MK 571leukotriene D4 receptor antagonist, orally active CAS# 115104-28-4 |
- Zafirlukast
Catalog No.:BCC4881
CAS No.:107753-78-6
- MK 571
Catalog No.:BCC7334
CAS No.:115104-28-4
- LY 255283
Catalog No.:BCC7290
CAS No.:117690-79-6
- Cinalukast
Catalog No.:BCC7244
CAS No.:128312-51-6
- Leukotriene B4
Catalog No.:BCC7322
CAS No.:71160-24-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 115104-28-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281888 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H27ClN2O3S2 | M.Wt | 515.09 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | L-660711 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
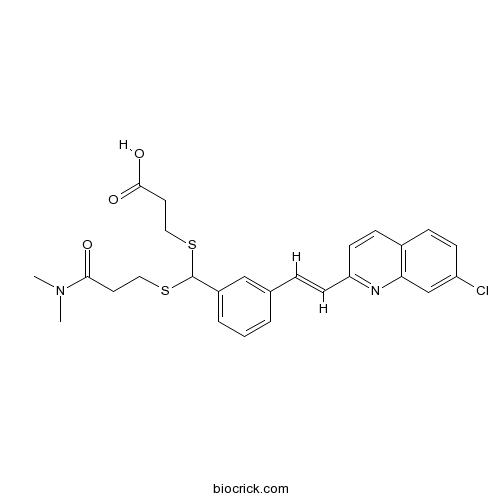
| Chemical Name | 3-[[3-[(E)-2-(7-chloroquinolin-2-yl)ethenyl]phenyl]-[3-(dimethylamino)-3-oxopropyl]sulfanylmethyl]sulfanylpropanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)C(=O)CCSC(C1=CC=CC(=C1)C=CC2=NC3=C(C=CC(=C3)Cl)C=C2)SCCC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AXUZQJFHDNNPFG-UXBLZVDNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H27ClN2O3S2/c1-29(2)24(30)12-14-33-26(34-15-13-25(31)32)20-5-3-4-18(16-20)6-10-22-11-8-19-7-9-21(27)17-23(19)28-22/h3-11,16-17,26H,12-15H2,1-2H3,(H,31,32)/b10-6+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent CysLT1 (LTD4) leukotriene receptor inverse agonist (EC50 = 1.3 nM). Antagonizes LTD4-induced contractions of guinea pig trachea and ileum (pA2 values are 9.4 and 10.5 respectively). Also inhibitor of multidrug resistance protein-1 (MRP1) mediated transport; in vitro augments the effects of cytotoxic agents on malignant cells. |

MK 571 Dilution Calculator

MK 571 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9414 mL | 9.707 mL | 19.4141 mL | 38.8282 mL | 48.5352 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3883 mL | 1.9414 mL | 3.8828 mL | 7.7656 mL | 9.707 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1941 mL | 0.9707 mL | 1.9414 mL | 3.8828 mL | 4.8535 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0388 mL | 0.1941 mL | 0.3883 mL | 0.7766 mL | 0.9707 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0194 mL | 0.0971 mL | 0.1941 mL | 0.3883 mL | 0.4854 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
MK 571 (L-660,711) is a novel potent and selective antagonist of leukotriene D4 receptor with Ki values of 0.22 nM and 2.1 nM in guinea pig and human lung membranes, respectively [1]. MK 571 is also a specific inhibitor of the multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) [2].
Leukotriene D4 (LTD4) is one of the leukotrienes and is released by basophils. LTD4 induces the contraction of smooth muscle and increases vascular permeability. Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 (cysLT1 receptor, LTD4 receptor) is a G protein-coupled receptor activated by LTD4 [3].
MK 571 (L-660,711) is a potent, selective and orally active leukotriene D4 receptor antagonist. MK 571 competitively antagonized contractions of guinea pig trachea and ileum induced by LTD4 (pA2 values, 9.4 and 10.5) and LTE4 (pA2 values, 9.1 and 10.4) , and antagonized contractions of human trachea induced by LTD4 with pA2 value of 8.5 [1].
In anesthetized guinea pigs, MK 571 antagonized bronchoconstriction induced by LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 [1]. In mice, MK 571 (1, 10, 100 mg/kg) inhibited inflammatory cell infiltration in the bronchoalveolar lavage in a dose-dependent way with maximal inhibition of 90%. MK 571 also inhibited bronchial hyperreactivity and reduced lung microvascular leakage by 22% at 10 mg/kg [3].
References:
[1]. Jones TR, Zamboni R, Belley M, et al. Pharmacology of L-660,711 (MK-571): a novel potent and selective leukotriene D4 receptor antagonist. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 1989, 67(1): 17-28.
[2]. Vellenga E, Tuyt L, Wierenga BJ, et al. Interleukin-6 production by activated human monocytic cells is enhanced by MK-571, a specific inhibitor of the multi-drug resistance protein-1. Br J Pharmacol, 1999, 127(2): 441-448.
[3]. Blain JF, Sirois P. Involvement of LTD(4) in allergic pulmonary inflammation in mice: modulation by cysLT(1)antagonist MK-571. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 2000, 62(6): 361-368.
- MK-571 sodium salt hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC8076
CAS No.:115103-85-0
- Tiagabine
Catalog No.:BCC5243
CAS No.:115103-54-3
- Carmoxirole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7278
CAS No.:115092-85-8
- Soyacerebroside II
Catalog No.:BCN6029
CAS No.:115074-93-6
- CNQX
Catalog No.:BCC6569
CAS No.:115066-14-3
- Desmethylxanthohumol
Catalog No.:BCN2997
CAS No.:115063-39-3
- 29-Norcycloart-23-ene-3,25-diol
Catalog No.:BCN4727
CAS No.:115040-04-5
- Pseudolaric acid D
Catalog No.:BCN6028
CAS No.:115028-67-6
- SR 16584
Catalog No.:BCC6176
CAS No.:1150153-86-8
- Icariside F2
Catalog No.:BCN6435
CAS No.:115009-57-9
- Cyclo(L-Leu-trans-4-hydroxy-L-Pro)
Catalog No.:BCN3994
CAS No.:115006-86-5
- 9-Phenylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN2259
CAS No.:1150-62-5
- Antagonist G
Catalog No.:BCC5858
CAS No.:115150-59-9
- Boc-D-Lys(Fmoc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3422
CAS No.:115186-31-7
- 6-Epiharpagoside
Catalog No.:BCN3981
CAS No.:1151862-67-7
- Caprarioside
Catalog No.:BCN7278
CAS No.:1151862-69-9
- ICI 199,441 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6792
CAS No.:115199-84-3
- Z-Asp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2793
CAS No.:1152-61-0
- Z-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2760
CAS No.:1152-62-1
- 8-pCPT-2-O-Me-cAMP-AM
Catalog No.:BCC6305
CAS No.:1152197-23-3
- VX-661
Catalog No.:BCC1241
CAS No.:1152311-62-0
- Dofetilide
Catalog No.:BCC3770
CAS No.:115256-11-6
- A 1120
Catalog No.:BCC7775
CAS No.:1152782-19-8
- 3-Bromo-N-phenylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN2260
CAS No.:1153-85-1
Hepatic Warm Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Increase in Pulmonary Capillary Filtration Is Ameliorated by Administration of a Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 1 Inhibitor and Leukotriene D4 Antagonist (MK-571) Through Reducing Neutrophil Infiltration and Pulmonary Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rats.[Pubmed:26036526]
Transplant Proc. 2015 May;47(4):1087-91.
BACKGROUND: Hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) is the major complication subsequent to liver ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury after resection or transplantation of liver. Hallmarks of HPS include increases in pulmonary leukotrienes and neutrophil recruitment and infiltrating across capillaries. We aimed to investigate the protective efficacy of MK-571, a multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 inhibitor and leukotriene D4 agonist, against hepatic I/R injury-associated change in capillary filtration. METHODS: Eighteen Sprague-Dawley male rats were evenly divided into a sham-operated group, a hepatic I/R group, and an MK-571-treated I/R group. MK-571 was administered intraperitoneally 15 min before hepatic ischemia and every 12 hours during reperfusion. Ischemia was conducted by occluding the hepatic artery and portal vein for 30 min, followed by removing the clamps and closing the incision. Forty-eight hours after hepatic ischemia, we assessed the pulmonary capillary filtration coefficient (Kfc) through the use of in vitro-isolated, perfused rat lung preparation. We also measured the lung wet-to-dry weight ratio (W/D) and protein concentration in broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (PCBAL). Lung inflammation and oxidative stress were evaluated by use of tissue tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and malondialdehyde levels and lavage differential macrophage and neutrophil cell count. RESULTS: Hepatic I/R injury markedly increased Kfc, W/D, PCBAL, tissue TNF-alpha level, and differential neutrophil cell count (P < .05). MK-571 treatment reduced neutrophil infiltration and lung inflammation and improved pulmonary capillary filtration, collectively suggesting lung protection. CONCLUSIONS: Treatment with MK-571 before and during hepatic ischemia and reperfusion protects lung against pulmonary capillary barrier function impairment through decreasing pulmonary lung inflammation and lavage neutrophils.
MK-571 attenuates kidney ischemia and reperfusion-induced airway hypersensitivity in rats.[Pubmed:24815144]
Transplant Proc. 2014 May;46(4):1127-30.
OBJECTIVE: Reperfusion of the rat kidney has been shown to up-regulate cysteinyl leukotriene-1 receptor, an asthma-associated gene in human bronchioles, and increase expression of leukotriene D4. In this study, we aimed to investigate the efficacy of MK-571, a leukotriene D4 inhibitor, against hypersensitivity induced by kidney ischemia and reperfusion (I/R)-associated acute kidney injury. METHODS: Sprague-Dawley male rats were divided into 3 study groups: a sham-operated group, a kidney I/R group, and a group treated with MK-571 before the kidney I/R injury: MK-571 (5 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally 15 minutes before ischemia and every 12 hours after reperfusion up to 24 hours. Ischemia was conducted by bilateral occlusion of renal pedicles for 45 minutes, followed by releasing the clamps and closing the abdominal incision. Respiratory function was tested 24 hours after reperfusion, with the use of a 2-chamber whole body plethysmograph for conscious rats. Blood samples, pulmonary bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and lung tissues were collected at the end of study. In 10 rats, urine was collected at baseline and the end of study. RESULTS: Compared with the sham group, kidney I/R injury markedly increased enhanced pause (Penh) index during methacholine challenge test (P < .05), suggesting airway hypersensitivity; it also increased in inflammatory response and levels of hydroxyl radical production and lipid peroxidation in the lungs. In contrast, in MK-571-treated rats, Penh was muted during methacholine challenge test (P < .05). CONCLUSIONS: Kidney I/R injury induces airway hypersensitivity to methacholine challenge test and inflammatory response and oxidative stress in the lungs. Treatment with MK-571, a leukotriene D4 inhibitor, effectively attenuates airway hypersensitivity, pulmonary inflammatory response, and lung and kidney injury.
The effect of probenecid and MK-571 on the feto-maternal transfer of saquinavir in dually perfused human term placenta.[Pubmed:19454316]
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2009 Jul 12;37(5):588-92.
Human placenta, particularly the blood-placenta barrier, with various transporters has crucial role to protect the fetus and, on the other hand, to facilitate movement of compounds towards the fetal circulation. This study aimed to characterize the role of basal transporters of the syncytiotrophoblast, which appear to be yet less studied, in the fetal-to-maternal transfer of saquinavir by use of dually perfused human placentas. A dual perfusion of human placenta was performed to study effect of MK-571 and probenecid, inhibitors of the MRP1 and OATP transporters, expressed in the basal trophoblast membrane, on the transfer of saquinavir. The fetal-to-maternal placental transfer of saquinavir in the control group as measured by TPT(AUC)% (absolute fraction of the dose crossing placenta) was 14.0%, which is 73% less than the transfer of the freely diffusible antipyrine. The two inhibitors, MK-571 and probenecid caused a non-significant (P = 0.34 for ANOVA) reduction of 43% and 24%, respectively, in the mean amount of saquinavir transferred from the fetal to the maternal side. MK-571 also somewhat (by 31%) reduced the TPT(AUC)% of antipyrine, but this finding did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.25). Neither of the employed inhibitors had an effect on the placental transfer index of saquinavir transfer (P = 0.77). The present results indicated lack of significant effect by MK-571 and probenecid on the fetal-to-maternal transfer of saquinavir and suggest that MRP1 and, possibly, OATP2B1 do not play a significant role in the fetal-to-maternal transfer of saquinavir.
Expression levels of multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4) in human leukemia and lymphoma cell lines, and the inhibitory effects of the MRP-specific inhibitor MK-571 on methotrexate distribution in rats.[Pubmed:23181130]
Exp Ther Med. 2012 Sep;4(3):524-532.
In the development of anti-blood cancer drugs, the chronic myelocytic leukemia (KU812), acute myelocytic leukemia (KG-1) and lymphoma (U937) cell lines are commonly used in preclinical pharmacology studies as human cancer xenograft models in mice. In the present study, mRNA expression levels of typical human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in these human blood cancer cell lines were analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Based on the results, the expression level of multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4) was found to be extremely high in KU812 cells compared with those of other transporters. Additionally, MRP4 expression levels were found to be relatively high in U937, KG-1 and a blood cell line derived from a healthy subject (RPMI 1788). In addition, to elucidate the contribution of MRP4 to the methotrexate (MTX) distribution in normal blood cells and tissues, [(3)H]MTX was intravenously (i.v.) administered to two groups of rats. Animals in one group received [(3)H]MTX only; the other group was concomitantly administered i.v. MK-571, a typical inhibitor of MRP transporters. No marked difference was observed between the two groups; the Kp values (tissue concentration/plasma concentration) of the concomitant group showed slightly higher values compared with those of the MTX alone group in erythrocytes (1.4 times, P<0.001), spleen (1.3 times, P<0.05) and thymus (1.2 times, P<0.05), respectively. Although in the present study we could not evaluate the direct involvement of MRP4 in blood cancer cells in which MRP4 expression was excessively high, these results suggest a possible functional role of MRP4 in blood cancer cells and albeit only slightly in normal blood cells/tissues.
Inverse agonist activity of selected ligands of the cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor 1.[Pubmed:14718577]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Apr;309(1):102-8.
Cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLTs) are associated with several inflammatory processes, including asthma. Due to this association, considerable effort has been invested in the development of antagonists to the CysLT receptors (CysLT(1)R). Many of these molecules have been shown to specifically interact with CysLT(1)R, but little is known about their impact on the conformation of the receptor and its activity. We were especially interested in possible inverse agonist activity of the antagonists. Using a constitutively active mutant (N106A) of the human CysLT(1)R and the wild-type (WT) receptor coexpressed with the G(alphaq) subunit of the trimeric G protein, we were able to address this issue with ligands commonly used in therapy. We demonstrated that some of these molecules are inverse agonists, whereas others act as partial agonists. In cells expressing the CysLT(1)R mutant N106A exposed to Montelukast, Zafirlukast, or 3-[[3-[2-(7-chloroquinolin-2-yl)vinyl]phenyl]-(2-dimethylcarbamoylethylsulfanyl)m ethylsulfanyl] propionic acid (MK571), the basal inositol phosphate production was reduced by 53 +/- 6, 44 +/- 3, and 54 +/- 4%, respectively. On the other hand, 6(R)-(4-carboxyphenylthio)-5(S)-hydroxy-7(E),9(E),11(Z),14(Z)-eicosatetraenoic acid (BayU9773) and 1-[2-hydroxy-3-propyl-4-[4-(1H-tetrazole-5-YL)-butoxy]-phenyl ethanone] (LY171883) acted as partial agonists and alpha-pentyl-3-[2-quinolinylmethoxy] benzyl alcohol (REV 5901) as a neutral antagonist. However, in cells expressing CysLT(1)R and G(alphaq), all antagonists used had inverse agonist activity. The decrease in basal inositol phosphate production by ligands with inverse agonist activity could be inhibited by a more neutral antagonist, confirming the specificity of the reaction. We demonstrate here that Montelukast, MK571, and Zafirlukast can act as inverse agonists on the human CysLT(1) receptor.
Interleukin-6 production by activated human monocytic cells is enhanced by MK-571, a specific inhibitor of the multi-drug resistance protein-1.[Pubmed:10385244]
Br J Pharmacol. 1999 May;127(2):441-8.
1. The intracellular transport of leukotriene C4 (LTC4) in hematopoietic cells such as human monocytes is controlled by an ATP dependent carrier encoded by the multidrug resistance protein1 (MRPI) gene whose function can be blocked by the compound MK-571. Since LTs play a major role in control of cytokine expression in monocytes, we questioned whether blocking of the MRPI mediated function by MK-571 might affect cytokine production. 2. MK-571 strongly enhanced IL-6 expression at mRNA and protein level in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) stimulated human monocytes giving rise to 2.0+/-0.4 (x+/-s.d.) and 5.7+/-3.5 fold induction of IL-6 protein secretion. The increase in IL-6 secretion was accompanied by an enhanced phosphorylation of p38 but not of c-Jun-N terminal kinase. 3. The involvement of the kinase signalling pathways was further analysed by using SB203580 and PD98059, specific inhibitors of the p38 and ERK1/2 signalling route. MK-571 mediated upregulation of IL-6 in the presence of IL-1 was partially attenuated by SB203580 and PD98059. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrated that MK-571 did not affect the IL-1 induced DNA binding activity of Activator Protein-1 and Nuclear Factor-kappaB but rather enhanced the transactivational activity of an IL-6 promoter construct. Finally it was shown that the MK-571 mediated effects on IL-6 secretion could not be inhibited by the LT synthesis inhibitor SB203347 or by the anti-oxidant pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC). 4. These results indicate that the membrane transporter MRP1 is involved in the regulation of IL-6 expression in activated human peripheral blood monocytes.


