TC-MCH 7cSelective melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCH1R) antagonist CAS# 864756-35-4 |
- Nadifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4804
CAS No.:124858-35-1
- Calcipotriol monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1445
CAS No.:147657-22-5
- Halobetasol Propionate
Catalog No.:BCC4664
CAS No.:66852-54-8
- Dihydroartemisinin
Catalog No.:BCN6264
CAS No.:71939-50-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 864756-35-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11654412 | Appearance | Powder |
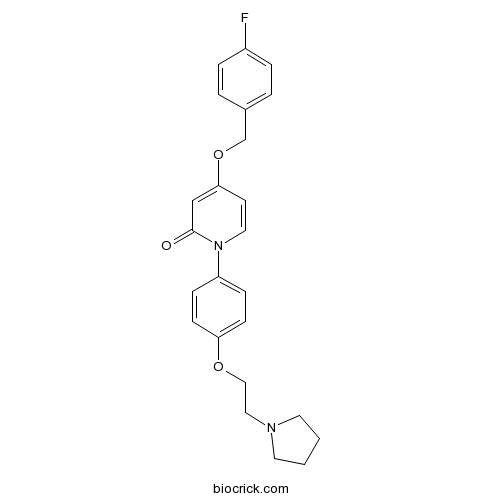
| Formula | C24H25FN2O3 | M.Wt | 408.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1eq. HCl and to 50 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy]-1-[4-(2-pyrrolidin-1-ylethoxy)phenyl]pyridin-2-one | ||
| SMILES | C1CCN(C1)CCOC2=CC=C(C=C2)N3C=CC(=CC3=O)OCC4=CC=C(C=C4)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ANCFKYJMXNMYNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H25FN2O3/c25-20-5-3-19(4-6-20)18-30-23-11-14-27(24(28)17-23)21-7-9-22(10-8-21)29-16-15-26-12-1-2-13-26/h3-11,14,17H,1-2,12-13,15-16,18H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCH1R) antagonist (IC50= 5.6 nM in hMCH1R-expressing CHO cells). Displays selectivity for MCH1R over MCH2R (IC50 = > 10 μM). Decreases body weight in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity. Brain penetrant; orally active. |

TC-MCH 7c Dilution Calculator

TC-MCH 7c Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4482 mL | 12.2408 mL | 24.4816 mL | 48.9632 mL | 61.204 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4896 mL | 2.4482 mL | 4.8963 mL | 9.7926 mL | 12.2408 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2448 mL | 1.2241 mL | 2.4482 mL | 4.8963 mL | 6.1204 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.049 mL | 0.2448 mL | 0.4896 mL | 0.9793 mL | 1.2241 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0245 mL | 0.1224 mL | 0.2448 mL | 0.4896 mL | 0.612 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- SB 699551
Catalog No.:BCC7594
CAS No.:864741-95-7
- Sequosempervirin D
Catalog No.:BCN4562
CAS No.:864719-19-7
- Sequosempervirin B
Catalog No.:BCN4777
CAS No.:864719-17-5
- Nigrolineaxanthone V
Catalog No.:BCN4411
CAS No.:864516-31-4
- Sanggenone H
Catalog No.:BCN2946
CAS No.:86450-80-8
- Sanggenone K
Catalog No.:BCN3373
CAS No.:86450-77-3
- BNTX maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6838
CAS No.:864461-31-4
- C 021 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6047
CAS No.:864289-85-0
- AMG 548
Catalog No.:BCC6084
CAS No.:864249-60-5
- GSK429286A
Catalog No.:BCC2532
CAS No.:864082-47-3
- Empagliflozin (BI 10773)
Catalog No.:BCC2472
CAS No.:864070-44-0
- ZIP
Catalog No.:BCC4003
CAS No.:863987-12-6
- Gnetucleistol B
Catalog No.:BCN3585
CAS No.:864763-60-0
- Gnetucleistol C
Catalog No.:BCN3395
CAS No.:864763-61-1
- Resminostat (RAS2410)
Catalog No.:BCC2165
CAS No.:864814-88-0
- Leojaponin
Catalog No.:BCN7381
CAS No.:864817-63-0
- BMS-663068
Catalog No.:BCC1428
CAS No.:864953-29-7
- BMS-663068 Tris
Catalog No.:BCC1429
CAS No.:864953-39-9
- Vinblastine
Catalog No.:BCN2376
CAS No.:865-21-4
- Gelsempervine A
Catalog No.:BCN3929
CAS No.:865187-17-3
- AMG837
Catalog No.:BCC6387
CAS No.:865231-46-5
- 4,5-dihydroxy-3,8-dimethylnaphthalene-1,2-dione
Catalog No.:BCN8422
CAS No.:86533-36-0
- FR 180204
Catalog No.:BCC3669
CAS No.:865362-74-9
- N-Methylcalycinine
Catalog No.:BCN4412
CAS No.:86537-66-8
Hsa-let-7c-5p augments enterovirus 71 replication through viral subversion of cell signaling in rhabdomyosarcoma cells.[Pubmed:28101327]
Cell Biosci. 2017 Jan 14;7:7.
BACKGROUND: Human enterovirus 71 (EV71) causes severe hand, foot and mouse disease, accompanied by neurological complications. During the interaction between EV71 and the host, the virus subverts host cell machinery for its own replication. However, the roles of microRNAs (miRNAs) in this process remain obscure. RESULTS: In this study, we found that the miRNA hsa-let-7c-5p was significantly upregulated in EV71-infected rhabdomyosarcoma cells. The overexpression of hsa-let-7c-5p promoted replication of the virus, and the hsa-let-7c-5p inhibitor suppressed viral replication. Furthermore, hsa-let-7c-5p targeted mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (MAP4K4) and inhibited its expression. Interestingly, downregulation of MAP4K4 expression led to an increase in EV71 replication. In addition, MAP4K4 knockdown or transfection with the hsa-let-7c-5p mimic led to activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway, whereas the hsa-let-7c-5p inhibitor inhibited activation of this pathway. Moreover, EV71 infection promoted JNK pathway activation to facilitate viral replication. CONCLUSIONS: Our data suggested that hsa-let-7c-5p facilitated EV71 replication by inhibiting MAP4K4 expression, which might be related to subversion of the JNK pathway by the virus. These results may shed light on a novel mechanism underlying the defense of EV71 against cellular responses. In addition, these findings may facilitate the development of new antiviral strategies for use in future therapies.
MiR-199a-5p and let-7c cooperatively inhibit migration and invasion by targeting MAP4K3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.[Pubmed:28099144]
Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13666-13677.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has a high recurrence rate, and patients exhibit poor survival mainly because intrahepatic metastasis is common. We previously reported that let-7c down-regulation is significantly associated with poor differentiation level in HCC. In the present study, we demonstrate that miR-199a-5p and let-7c are frequently down-regulated in HCC cells and tissues, and low expression of miR-199a-5p is correlated with tumor size, liver envelope invasion. Furthermore, miR-199a-5p and let-7c cooperatively inhibit HCC cell migration and invasion in vitro. MAP4K3 is identified as the direct target of miR-199a-5p and let-7c and this regulation is further confirmed by luciferase reporter assays and Western blotting. In addition, MAP4K3 functions as a metastasis promoter since the results demonstrate that MAP4K3 could promote HCC cell migration and invasion. We also find that miR-199a-5p and let-7c increase the sensitivity of HCC cells to sorafenib. CONCLUSIONS: We report that miR-199a-5p and let-7c cooperatively and efficiently inhibit HCC cell migration and invasion by targeting the metastasis promoter MAP4K3 and MAP4K3-mediated drug sensitization, suggesting that the use of miRNAs and sorafenib in combination therapy may be a powerful approach to the treatment of HCC.
Feedback circuitry via let-7c between lncRNA CCAT1 and c-Myc is involved in cigarette smoke extract-induced malignant transformation of HBE cells.[Pubmed:28184029]
Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):19285-19297.
Cigarette smoking is a primary risk factor for the development of lung cancer, which is regarded as the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. The process of malignant transformation of cells, however, is complex and elusive. The present study investigated the roles of an lncRNA, CCAT1, and a transcriptional factor, c-Myc, in human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cell transformation induced by cigarette smoke extract. With acute and chronic treatment of HBE cells, cigarette smoke extract induced increases of CCAT1 and c-Myc levels and decreases of levels of let-7c, a microRNA. Down-regulation of c-Myc reduced the degree of malignancy and the invasion/migration capacity of HBE cells transformed by cigarette smoke extract. ChIP assays established that c-Myc, increased by cigarette smoke extract, binds to the promoter of CCAT1, activating its transcription. Further, let-7c suppressed the expression of c-Myc through binding to its 3'-UTR. In turn, CCAT1 promoted the accumulation of c-Myc through binding to let-7c and decreasing free let-7c, which influenced the neoplastic capacity of HBE cells transformed by cigarette smoke extract. These results indicate that a positive feedback loop ensures expression of cigarette smoke extract-induced CCAT1 and c-Myc via let-7c, which is involved in cigarette smoke extract-induced malignant transformation of HBE cells. Thus, the present research establishes a new mechanism for the reciprocal regulation between CCAT1 and c-Myc and provides an understanding of cigarette smoke extract-induced lung carcinogenesis.
Circulating miR-155, miR-145 and let-7c as diagnostic biomarkers of the coronary artery disease.[Pubmed:28205634]
Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 16;7:42916.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most prevalent cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide and the number of individuals at risk is increasing. To better manage cardiovascular diseases, improved tools for risk prediction including the identification of novel accurate biomarkers are needed. MicroRNA (miRNA) are essential post-transcriptional modulators of gene expression leading to mRNA suppression or translational repression. Specific expression profiles of circulating miRNA have emerged as potential noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers of diseases. The aim of this study was to identify the potential diagnostic value of circulating miRNA with CAD. Circulating miR-145, miR-155, miR-92a and let-7c were selected and validated by quantitative PCR in 69 patients with CAD and 30 control subjects from the cross-sectional study GENES. The expression of miR-145, miR-155 and let-7c showed significantly reduced expression in patients with CAD compared to controls. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that low levels of circulating let-7c, miR-145 and miR-155 were associated with CAD. Receiver operating curves analysis showed that let-7c, miR-145 or miR-155 were powerful markers for detecting CAD. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the combination of the three circulating miRNA managed to deliver a specific signature for diagnosing CAD.
Discovery of novel phenylpyridone derivatives as potent and selective MCH1R antagonists.[Pubmed:21190859]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Jan 15;19(2):883-93.
The design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of a novel class of N-phenylpyridone MCH1R antagonists are described. The core part of the N-phenylpyridone structure was newly designed and the side chain moieties that were attached to the core part were extensively explored. As a result of optimization of the N-phenylpyridone leads, we successfully developed the orally available, and brain-penetrable MCH1R selective antagonist 7c, exhibiting excellent anti-obese effect in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice.
Melanin-concentrating hormone 1-receptor antagonist suppresses body weight gain correlated with high receptor occupancy levels in diet-induced obesity mice.[Pubmed:19836369]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 10;624(1-3):77-83.
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), which is a neuropeptide expressed in the hypothalamus of the brain, is involved in regulating feeding behavior and energy homeostasis via the MCH(1) receptor in rodents. It is widely considered that MCH(1) receptor antagonists are worthy of development for medical treatment of obesity. Here we report on the development of an ex vivo receptor occupancy assay using a new radiolabeled MCH(1) receptor antagonist, [(35)S]-compound D. An MCH(1) receptor antagonist inhibited the binding of [(35)S]-compound D to brain slices in a dose-dependent manner. The result showed a good correlation between the receptor occupancy levels and plasma or brain levels of the MCH(1) receptor antagonist, suggesting that the ex vivo receptor binding assay using this radioligand is practical. Quantitative analysis in diet-induced obese mice showed that the efficacy of body weight reduction correlated with the receptor occupancy levels at 24h. Furthermore, more than 90% occupancy levels of MCH(1) receptor antagonists during 24h post-dosing are required for potent efficacy on body weight reduction. The present occupancy assay could be a useful pharmacodynamic marker to quantitatively estimate anti-obese efficacy, and would accelerate the development of MCH(1) receptor antagonists for treatment of obesity.


