ArtocarpesinCAS# 3162-09-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3162-09-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 399491 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H18O6 | M.Wt | 354.35 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
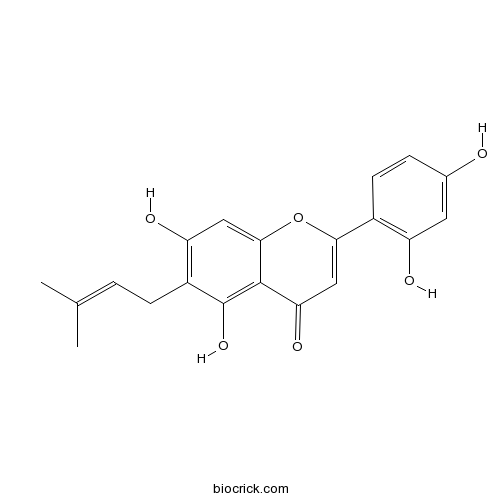
| Chemical Name | 2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-6-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCC1=C(C=C2C(=C1O)C(=O)C=C(O2)C3=C(C=C(C=C3)O)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YWUVFGZTDLJVCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H18O6/c1-10(2)3-5-13-15(23)8-18-19(20(13)25)16(24)9-17(26-18)12-6-4-11(21)7-14(12)22/h3-4,6-9,21-23,25H,5H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Artocarpesin displays cytotoxic effects at various extent on all the 9 tested cancer cell lines with IC50 values respectively below 106 uM. 2. Artocarpesin shows tyrosinase inhibitory activity. 3. Artocarpesin has interesting antimicrobial potency. 4. Artocarpesin has anti-inflammatory effects, it can suppress the LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2) through the down-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) protein expressions. |
| Targets | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | ROS | p53 | Tyrosinase | NO | NOS | PGE | COX | Antifection |

Artocarpesin Dilution Calculator

Artocarpesin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8221 mL | 14.1103 mL | 28.2207 mL | 56.4414 mL | 70.5517 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5644 mL | 2.8221 mL | 5.6441 mL | 11.2883 mL | 14.1103 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2822 mL | 1.411 mL | 2.8221 mL | 5.6441 mL | 7.0552 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0564 mL | 0.2822 mL | 0.5644 mL | 1.1288 mL | 1.411 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0282 mL | 0.1411 mL | 0.2822 mL | 0.5644 mL | 0.7055 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- SCH 442416
Catalog No.:BCC7372
CAS No.:316173-57-6
- Moroxydine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4802
CAS No.:3160-91-6
- Z-Ile-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2593
CAS No.:3160-59-6
- Z-Asp(OMe)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2790
CAS No.:3160-47-2
- Emetine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN8307
CAS No.:316-42-7
- Berberine Sulphate
Catalog No.:BCC8131
CAS No.:316-41-6
- Heraclenol
Catalog No.:BCN5234
CAS No.:31575-93-6
- 4EGI-1
Catalog No.:BCC5337
CAS No.:315706-13-9
- PTC-209
Catalog No.:BCC5111
CAS No.:315704-66-6
- JK 184
Catalog No.:BCC3936
CAS No.:315703-52-7
- STF-62247
Catalog No.:BCC4960
CAS No.:315702-99-9
- TC-DAPK 6
Catalog No.:BCC1989
CAS No.:315694-89-4
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN5235
CAS No.:3162-45-6
- 9-Anthracenylmethyl acrylate
Catalog No.:BCC8798
CAS No.:31645-34-8
- Palifosfamide
Catalog No.:BCC1833
CAS No.:31645-39-3
- 6-Aminonicotinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8764
CAS No.:3167-49-5
- Gatifloxacin mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4225
CAS No.:316819-28-0
- Pinusolide
Catalog No.:BCN5236
CAS No.:31685-80-0
- Levomefolic acid
Catalog No.:BCC1703
CAS No.:31690-09-2
- Aminophylline
Catalog No.:BCC2300
CAS No.:317-34-0
- Hesperetin 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5237
CAS No.:31712-49-9
- 5,7-Dihydroxychromone
Catalog No.:BCN4652
CAS No.:31721-94-5
- 3,5,7-Trihydroxychromone
Catalog No.:BCN7479
CAS No.:31721-95-6
- GW501516
Catalog No.:BCC2268
CAS No.:317318-70-0
Artocarpus plants as a potential source of skin whitening agents.[Pubmed:21941923]
Nat Prod Commun. 2011 Sep;6(9):1397-402.
Artocarpus plants have been a focus of constant attention due to the potential for skin whitening agents. In the in vitro experiment, compounds from the Artocarpus plants, such as artocarpanone, norartocarpetin, Artocarpesin, artogomezianol, andalasin, artocarbene, and chlorophorin showed tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Structure-activity investigations revealed that the 4-substituted resorcinol moiety in these compounds was responsible for their potent inhibitory activities on tyrosinase. In the in vitro assay, using B16 melanoma cells, the prenylated polyphenols isolated from Artocarpus plants, such as artocarpin, cudraflavone C, 6-prenylapigenin, kuwanon C, norartocarpin, albanin A, cudraflavone B, and brosimone I showed potent inhibitory activity on melanin formation. Structure-activity investigations revealed that the introduction of an isoprenoid moiety to a non-isoprenoid-substituted polyphenol enhanced the inhibitory activity of melanin production in B16 melanoma cells. In the in vivo investigation, the extract of the wood of Artocarpus incisus and a representative isolated compound from it, artocarpin had a lightening effect on the skin of guinea pigs' backs. Other in vivo experiments using human volunteers have shown that water extract of Artocarpus lakoocha reduced the melanin formation in the skin of volunteers. These results indicate that the extracts of Artocarpus plants are potential sources for skin whitening agents.
Anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the fruits of Artocarpus heterophyllus.[Pubmed:18500810]
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Jun 25;56(12):4463-8.
Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam is a large evergreen tree cultivated throughout Southeast Asia for its fruits. Its leaves and roots have been used for medicinal purposes. The aim of this work was to study the in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds isolated from the ethyl acetate extracts of the fruits of Artocarpus heterophyllus. Three phenolic compounds were characterized as Artocarpesin [5,7,2',4'-tetrahydroxy-6-(3-methylbut-3-enyl) flavone] ( 1), norartocarpetin (5,7,2',4'-tetrahydroxyflavone) ( 2), and oxyresveratrol [ trans-2,4,3',5'-tetrahydroxystilbene] ( 3) by spectroscopic methods and through comparison with data reported in the literatures. The anti-inflammatory effects of the isolated compounds ( 1- 3) were evaluated by determining their inhibitory effects on the production of proinflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells. These three compounds exhibited potent anti-inflammatory activity. The results indicated that Artocarpesin ( 1) suppressed the LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2) through the down-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) protein expressions. Thus, Artocarpesin ( 1) may provide a potential therapeutic approach for inflammation-associated disorders.
Cytotoxicity of three naturally occurring flavonoid derived compounds (artocarpesin, cycloartocarpesin and isobavachalcone) towards multi-factorial drug-resistant cancer cells.[Pubmed:26547532]
Phytomedicine. 2015 Nov 15;22(12):1096-102.
INTRODUCTION: Cancer remains an aggressive deadly disease, if drug resistance develops. This problem is aggravated by the fact that multiple rather than single mechanisms are involved in resistance and that multidrug resistance (MDR) phenomena cause inefficacy of many clinical established anticancer drugs. We are seeking for novel cytotoxic phytochemicals to combat drug-resistant tumour cells. METHODS: In the present study, we investigated the cytotoxicity of three naturally occurring flavonoids including two flavones Artocarpesin (1) and cycloArtocarpesin (2) and one chalcone, isobavachalcone (3) against 9 drug-sensitive and MDR cancer cell lines. The resazurin reduction assay was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of these compounds, whilst caspase-Glo assay was used to detect caspase activation. Cell cycle, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were all analysed via flow cytometry. RESULTS: Flavones 1 and 2 as well as chalcone 3 displayed cytotoxic effects at various extent on all the 9 tested cancer cell lines with IC50 values respectively below 106 microM, 50 microM and 25 microM. The IC50 values for the three investigational flavonoids ranged from 23.95 microM (towards hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells) to 105 microM [towards colon carcinoma HCT116 (p53(-/-)) cells] for 1, from 15.51 microM (towards leukemia CCRF-CEM cells) to 49.83 microM [towards glioblastoma U87MG.DeltaEGFR cells] for 2 and from 2.30 microM (towards CCRF-CEM cells) to 23.80 microM [towards colon carcinoma HCT116 (p53(+/+)) cells] for 3 and from 0.20 microM (towards CCRF-CEM cells) to 195.12 microM (towards leukemia CEM/ADR5000 cells) for doxorubicin. Compounds 2 and 3 induced apoptosis in CCRF-CEM leukemia cells, mediated by caspase activation and the disruption of MMP. CONCLUSIONS: The three tested flavonoids and mostly chalcone 3 are potential cytotoxic natural products that deserve more investigations to develop novel antineoplastic drugs against multifactorial drug-resistant cancers.
Isolation of tyrosinase inhibitors from Artocarpus heterophyllus and use of its extract as antibrowning agent.[Pubmed:18683821]
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 Dec;52(12):1530-8.
A new furanoflavone, 7-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4-hydroxy-2-(2-hydroxy propan-2-yl)-2, 3-dihydrofuro(3, 2-g)chromen-5-one (artocarpfuranol, 1), together with 14 known compounds, dihydromorin (2), steppogenin (3), norartocarpetin (4), artocarpanone (5), Artocarpesin (6), artocarpin (7), cycloartocarpin (8), cycloArtocarpesin (9), artocarpetin (10), brosimone I (11), cudraflavone B (12), carpachromene (13), isoArtocarpesin (14), and cyanomaclurin (15) were isolated from the wood of Artocarpus heterophyllus. Their structures were identified by interpretation of MS,( 1)H-NMR,( 13)C-NMR, HMQC, and HMBC spectroscopic data. Among them, compounds 1-6 and 14 showed strong mushroom tyrosinase inhibitory activity with IC(50) values lower than 50 microM, more potent than kojic acid (IC(50) = 71.6 microM), a well-known tyrosinase inhibitor. In addition, extract of A. heterophyllus was evaluated for its antibrowning effect on fresh-cut apple slices. It was discovered that fresh-cut apple slices treated by dipping in solution of 0.03 or 0.05% of A. heterophyllus extract with 0.5% ascorbic acid did not undergo any substantial browning reaction after storage at room temperature for 24 h. The antibrowning effect was significantly better than samples treated with the extract (0.03 or 0.05%) or ascorbic acid (0.5%) alone. The results provide preliminary evidence supporting the potential of this natural extract as antibrowning agent in food systems.
Antimicrobial activity of the methanolic extract and compounds from Morus mesozygia stem bark.[Pubmed:19450674]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jul 30;124(3):551-5.
AIM OF THE STUDY: This study was aimed at investigating the antimicrobial activity of the methanolic extract (MMB) and compounds isolated from the stem bark of Morus mesozygia, namely 3beta-acetoxyurs-12-en-11-one (1), moracin Q (2), moracin T (3), Artocarpesin (4), cycloArtocarpesin (5), moracin R (6), moracin U (8), moracin C (9), and moracin M (10). MATERIALS AND METHODS: The liquid microdilution assay was used in the determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and the minimal microbicidal concentration (MMC), against nine bacterial and two fungal species. RESULTS: The results of the MIC determination showed that the compounds 3, 4, 8 and 9 were able to prevent the growth of all tested microbial species. All other samples showed selective activities. Their inhibitory effects were noted on 90.9% studied organisms for the crude extract, 81.8% for compound 6, 72.7% for compound 10, 63.6% for compound 1, 54.5% for compound 5, and 45.5% for compound 2. The lowest MIC value of 39 microg/ml was obtained with the crude extract against Escherichia coli. The corresponding value for compounds (5 microg/ml) was registered with compound 9 on Shigella dysenteriae and compound 3 on E. coli, S. dysenteriae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhi and Bacillus cereus. The lowest MIC value (39 microg/ml) observed with the crude extract (on E. coli) was only eightfold greater than that of gentamycin used as reference antibiotic (RA) while the corresponding value (5 microg/ml) recorded with compounds 3 and 9 was equal to that of RA on the corresponding microorganisms. CONCLUSIONS: The obtained results highlighted the interesting antimicrobial potency of M. mesozygia as well as that of the studied compounds, and provided scientific basis for the traditional use of this species.


