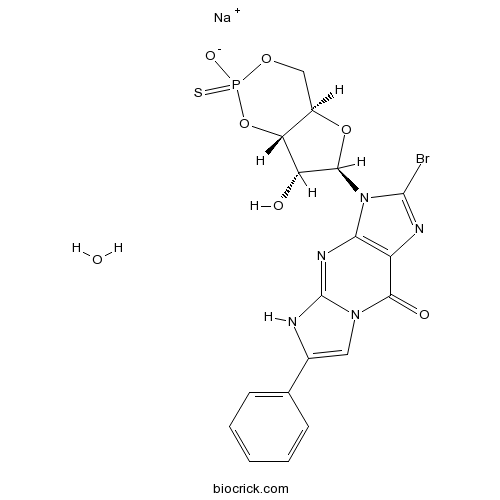
Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPSProtein kinase G inhibitor CAS# 185246-32-6 |
- Perindopril Erbumine
Catalog No.:BCC3586
CAS No.:107133-36-8
- Losartan Potassium (DuP 753)
Catalog No.:BCC1080
CAS No.:124750-99-8
- Candesartan
Catalog No.:BCC2558
CAS No.:139481-59-7
- Telmisattan
Catalog No.:BCC3863
CAS No.:144701-48-4
- Imidapril HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3792
CAS No.:89396-94-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 185246-32-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23695925 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H14BrN5NaO6PS | M.Wt | 562.27 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 20 mM in water and to 40 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;3-[(4aR,6R,7R,7aS)-7-hydroxy-2-oxido-2-sulfanylidene-4a,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-4H-furo[3,2-d][1,3,2]dioxaphosphinin-6-yl]-2-bromo-6-phenyl-5H-imidazo[1,2-a]purin-9-one;hydrate | ||
| SMILES | C1C2C(C(C(O2)N3C4=C(C(=O)N5C=C(NC5=N4)C6=CC=CC=C6)N=C3Br)O)OP(=S)(O1)[O-].O.[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PNUXBFRWMZKKAJ-IPZAVTHYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H15BrN5O6PS.Na.H2O/c19-17-21-11-14(24(17)16-12(25)13-10(29-16)7-28-31(27,32)30-13)22-18-20-9(6-23(18)15(11)26)8-4-2-1-3-5-8;;/h1-6,10,12-13,16,25H,7H2,(H,20,22)(H,27,32);;1H2/q;+1;/p-1/t10-,12-,13-,16-,31?;;/m1../s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Competitive, reversible cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor; cGMP analog. |

Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS Dilution Calculator

Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7785 mL | 8.8925 mL | 17.785 mL | 35.5701 mL | 44.4626 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3557 mL | 1.7785 mL | 3.557 mL | 7.114 mL | 8.8925 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1779 mL | 0.8893 mL | 1.7785 mL | 3.557 mL | 4.4463 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0356 mL | 0.1779 mL | 0.3557 mL | 0.7114 mL | 0.8893 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0178 mL | 0.0889 mL | 0.1779 mL | 0.3557 mL | 0.4446 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Ceplignan
Catalog No.:BCN3626
CAS No.:185244-78-4
- Loganin
Catalog No.:BCN1153
CAS No.:18524-94-2
- Scabertopin
Catalog No.:BCN4685
CAS No.:185213-52-9
- Butabindide oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7020
CAS No.:185213-03-0
- Chrysin 6-C-glucoside 8-C-arabinoside
Catalog No.:BCN1516
CAS No.:185145-34-0
- Chrysin 6-C-arabinoside 8-C-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1517
CAS No.:185145-33-9
- Ethyl 1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC8299
CAS No.:18513-76-3
- Decoquinate
Catalog No.:BCC4654
CAS No.:18507-89-6
- R 715
Catalog No.:BCC6014
CAS No.:185052-09-9
- Liquidambaric lactone
Catalog No.:BCN2301
CAS No.:185051-75-6
- Brevifolincarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3884
CAS No.:18490-95-4
- 5-Benzyl-1H-tetrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8741
CAS No.:18489-25-3
- GR 46611
Catalog No.:BCC5679
CAS No.:185259-85-2
- (R)-(+)-1,1'-Bi-2-naphthol
Catalog No.:BCC8393
CAS No.:18531-94-7
- Fmoc-3-(2-Pyridyl)-D-Alanine
Catalog No.:BCC2569
CAS No.:185379-39-9
- Fmoc-3-(2-Pyridyl)-Alanine
Catalog No.:BCC2568
CAS No.:185379-40-2
- TCS 1105
Catalog No.:BCC6087
CAS No.:185391-33-7
- O-Acetylethanolamine
Catalog No.:BCN1757
CAS No.:1854-30-4
- AF 12198
Catalog No.:BCC5812
CAS No.:185413-30-3
- Corchoionoside C
Catalog No.:BCN1154
CAS No.:185414-25-9
- Timorsaponin C
Catalog No.:BCN2899
CAS No.:185432-00-2
- ONO 2506
Catalog No.:BCC7943
CAS No.:185517-21-9
- BMS 961
Catalog No.:BCC7680
CAS No.:185629-22-5
- Viroallosecurinine
Catalog No.:BCN6743
CAS No.:1857-30-3
The commonly used cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I (cGKI) inhibitor Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS can activate cGKI in vitro and in intact cells.[Pubmed:19008225]
J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 2;284(1):556-62.
Small-molecule modulators of cGMP signaling are of interest to basic and clinical research. The cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I (cGKI) is presumably a major mediator of cGMP effects, and the cGMP analogue Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS (Rp-PET) (chemical name: beta-phenyl-1,N2-etheno-8-bromoguanosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate, Rp-isomer) is currently considered one of the most permeable, selective, and potent cGKI inhibitors available for intact cell studies. Here, we have evaluated the properties of Rp-PET using cGKI-expressing and cGKI-deficient primary vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), purified cGKI isozymes, and an engineered cGMP sensor protein. cGKI activity in intact VSMCs was monitored by cGMP/cGKI-stimulated cell growth and phosphorylation of vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein. Unexpectedly, Rp-PET (100 microm) did not efficiently antagonize activation of cGKI by the agonist 8-Br-cGMP (100 microm) in intact VSMCs. Moreover, in the absence of 8-Br-cGMP, Rp-PET (100 microm) stimulated cell growth in a cGKIalpha-dependent manner. Kinase assays with purified cGKI isozymes confirmed the previously reported inhibition of the cGMP-stimulated enzyme by Rp-PET in vitro. However, in the absence of the agonist cGMP, Rp-PET partially activated the cGKIalpha isoform. Experiments with a fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based construct harboring the cGMP binding sites of cGKI suggested that binding of Rp-PET induces a conformational change similar to the agonist cGMP. Together, these findings indicate that Rp-PET is a partial cGKIalpha agonist that under certain conditions stimulates rather than inhibits cGKI activity in vitro and in intact cells. Data obtained with Rp-PET as cGKI inhibitor should be interpreted with caution and not be used as sole evidence to dissect the role of cGKI in signaling processes.
Protein kinase G regulates the basal tension and plays a major role in nitrovasodilator-induced relaxation of porcine coronary veins.[Pubmed:17891157]
Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Dec;152(7):1060-9.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Coronary venous activity is modulated by endogenous and exogenous nitrovasodilators. The present study was to determine the role of protein kinase G (PKG) in the regulation of the basal tension and nitrovasodilator-induced relaxation of coronary veins. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: Effects of a PKG inhibitor on the basal tension and responses induced by nitroglycerin, DETA NONOate, and 8-Br-cGMP in isolated porcine coronary veins were determined. Cyclic cGMP was measured with radioimmunoassay. PKG activity was determined by measuring the incorporation of 32P from gamma-32P-ATP into the specific substrate BPDEtide. KEY RESULTS: Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS, a specific PKG inhibitor, increased the basal tension of porcine coronary veins and decreased PKG activity. The increase in tension was 38% of that caused by nitro-L-arginine. Relaxation of the veins induced by nitroglycerin and DETA NONOate was accompanied with increases in cGMP content and PKG activity. These effects were largely eliminated by inhibiting soluble guanylyl cyclase with ODQ. The increase in PKG activity induced by the nitrovasodilators was abolished by Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS. The relaxation caused by these dilators and by 8-Br-cGMP at their EC50 was attenuated by the PKG inhibitor by 51-66%. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: These results suggest that PKG is critically involved in nitric oxide-mediated regulation of the basal tension in porcine coronary veins and that it plays a primary role in relaxation induced by nitrovasodilators. Since nitric oxide plays a key role in modulating coronary venous activity, augmentation of PKG may be a therapeutic target for improving coronary blood flow.
Identification of competitive antagonists of the rod photoreceptor cGMP-gated cation channel: beta-phenyl-1,N2-etheno-substituted cGMP analogues as probes of the cGMP-binding site.[Pubmed:8988020]
Biochemistry. 1996 Dec 24;35(51):16815-23.
cGMP is the natural activator of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel originally isolated from rod photoreceptors but now known to be expressed in a wide variety of neural and non-neural cells. To identify antagonists of cGMP action and to better understand the interaction between cGMP and the channel protein, experimental studies were undertaken using four synthetic cGMP analogues, PET-cGMP, 8-Br-PET-cGMP, Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS, and Sp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS. With excised patches from either Xenopus oocytes expressing a cloned rat rod channel alpha-subunit or from native Xenopus rod photoreceptors, Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS competitively suppressed the cGMP-induced current with an IC50 of 25 microM and Sp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS inhibited this current with an IC50 of 105 microM. On the expressed rat rod channel, 8-Br-PET-cGMP behaved as a very weak partial agonist at high concentrations and an antagonist (IC50 = 64 microM) at lower concentrations when coapplied with cGMP. PET-cGMP did not activate channel currents alone but showed a synergism when coapplied with subsaturating concentrations of cGMP. Because Sp-8-Br-PET-cGMPS is a potent activator of type I cGMP-dependent protein kinase, but a competitive antagonist of channel activation, it will be a useful reagent for discriminating between those effects of cGMP that are mediated by a protein kinase and those mediated by channel activation. Because the PET derivatives all contain a phenyl-substituted 5-membered ring system fused to the amino group in position 2 and the nitrogen in position 1 of the guanine ring, the results support the idea that N1 and N2 are important for channel activation. They also suggest a minor role for the cyclic phosphate group in binding or activation.


