.0 microm particle diameter column that consists of bonded and cross-linked polyethylene glycol as a stationary phase by passing helium as the carrier gas. The analytes were extracted in dichloromethane and monitored by gas chromatography electron ionization mass spectrometry (GC-EI-MS) with selective ion monitoring (SIM) mode. The performance of the method was assessed by evaluating specificity, precision (repeatability and reproducibility), sensitivity, linearity and accuracy. The limit of detection and limit of quantification established for CHP, DCP, CPA and CHE were in the range of 0.05-0.08 microg mL(-1) and 0.10-0.17 microg mL(-1), respectively. The recoveries for CHP, DCP, CPA and CHE were in the range of 92.0-101.5%. The results proved that the method is suitable for the simultaneous determination of contents of CHP, DCP, CPA and CHE in Fudosteine.
Effect of fudosteine, a cysteine derivative, on airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation, and remodeling in a murine model of asthma.[Pubmed:23583570]
Life Sci. 2013 May 30;92(20-21):1015-23.
AIMS: Fudosteine is a cysteine derivative that is used as an expectorant in chronic bronchial inflammatory disorders. It has been shown to decrease the number of goblet cells in an animal model. This study examined the effects of Fudosteine on airway inflammation and remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. MAIN METHODS: BALB/c mice were sensitized by an intraperitoneal injection of ovalbumin (OVA), and subsequently challenged with nebulized ovalbumin three days a week for four weeks. Seventy-two hours after the fourth challenge, airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) and the cell composition of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid were assessed. Fudosteine was administered orally at 10mg/kg or 100mg/kg body weight from the first to the fourth challenge. KEY FINDINGS: We investigated the effects of Fudosteine on the development of allergic airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness after chronic allergen challenges. The administration of Fudosteine during the challenge with ovalbumin prevented the development of airway hyperresponsiveness and accumulation of lymphocytes in the airways. Eotaxin, IL-4, and TGF-beta levels and the relative intensity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in BAL fluid were reduced by the Fudosteine treatment; however, the number of eosinophils in BAL fluid and serum IgE levels did not change. The expression of TGF-beta, the development of goblet cell hyperplasia, subepithelial collagenization, and basement membrane thickening were also reduced by the Fudosteine treatment. SIGNIFICANCE: These results indicate that Fudosteine is effective in reducing airway hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation, and airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma.
Peroxynitrite elevation in exhaled breath condensate of COPD and its inhibition by fudosteine.[Pubmed:19188555]
Chest. 2009 Jun;135(6):1513-1520.
BACKGROUND: Peroxynitrite (PN) formed by the reaction of nitric oxide and superoxide is a powerful oxidant/nitrosant. Nitrative stress is implicated in COPD pathogenesis, but PN has not been detected due to a short half-life (< 1 s) at physiologic condition. Instead, 3-nitrotyrosine has been measured as a footprint of PN release. METHOD: PN was measured using oxidation of 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein (DCDHF) in exhaled breath condensate (EBC) collected in high pH and sputum cells. The PN scavenging effect was also evaluated by the same system as PN-induced bovine serum albumin (BSA) nitration. RESULTS: The mean (+/- SD) PN levels in EBC of COPD patients (7.9 +/- 3.0 nmol/L; n = 10) were significantly higher than those of healthy volunteers (2.0 +/- 1.1 nmol/L; p < 0.0001; n = 8) and smokers (2.8 +/- 0.9 nmol/L; p = 0.0017; n = 6). There was a good correlation between PN level and disease severity (FEV(1)) in COPD (p = 0.0016). Fudosteine (FDS), a unique mucolytic antioxidant, showed a stronger scavenging effect of PN than N-acetyl-cysteine on DCDHF oxidation in vitro and in sputum macrophages, and also on PN-induced BSA nitration. FDS (0.1 mmol/L) reduced PN-enhanced interleukin (IL)-1beta-induced IL-8 release and restored corticosteroid sensitivity defected by PN more potently than those induced by H(2)O(2) in A549 airway epithelial cells. CONCLUSION: This noninvasive PN measurement in EBC may be useful for monitoring airway nitrative stress in COPD. Furthermore, FDS has the potential to inhibit PN-induced events in lung by its scavenging effect.


