ToddalolactoneCAS# 483-90-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 483-90-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 160485 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C16H20O6 | M.Wt | 308.33 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO and methan | ||
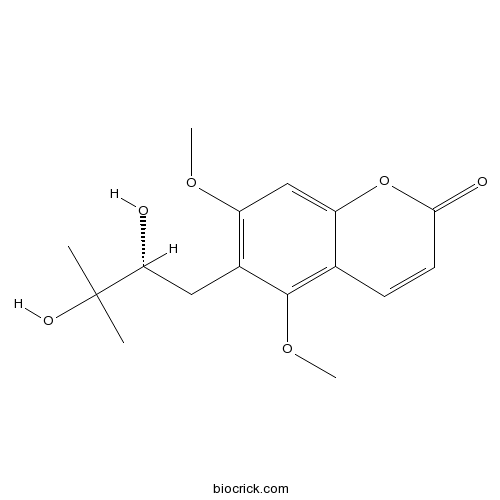
| Chemical Name | 6-[(2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutyl]-5,7-dimethoxychromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C(CC1=C(C=C2C(=C1OC)C=CC(=O)O2)OC)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GLWPLQBQHWYKRK-CYBMUJFWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H20O6/c1-16(2,19)13(17)7-10-11(20-3)8-12-9(15(10)21-4)5-6-14(18)22-12/h5-6,8,13,17,19H,7H2,1-4H3/t13-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Toddalolactone, a natural coumarin, inhibits the activity of recombinant human Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in a dose-dependent manner, yielding an IC50 value of 37.31 ± 3.23 μM. |
| Targets | PAI-1 |
| In vitro | Spasmolytic activity of Toddalia asiatica Var. floribunda.[Pubmed: 12164278 ]Phytother Res. 2002 May;16(3):281-2.The spasmolytic activity of the aerial parts of Toddalia asiatica var. floribunda (family Rutaceae) was evaluated. Inhibition of PAI-1 Activity by Toddalolactone as a Mechanism for Promoting Blood Circulation and Removing Stasis by Chinese Herb Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum.[Pubmed: 28785222 ]Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jul 21;8:489.Traditional Chinese medicine has been used to treat a variety of human diseases for many centuries. Zanthoxylum nitidum var. tomentosum is used as an adjuvant to promote blood circulation and remove stasis. However, the mechanisms of improving circulation and other biological activities of Z. nitidum var. tomentosum are still unclear. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) regulates the plasminogen activation system through inhibition of tissue-type and urokinase-type plasminogen activators (tPA and uPA). PAI-1 has been linked to fibrin deposition that evolves into organ fibrosis and atherosclerosis. |
| Structure Identification | Yakugaku Zasshi. 1991 Jul;111(7):376-85.Studies on the chemical constituents of rutaceous plants. LXVII. The chemical constituents of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. (T. aculeata Pers). Examination of coumarins using supercritical fluid and soxhlet extraction. Is toddalolactone a genuine natural co[Pubmed: 1783986]It is well known that Toddalolactone (1) is a main component of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. (T. aculeata Pers.) (Rutaceae). However, supercritical fluid (SCF) extraction of the plant by using CO2 showed that a main component of the extract was not Toddalolactone, but aculeatin (2), a coumarin having an epoxy ring on the side chain. These facts strongly suggested that Toddalolactone, corresponding to the hydrate of 2, was an artefact derived from 2 during extraction.
|

Toddalolactone Dilution Calculator

Toddalolactone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2433 mL | 16.2164 mL | 32.4328 mL | 64.8656 mL | 81.082 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6487 mL | 3.2433 mL | 6.4866 mL | 12.9731 mL | 16.2164 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3243 mL | 1.6216 mL | 3.2433 mL | 6.4866 mL | 8.1082 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0649 mL | 0.3243 mL | 0.6487 mL | 1.2973 mL | 1.6216 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0324 mL | 0.1622 mL | 0.3243 mL | 0.6487 mL | 0.8108 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sphondin
Catalog No.:BCN5579
CAS No.:483-66-9
- Cheilanthifoline
Catalog No.:BCN7827
CAS No.:483-44-3
- (-)-Isocorypalmine
Catalog No.:BCN2723
CAS No.:483-34-1
- Cephaeline
Catalog No.:BCC8143
CAS No.:483-17-0
- Dihydroberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2573
CAS No.:483-15-8
- 9-Hydroxycalabaxanthone hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5325
CAS No.:483-14-7
- Isorauhimbine
Catalog No.:BCN5578
CAS No.:483-09-0
- Ajmalicine
Catalog No.:BCN5577
CAS No.:483-04-5
- 14-Dehydrobrowniine
Catalog No.:BCN8109
CAS No.:4829-56-5
- Tetrahydroamentoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5571
CAS No.:48236-96-0
- RG 108
Catalog No.:BCC1134
CAS No.:48208-26-0
- Aricine
Catalog No.:BCN5576
CAS No.:482-91-7
- Calycanthoside
Catalog No.:BCN5580
CAS No.:483-91-0
- Luvangetin
Catalog No.:BCN7527
CAS No.:483-92-1
- SB-674042
Catalog No.:BCC1931
CAS No.:483313-22-0
- Purmorphamine
Catalog No.:BCC3641
CAS No.:483367-10-8
- N4-Benzoyl-2'-deoxycytidine
Catalog No.:BCC9071
CAS No.:4836-13-9
- N-Demethylloine
Catalog No.:BCN2004
CAS No.:4839-19-4
- Chrysophanol 1-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCC8146
CAS No.:4839-60-5
- Osthol
Catalog No.:BCN5581
CAS No.:484-12-8
- Osthenol
Catalog No.:BCN8342
CAS No.:484-14-0
- 9-Phenanthrol
Catalog No.:BCC7989
CAS No.:484-17-3
- Bergapten
Catalog No.:BCN5582
CAS No.:484-20-8
- Dictamnine
Catalog No.:BCN1273
CAS No.:484-29-7
Spasmolytic activity of Toddalia asiatica Var. floribunda.[Pubmed:12164278]
Phytother Res. 2002 May;16(3):281-2.
The spasmolytic activity of the aerial parts of Toddalia asiatica var. floribunda (family Rutaceae) was evaluated. The ethanol extract exhibited significant spasmolytic activity and was then partitioned into five fractions. The activity was found to be concentrated only in the hexane and chloroform fractions. This activity was shown not to be due to the coumarins, Toddalolactone and toddanone, as was previously thought.
[Studies on the chemical constituents of rutaceous plants. LXVII. The chemical constituents of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. (T. aculeata Pers). Examination of coumarins using supercritical fluid and soxhlet extraction. Is toddalolactone a genuine natural coumarin?].[Pubmed:1783986]
Yakugaku Zasshi. 1991 Jul;111(7):376-85.
It is well known that Toddalolactone (1) is a main component of Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam. (T. aculeata Pers.) (Rutaceae). However, supercritical fluid (SCF) extraction of the plant by using CO2 showed that a main component of the extract was not 1, but aculeatin (2), a coumarin having an epoxy ring on the side chain. The same result was obtained from Soxhlet extraction by using aprotic solvents. On the other hand, Soxhlet extraction by using methanol yielded 13, corresponding to a methanol adduct of 2, as an additional component, which was able to be also produced in 50.2% yield only by heating pure 2 in methanol, indicating that the epoxy ring in 2 can be easily attacked by a weak nucleophile like methanol. These facts strongly suggested that 1, corresponding to the hydrate of 2, was an artefact derived from 2 during extraction. SCF extraction under various conditions was examined in detail by quantitative analyses of 1 and 2 by high performance liquid chromatography and the optimum condition extracting the both components was found to be at 40 degrees C and at 300 kg/cm2. The condition was applied to the plant treated with aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate in order to remove any acidic substances and 1 was still detected in the extract. Thus, it is conclude that 1 should be a genuine natural coumarin but that previous isolation of 1 as a main component resulted in an isolation of an artefact derived from 2. SCF extraction was suggested to be a useful extraction method.


