NGD 94-1Selective D4 receptor ligand CAS# 178928-68-2 |
- Calyculin A
Catalog No.:BCC2457
CAS No.:101932-71-2
- Calcineurin Autoinhibitory Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2456
CAS No.:148067-21-4
- DL-AP3
Catalog No.:BCC2459
CAS No.:20263-06-3
- Ceramide
Catalog No.:BCC2458
CAS No.:3102-57-6
- Fostriecin sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2460
CAS No.:87860-39-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 178928-68-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 188942 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H20N6 | M.Wt | 320.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. HCl and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
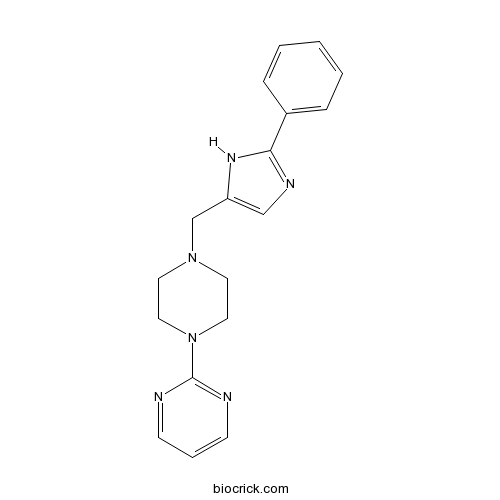
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-[(2-phenyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl]pyrimidine | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCN1CC2=CN=C(N2)C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=NC=CC=N4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OTVQCHUIPJYASM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H20N6/c1-2-5-15(6-3-1)17-21-13-16(22-17)14-23-9-11-24(12-10-23)18-19-7-4-8-20-18/h1-8,13H,9-12,14H2,(H,21,22) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | High affinity D4 receptor ligand; selective over D1, D2, D3 and D5 receptors. Displays antagonist activity at the human D4.2 receptor (Ki = 3.6 nM in transfected CHO cells) and exhibits agonist activity at the D4.4 receptor in HEK 293 cells. |

NGD 94-1 Dilution Calculator

NGD 94-1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1212 mL | 15.606 mL | 31.212 mL | 62.4239 mL | 78.0299 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6242 mL | 3.1212 mL | 6.2424 mL | 12.4848 mL | 15.606 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3121 mL | 1.5606 mL | 3.1212 mL | 6.2424 mL | 7.803 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0624 mL | 0.3121 mL | 0.6242 mL | 1.2485 mL | 1.5606 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0312 mL | 0.1561 mL | 0.3121 mL | 0.6242 mL | 0.7803 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Salviaflaside
Catalog No.:BCN8330
CAS No.:178895-25-5
- Myricadiol
Catalog No.:BCN1135
CAS No.:17884-88-7
- Vitexolide D
Catalog No.:BCN6739
CAS No.:1788090-69-6
- SNC 162
Catalog No.:BCC7103
CAS No.:178803-51-5
- 12-Hydroxyisobakuchiol
Catalog No.:BCN3609
CAS No.:178765-55-4
- 3-Hydroxybakuchiol
Catalog No.:BCN3610
CAS No.:178765-54-3
- Delta3,2-Hydroxylbakuchiol
Catalog No.:BCN3707
CAS No.:178765-49-6
- Agrocybenine
Catalog No.:BCN4755
CAS No.:178764-92-6
- rel-(8R,8'R)-dimethyl-(7S,7'R)-bis(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)tetrahydro-furan
Catalog No.:BCN1521
CAS No.:178740-32-4
- CFM-2
Catalog No.:BCC6931
CAS No.:178616-26-7
- U-104
Catalog No.:BCC2312
CAS No.:178606-66-1
- Oleoside
Catalog No.:BCN1134
CAS No.:178600-68-5
- 3-(4-Pyridyl)-Alanine
Catalog No.:BCC2651
CAS No.:178933-04-5
- FT-207 (NSC 148958)
Catalog No.:BCC4455
CAS No.:17902-23-7
- CPCCOEt
Catalog No.:BCC6896
CAS No.:179067-99-3
- PHCCC
Catalog No.:BCC6895
CAS No.:179068-02-1
- H-Asp(OtBu)-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2893
CAS No.:1791-13-5
- Curzerene
Catalog No.:BCN2352
CAS No.:17910-09-7
- N-Arachidonylglycine
Catalog No.:BCC7069
CAS No.:179113-91-8
- Myricitrin
Catalog No.:BCN1136
CAS No.:17912-87-7
- Zearalenone
Catalog No.:BCC7831
CAS No.:17924-92-4
- Src I1
Catalog No.:BCC7733
CAS No.:179248-59-0
- Sugetriol 6,9-diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6960
CAS No.:17928-63-1
- Bortezomib (PS-341)
Catalog No.:BCC1238
CAS No.:179324-69-7
II. Localization and characterization of dopamine D4 binding sites in rat and human brain by use of the novel, D4 receptor-selective ligand [3H]NGD 94-1.[Pubmed:9262371]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Aug;282(2):1020-7.
The dopamine D4 selective ligand, [H]NGD 94-1, was used in these studies to characterize binding sites in rat and human brain tissue by membrane binding and autoradiography techniques. Autoradiographic analysis of rat brain showed that specific [3H]NGD 94-1 binding was greatest in entorhinal cortex, lateral septal nucleus, hippocampus and the medial preoptic area of the hypothalamus. This nonstriatal distribution of [3H]NGD 94-1 binding was distinct from the autoradiographic distribution of dopamine D2 and D3 receptor subtypes. In homogenate preparations from rat brain regions, [3H]NGD 94-1 binding sites were low in density (<30.0 fmol/mg protein). The low density of D4 binding sites was corroborated by autoradiographic comparisons in which binding density for D4 receptors as measured by [3H]NGD 94-1 was only 1/7 of D2 and 1/5 of D3 receptor densities, despite corrections for differing radioligand binding characteristics. Pharmacological evaluation showed high affinity at rat [3H]NGD 94-1 binding sites for compounds with known D4 receptor affinity and little displacement by compounds with affinity for dopamine D1/D2/D3 receptor subtypes. Specific, high-affinity [3H]NGD 94-1 binding was also present in several human brain regions, including hippocampus, hypothalamus, dorsal medial thalamus, entorhinal cortex, prefrontal cortex and lateral septal nucleus. High-affinity [3H]NGD 94-1 binding was not present in any human striatal region examined. The pharmacological profile of [3H]NGD 94-1 binding sites in human brain was consistent with that previously demonstrated for cloned human D4 receptors expressed in mammalian cells. These findings suggest that specific, high-affinity [3H]NGD 94-1 binding exists in rat and human brain and that these sites reflect populations of dopamine D4 receptors with a distribution unique among dopamine receptor subtypes.
Direct determination of dopamine D4 receptors in normal and schizophrenic postmortem brain tissue: a [3H]NGD-94-1 study.[Pubmed:9857979]
Mol Psychiatry. 1998 Nov;3(6):528-33.
Using an indirect subtraction binding technique and human postmortem tissue, several laboratories reported finding increases in dopamine D4 receptors in caudate nuclei of schizophrenic patients, although others have not replicated these findings. NGD-94-1 is a selective D4 antagonist with low affinity for the D2 and D3 receptors. [3H]NGD-94-1 has been used in this study to directly determine the density of D4 receptors in normals (n = 13) and schizophrenic subjects (n = 7) off antipsychotic drugs for at least 3 months prior to death, or on antipsychotic (n = 7) drugs at the time of death. Human postmortem coronal brain sections were incubated with [3H]NGD-94-1 and autoradiograms developed; and binding in pertinent regions was quantified. In normals, the highest density of [3H]NGD-94-1 binding was in the hippocampus (68 fmol mg(-1), temporal (33), insular (30), and entorhinal cortices (24.9). Significant increases in [3H]NGD-94-1 density in schizophrenics (n = 14) vs normals (n = 13) were observed in the entorhinal cortex (46%) at both low and high magnifications. The increases observed in the schizophrenics were found in both schizophrenics off antipsychotic drugs for at least 3 months prior to death and those on antipsychotic drugs at the time of death. Thus, the changes may be disease-related and not a consequence of pharmacological treatment. No significant differences were found between the two schizophrenic groups in any brain area studied.
NGD 94-1 as an agonist at human recombinant dopamine D4.4 receptors expressed in HEK293 cells.[Pubmed:10395031]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 May 21;372(3):R9-10.
The atypical antipsychotic, clozapine has some selectivity for dopamine D4 receptors and is a silent antagonist at these receptors. NGD 94-1 (2-phenyl-4(5)-[4-(2-pyrimidinyl)-piperazin-1-yl-methyl]-imidazole ) is a highly selective dopamine D4 receptor ligand recently introduced as a putative antipsychotic mimicking the dopamine D4 receptor antagonist effects of clozapine. We show that NGD 94-1 is not silent. It behaved as an agonist in human embryonic kidney 293 cells expressing human recombinant dopamine D4.4 receptors. This questions the clinical use of NGD 94-1.
I. NGD 94-1: identification of a novel, high-affinity antagonist at the human dopamine D4 receptor.[Pubmed:9262370]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Aug;282(2):1011-9.
NGD 94-1 was evaluated for selectivity and in vitro functional activity at the recombinant human D4.2 receptor stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. NGD 94-1 showed high affinity for the cloned human D4.2 receptor (Ki = 3.6 +/- 0.6 nM) and had greater than 600-fold selectivity for the D4.2 receptor subtype compared with a wide variety of monoamine or other neurotransmitter receptor or modulatory sites except for 5-HT1A and 5-HT3 receptors, in which NGD 94-1 was approximately 50- and 200-fold selective, respectively, for the D4.2 receptor. In measures of in vitro functional activity, NGD 94-1 showed an antagonist profile at the cloned human D4.2 receptor subtype. NGD 94-1 completely reversed the decrease in forskolin-stimulated cAMP levels produced by the dopamine receptor full agonist quinpirole. Furthermore, NGD 94-1 produced a complete reversal of GTPgamma35S binding induced by quinpirole, but was unable on its own to affect GTPgamma35S binding. These data suggest that NGD 94-1 functions as an antagonist rather than a full or partial agonist at the human D4.2 receptor. In addition, NGD 94-1 binding affinity at the D4.2 receptor subtype was unaffected by G-protein activation by GTP, consistent with the binding affinity seen for other antagonists at the D4 receptor. The binding of tritiated NGD 94-1 was saturable and of high affinity at cloned human D4.2 receptors. Furthermore, the binding of [3H]NGD 94-1 to cloned human D4.2 receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells displayed a pharmacological profile similar to that observed with the nonselective dopamine receptor ligand [3H]YM 09151-2. Saturation and pharmacological analyses of [3H]NGD 94-1 binding at cloned human D4.2, D4.4 and D4.7 receptor variants showed no difference between the three variants. NGD 94-1 is a novel, high-affinity, D4 receptor-selective antagonist. The clinical use of this subtype-specific compound should permit direct evaluation of the role of D4 receptors in psychiatric disorders.


