SphondinCAS# 483-66-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 483-66-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 108104 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H8O4 | M.Wt | 216.2 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
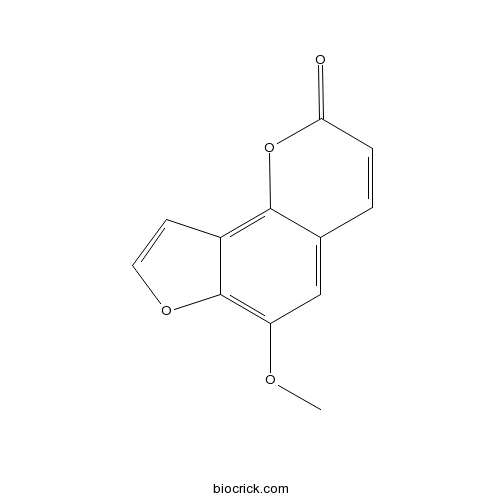
| Chemical Name | 6-methoxyfuro[2,3-h]chromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C2C(=C3C(=C1)C=CC(=O)O3)C=CO2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DLCJNIBLOSKIQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H8O4/c1-14-9-6-7-2-3-10(13)16-11(7)8-4-5-15-12(8)9/h2-6H,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Sphondin possesses an inhibitory effect on IL-1beta-induced increase in the level of COX-2 protein and PGE(2) release in A549 cells through suppression of NF-kappaB activity, it may have the therapeutic potential as an anti-inflammatory drug on airway inflammation. 2. Sphondin, 8-methoxypsoralen, and khellin have delayed phototoxic effects inAedes aegypti. 3. Sphondin has NO production inhibitory activity, due to the effect of iNOS expression, it may act as a potent inhibitor of NO production under tissue-damaging inflammatory conditions. 4. Sphondin may have anticonvulsant activity. 5. Sphondin shows anti-proliferative activity and causes G2/M arrest at concentrations of 0.05-15.0 uM, it may have anti-tumor effects. |
| Targets | COX | PGE | IL Receptor | p38MAPK | JNK | p65 | NF-kB | Chk | NO | NOS |

Sphondin Dilution Calculator

Sphondin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6253 mL | 23.1267 mL | 46.2535 mL | 92.5069 mL | 115.6337 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9251 mL | 4.6253 mL | 9.2507 mL | 18.5014 mL | 23.1267 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4625 mL | 2.3127 mL | 4.6253 mL | 9.2507 mL | 11.5634 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0925 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.9251 mL | 1.8501 mL | 2.3127 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0463 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4625 mL | 0.9251 mL | 1.1563 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cheilanthifoline
Catalog No.:BCN7827
CAS No.:483-44-3
- (-)-Isocorypalmine
Catalog No.:BCN2723
CAS No.:483-34-1
- Cephaeline
Catalog No.:BCC8143
CAS No.:483-17-0
- Dihydroberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2573
CAS No.:483-15-8
- 9-Hydroxycalabaxanthone hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5325
CAS No.:483-14-7
- Isorauhimbine
Catalog No.:BCN5578
CAS No.:483-09-0
- Ajmalicine
Catalog No.:BCN5577
CAS No.:483-04-5
- 14-Dehydrobrowniine
Catalog No.:BCN8109
CAS No.:4829-56-5
- Tetrahydroamentoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5571
CAS No.:48236-96-0
- RG 108
Catalog No.:BCC1134
CAS No.:48208-26-0
- Aricine
Catalog No.:BCN5576
CAS No.:482-91-7
- Indigo
Catalog No.:BCN1091
CAS No.:482-89-3
- Toddalolactone
Catalog No.:BCN2393
CAS No.:483-90-9
- Calycanthoside
Catalog No.:BCN5580
CAS No.:483-91-0
- Luvangetin
Catalog No.:BCN7527
CAS No.:483-92-1
- SB-674042
Catalog No.:BCC1931
CAS No.:483313-22-0
- Purmorphamine
Catalog No.:BCC3641
CAS No.:483367-10-8
- N4-Benzoyl-2'-deoxycytidine
Catalog No.:BCC9071
CAS No.:4836-13-9
- N-Demethylloine
Catalog No.:BCN2004
CAS No.:4839-19-4
- Chrysophanol 1-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCC8146
CAS No.:4839-60-5
- Osthol
Catalog No.:BCN5581
CAS No.:484-12-8
- Osthenol
Catalog No.:BCN8342
CAS No.:484-14-0
- 9-Phenanthrol
Catalog No.:BCC7989
CAS No.:484-17-3
- Bergapten
Catalog No.:BCN5582
CAS No.:484-20-8
Delayed phototoxic effects of 8-methoxypsoralen, khellin, and sphondin inAedes aegypti.[Pubmed:24306978]
J Chem Ecol. 1986 Apr;12(4):899-914.
At concentrations up to 6.7 ppm, 8-methoxypsoralen, Sphondin, and khellin are not toxic to first-instar larvae of the mosquitoAedes aegypti. The irradiation of sensitized larvae with long-wavelength ultraviolet light did not always produce any immediate toxicity enhancement, but delayed effects were clearly visible. These were observed over the development of the organisms from first-instar larvae to adults. No adverse effects were noted when larvae were irradiated in the absence of sensitizers, or when they were placed in solutions of sensitizers which had been previously irradiated with the same light sources. 8-Methoxypsoralen was slightly more phototoxic than its isomer Sphondin. Khellin, recently reported to undergo photoinduced cyclization with DNA components, showed minimal phototoxicity in the concentration range used.
Anti-tumor effects of various furocoumarins isolated from the roots, seeds and fruits of Angelica and Cnidium species under ultraviolet A irradiation.[Pubmed:23649674]
J Nat Med. 2014 Jan;68(1):83-94.
We examined the effects on cell proliferation of 10 methoxyfurocoumarins and 7 dihydrofurocumarins isolated from Umbelliferae medicinal plants, and their mechanisms of action against B16F10 melanoma cells or in melanin-possessing hairless mice implanted with B16F10 melanoma cells, under UVA irradiation. Furocoumarins having a methoxy group, such as bergapten (1), xanthotoxin (2), phellopterin (4), byakangelicin (6), neobyakangelicin (8), isobergapten (9) and Sphondin (10), showed anti-proliferative activity and caused G2/M arrest at concentrations of 0.05-15.0 muM. The 7 dihydrofurocoumarins had no effect. UVA plus 1, 2, 4, 6 and sec-O-acetylbyakagelicin (7), having one methoxy group at the C-5 position and a linear-type conformation, reduced tumor growth and final tumor weight in B16F10-bearing mice at 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection). UVA plus 1 and 2 increased Chk1 phosphorylation and decreased cdc2 (Thr 161) phosphorylation in the melanoma cells. The anti-tumor actions of UVA plus furocoumarins having a methoxy group might be due to the arrest of the cell cycle at G2/M through an increase in phospho-Chk1 and reduction in phospho-cdc2.
Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors of Chinese herbs. Part 2: naturally occurring furanocoumarins.[Pubmed:11131161]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2000 Dec;8(12):2701-7.
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-dependent production of nitric oxide (NO) plays an important role in inflammation. The effects of various naturally occurring furanocoumarins on NO production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells were evaluated in vitro. The results showed that angelicin, pimpinellin, Sphondin, byakangelicol, oxypeucedanin, oxypeucedanin hydrate, xanthotoxin, and cnidilin are potential NO production inhibitors, and their IC50 values for inhibition of nitrite production were 19.5, 15.6, 9.8, 16.9, 16.8, 15.8, 16.6, and 17.7 microg/mL, respectively. Distinct structure-activity relationships were also revealed for the NO production inhibitory activities of these furanocoumarins. Activities of the angelicin type such as pimpinellin and Sphondin were more potent than those of the psoralen type. Presence of a methoxy at the C6 position in the angelicin type seemed to be essential to augment the activity. Western blot analysis demonstrated that only Sphondin dose-dependently inhibited the expression of the iNOS protein at 2.5-20 microg/mL. However, iNOS enzyme activity was stimulated with LPS for 12 h and Sphondin was administered (20 microg/mL) for 24 h, which did not reasonably inhibit iNOS enzyme activity. L-NAME (100 microM), a known specific inhibitor of iNOS, was employed as a positive control with the same protocol and showed more than 50% inhibition activity. The results demonstrate that the NO production inhibitory activity of Sphondin is due to the effect of iNOS expression, but not by direct inhibition of iNOS enzyme activity. Thus, Sphondin may act as a potent inhibitor of NO production under tissue-damaging inflammatory conditions.
Effects of sphondin, isolated from Heracleum laciniatum, on IL-1beta-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells.[Pubmed:12417253]
Life Sci. 2002 Nov 29;72(2):199-213.
Recently, under large-scale screening experiments, we found that Sphondin, a furanocoumarin derivative isolated from Heracleum laciniatum, possessed an inhibitory effect on IL-1beta-induced increase in the level of COX-2 protein and PGE(2) release in A549 cells. Accordingly, we examined in the present study the action mechanism of Sphondin on the inhibition of IL-1beta-induced COX-2 protein expression and PGE(2) release in a human pulmonary epithelial cell line (A549). Pretreatment of cells with Sphondin (10-50 microM) concentration-dependently attenuated IL-1beta-induced COX-2 protein expression and PGE(2) release. The IL-1beta-induced increase in COX-2 mRNA expression was also attenuated by Sphondin (50 microM). The selective COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398 (0.01-1 microM), inhibited the activity of the COX-2 enzyme in a concentration-dependent manner, while Sphondin (10-50 microM) had no effect. Sphondin (50 microM) did not affect the IL-1beta-induced activations of p44/42 MAPK, p38 MAPK, and JNK. Treatment of cells with Sphondin (50 microM) or the NF-kappaB inhibitor, PDTC (50 microM) partially inhibited IL-1beta-induced degradation of IkappaB-alpha in the cytosol and translocation of p65 NF-kappaB from the cytosol to the nucleus. Furthermore, IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB-specific DNA-protein complex formation in the nucleus was partially inhibited by Sphondin (50 microM) or PDTC (50 microM). Taken together, we demonstrate that Sphondin inhibits IL-1beta-induced PGE(2) release in A549 cells; this inhibition is mediated by suppressing of COX-2 expression, rather than by inhibiting COX-2 enzyme activity. The inhibitory mechanism of Sphondin on IL-1beta-induced COX-2 expression may be, at least in part, through suppression of NF-kappaB activity. We conclude that Sphondin may have the therapeutic potential as an anti-inflammatory drug on airway inflammation.
Phototoxicity from furocoumarins (psoralens) of Heracleum laciniatum in a patient with vitiligo. Action spectrum studies on bergapten, pimpinellin, angelicin and sphondin.[Pubmed:6627920]
Contact Dermatitis. 1983 Sep;9(5):364-6.
Investigations on light reactions in a patient with vitiligo are presented. The minimal erythema dose (MED) in the UVB area was approximately 1/3 of that in persons of skin type II. The application of furocoumarins (psoralens) increased light tolerance by 1 MED at 300-310 nm. Action spectrum studies with furocoumarins from Heracleum laciniatum showed the following order of potency: bergapten, pimpinellin, angelicin and Sphondin. The efficacy was highest at 325-350 nm, with maxima at 330-335 nm. Pimpinellin was recently found to be phototoxic, but an action spectrum of Sphondin is reported for the first time.


