LuvangetinCAS# 483-92-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 483-92-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 343582 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H14O4 | M.Wt | 258.27 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
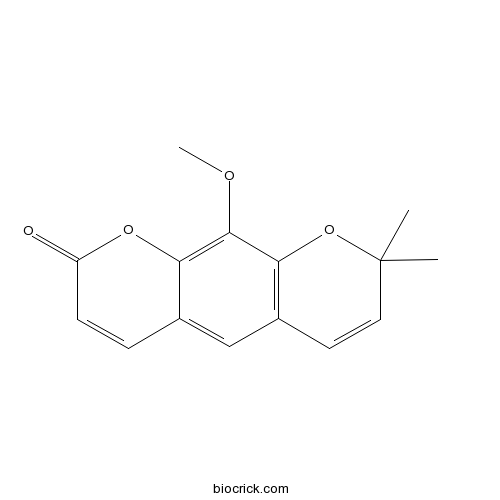
| Chemical Name | 10-methoxy-2,2-dimethylpyrano[3,2-g]chromen-8-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C=CC2=C(O1)C(=C3C(=C2)C=CC(=O)O3)OC)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XYPWCJWXFYYGPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14O4/c1-15(2)7-6-10-8-9-4-5-11(16)18-12(9)14(17-3)13(10)19-15/h4-8H,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Luvangetin can inhibit NO and PGE2 production in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells, it may have anti-inflammatory activity. 2. Luvangetin shows significant protection against pylorus-ligated and aspirin-induced gastric ulcers in rats and cold restraint stress-induced gastric ulcers in rats and guinea pigs. |
| Targets | NO | PGE | COX | Antifection |

Luvangetin Dilution Calculator

Luvangetin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8719 mL | 19.3596 mL | 38.7192 mL | 77.4383 mL | 96.7979 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7744 mL | 3.8719 mL | 7.7438 mL | 15.4877 mL | 19.3596 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3872 mL | 1.936 mL | 3.8719 mL | 7.7438 mL | 9.6798 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0774 mL | 0.3872 mL | 0.7744 mL | 1.5488 mL | 1.936 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0387 mL | 0.1936 mL | 0.3872 mL | 0.7744 mL | 0.968 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Calycanthoside
Catalog No.:BCN5580
CAS No.:483-91-0
- Toddalolactone
Catalog No.:BCN2393
CAS No.:483-90-9
- Sphondin
Catalog No.:BCN5579
CAS No.:483-66-9
- Cheilanthifoline
Catalog No.:BCN7827
CAS No.:483-44-3
- (-)-Isocorypalmine
Catalog No.:BCN2723
CAS No.:483-34-1
- Cephaeline
Catalog No.:BCC8143
CAS No.:483-17-0
- Dihydroberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2573
CAS No.:483-15-8
- 9-Hydroxycalabaxanthone hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5325
CAS No.:483-14-7
- Isorauhimbine
Catalog No.:BCN5578
CAS No.:483-09-0
- Ajmalicine
Catalog No.:BCN5577
CAS No.:483-04-5
- 14-Dehydrobrowniine
Catalog No.:BCN8109
CAS No.:4829-56-5
- Tetrahydroamentoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5571
CAS No.:48236-96-0
- SB-674042
Catalog No.:BCC1931
CAS No.:483313-22-0
- Purmorphamine
Catalog No.:BCC3641
CAS No.:483367-10-8
- N4-Benzoyl-2'-deoxycytidine
Catalog No.:BCC9071
CAS No.:4836-13-9
- N-Demethylloine
Catalog No.:BCN2004
CAS No.:4839-19-4
- Chrysophanol 1-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCC8146
CAS No.:4839-60-5
- Osthol
Catalog No.:BCN5581
CAS No.:484-12-8
- Osthenol
Catalog No.:BCN8342
CAS No.:484-14-0
- 9-Phenanthrol
Catalog No.:BCC7989
CAS No.:484-17-3
- Bergapten
Catalog No.:BCN5582
CAS No.:484-20-8
- Dictamnine
Catalog No.:BCN1273
CAS No.:484-29-7
- Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC1004
CAS No.:484-42-4
- Isodictamnine
Catalog No.:BCN7066
CAS No.:484-74-2
Antiulcer activity of naturally occurring pyrano-coumarin and isocoumarins and their effect on prostanoid synthesis using human colonic mucosa.[Pubmed:9475044]
Indian J Exp Biol. 1997 Oct;35(10):1080-3.
Oral administration of bergenin and norbergenin, two isocoumarins, isolated from the leaves and roots of Flueggea microcarpa and Luvangetin, a pyranocoumarin isolated from the seeds of Aegle marmelos Correa, showed significant protection against pylorus-ligated and aspirin-induced gastric ulcers in rats and cold restraint stress-induced gastric ulcers in rats and guinea pigs. The study on prostaglandins release by human colonic mucosal incubates, indicated a concentration-dependent (1-10 micrograms/ml) stimulatory effect of bergenin and norbergenin, while Luvangetin (1-10 micrograms/ml) did not produce any effect. The results suggest that gastroprotective effects of bergenin and norbergenin could be due to increased prostaglandin production while, some other mucosal defensive factors may be involved for Luvangetin.
Anti-inflammatory coumarins from Paramignya trimera.[Pubmed:28245363]
Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):1195-1201.
CONTEXT: Paramignya trimera (Oliv.) Burkill (Rutaceae) has been used to treat liver diseases and cancer. However, the anti-inflammatory effects of this medicinal plant and its components have not been elucidated. OBJECTIVE: This study investigated chemical constituents of the P. trimera stems and evaluated anti-inflammatory effects of isolated compounds. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Cytotoxicity of isolated compounds (5-40 muM) toward BV2 cells was tested using 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) for 24 h. Inhibitory effects of isolated compounds (5-40 muM) on nitrite and PGE2 concentrations were determined using Griess reaction and PGE2 ELISA kit, respectively (pretreated with the compounds for 3 h and then stimulated for 18 h with LPS). Inhibitory effects of compounds (5-40 muM) on iNOS and COX-2 protein expression were evaluated by Western blot analysis (pretreated with the compounds for 3 h and then stimulated for 24 h with LPS). RESULTS: Seven coumarins were isolated and identified as: ostruthin (1), ninhvanin (2), 8-geranyl-7-hydroxycoumarin (3), 6-(6',7'-dihydroxy-3',7'-dimethylocta-2'-enyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin (4), 6-(7-hydroperoxy-3,7-dimethylocta-2,5-dienyl)-7-hydroxycoumarin (5), 6-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran (6), and Luvangetin (7). Compounds 1-4 and 7 inhibited NO and PGE2 production in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells, with IC50 values ranging from 9.8 to 46.8 and from 9.4 to 52.8 muM, respectively. Ostruthin (1) and ninhvanin (2) were shown to suppress LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 protein expression. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION: The present study provides a scientific rationale for the use of P. trimera in the prevention and treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases. Ostruthin and ninhvanin might have potential therapeutic effects and should be considered for further development as new anti-neuroinflammatory agents.


