Bz-Arg-OHCAS# 154-92-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 154-92-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 97369 | Appearance | Powder |
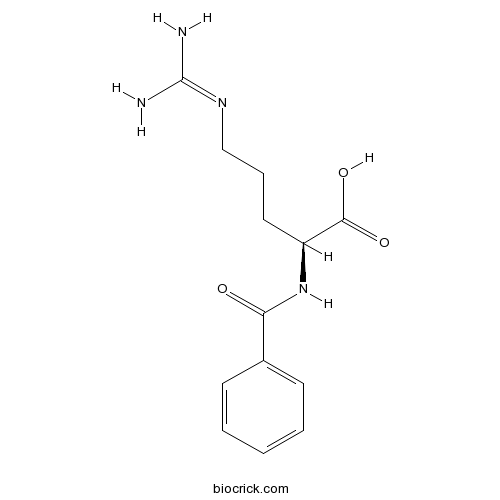
| Formula | C13H18N4O3 | M.Wt | 278.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-benzamido-5-(diaminomethylideneamino)pentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)NC(CCCN=C(N)N)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RSYYQCDERUOEFI-JTQLQIEISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H18N4O3/c14-13(15)16-8-4-7-10(12(19)20)17-11(18)9-5-2-1-3-6-9/h1-3,5-6,10H,4,7-8H2,(H,17,18)(H,19,20)(H4,14,15,16)/t10-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Bz-Arg-OH Dilution Calculator

Bz-Arg-OH Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5932 mL | 17.9662 mL | 35.9324 mL | 71.8649 mL | 89.8311 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7186 mL | 3.5932 mL | 7.1865 mL | 14.373 mL | 17.9662 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3593 mL | 1.7966 mL | 3.5932 mL | 7.1865 mL | 8.9831 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0719 mL | 0.3593 mL | 0.7186 mL | 1.4373 mL | 1.7966 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0359 mL | 0.1797 mL | 0.3593 mL | 0.7186 mL | 0.8983 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bz-Arg-OH
- Tripelennamine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4523
CAS No.:154-69-8
- Primulaverin
Catalog No.:BCC8235
CAS No.:154-61-0
- Primverin
Catalog No.:BCC8238
CAS No.:154-60-9
- 1,5-Anhydro-D-glucitol
Catalog No.:BCN2234
CAS No.:154-58-5
- Thioguanine
Catalog No.:BCC2220
CAS No.:154-42-7
- Catechin
Catalog No.:BCN1688
CAS No.:154-23-4
- Lincomycin
Catalog No.:BCC9010
CAS No.:154-21-2
- 2-Deoxy-D-glucose
Catalog No.:BCC4048
CAS No.:154-17-6
- ANQ 11125
Catalog No.:BCC6359
CAS No.:153966-48-4
- p-Hydroxyphenethyl vanillate
Catalog No.:BCN7555
CAS No.:1539303-03-1
- NBOH-2C-CN hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8025
CAS No.:1539266-32-4
- Boc-Gln-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3383
CAS No.:15387-45-8
- Carmustine
Catalog No.:BCC5244
CAS No.:154-93-8
- Ipecoside
Catalog No.:BCN8301
CAS No.:15401-60-2
- Berberrubine
Catalog No.:BCN2651
CAS No.:15401-69-1
- Marimastat
Catalog No.:BCC2118
CAS No.:154039-60-8
- Fuscaxanthone C
Catalog No.:BCN3885
CAS No.:15404-76-9
- Isonormangostin
Catalog No.:BCN1687
CAS No.:15404-80-5
- 3-(Bromomethyl)-2-cyclopropyl-4-(4'-fluorophenyl)quinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8591
CAS No.:154057-56-4
- ((2-cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinolin-3-yl)methyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide
Catalog No.:BCC8373
CAS No.:154057-58-6
- 2-(3-Methoxypropyl)-4-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-thieno[3,2-e][1,2]thiazine-6-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
Catalog No.:BCC8480
CAS No.:154127-41-0
- 4-Hydroxy-2-(3-methoxypropyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-thieno[3,2-e][1,2]thiazine-6-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide
Catalog No.:BCC8707
CAS No.:154127-42-1
- PD 144418 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC7429
CAS No.:154130-99-1
- DMAB-anabaseine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7301
CAS No.:154149-38-9
Real-Time Imaging of Protease Action on Substrates Covalently Immobilised to Polymer Supports.[Pubmed:19779571]
Adv Synth Catal. 2007 Jun;349(8-9):1321-1326.
We report for the first time single bead spatially resolved activity measurements of solid-phase biocatalytic systems followed in real-time. Trypsin cleavage of Bz-Arg-OH and subtilisin cleavage of Z-Gly-Gly-Leu-OH each liberate a free amino group on aminocoumarin covalently immobilised to PEGA(1900) beads [a co-polymer of poly(ethylene glycol) with molecular mass of 1900 cross-linked with acrylamide]. This restores fluorescence which is imaged in optical sections by two-photon microscopy. For trypsin cleavage, fluorescence is restricted initially to surface regions, with more than 1 hour needed before reaction is fully underway in the bead centre, presumably reflecting slow enzyme diffusion. In contrast, for subtilisin cleavage fluorescence develops throughout the bead more quickly.
Protease-catalyzed tripeptide (RGD) synthesis.[Pubmed:10689065]
Enzyme Microb Technol. 2000 Feb 1;26(2-4):108-114.
The tripeptide Bz-Arg-Gly-Asp(-OMe)-OH was synthesized by enzymatic method. Bz-Arg-Gly-OEt was synthesized by trypsin in ethanol containing 0.1 M Tris/HCl buffer (pH 8.0), and then H-Asp(-OMe)(2) was incorporated into the Bz-Arg-Gly-OEt using chymopapain in 0.25M CHES/NaOH buffer (pH = 9.0, EDTA 10 mM). The yield of Bz-Arg-Gly-OEt and Bz-Arg-Gly-Asp(-OMe)-OH were 80% and 70% using 1M Bz-Arg-OEt and 0.5M Bz-Arg-Gly-OEt, respectively. For Bz-Arg-Gly-OEt synthesis reaction at high concentrations of the substrates, the buffer content in ethanol was a key factor to determine the optimal reaction condition. In Bz-Arg-Gly-Asp(-OMe)-OH synthesis reaction, the yield was low in organic solvent due to various side products such as Bz-Arg-OH, Bz-Arg-Gly-OH, and Bz-Arg-Gly-Asp(-OMe)-Asp(-OMe)-OH, suggesting that chymopapain has a very broad substrate specificity of the S(1) site. The Bz-Arg-Gly-Asp(-OMe)-OH synthesis rate and its yield were dramatically elevated and the side reactions were reduced using only the CHES/NaOH buffer (pH = 9.0, EDTA 10 mM) as a reaction media. The final product Bz-Arg-Gly-Asp(-OMe)-OH was identified to be formed via C-terminal hydrolysis of Bz-Arg-Gly-Asp(-OMe)(2) after the nucleophile, H-Asp(-OMe)(2), was added.
Anhydrotrypsin: new features in ligand interactions revealed by affinity chromatography and thionine replacement.[Pubmed:16873]
J Biochem. 1977 Mar;81(3):647-56.
Anhydrotrypsin was isolated in high purity from the product of base elimination from phenylmethanesulfonyl-trypsin, by a single operation of affinity chromatography. The adsorbent used for the chromatography was an agarose derivative coupled with peptides containing C-terminal arginine residues. As the affinity of the adsorbent for anhydrotrypsin was high compared with that for trypsin, purification of the enzyme derivative was easily achieved without the prior inactivation of trypsin which had been regenerated during the elimination reaction. Comparative studies of the ligand interaction specificities with anhydrotrypsin and trypsin confirmed the stronger interaction of the former protein with product-type ligands such as Bz-Arg-OH. No marked differences were observed between them in affinities toward substrate-type ligands such as Bz-Arg-NH2. The higher affinity of anhydrotrypsin was found to be limited to product-type ligands of L-configuration, i.e., the protein displayed an ability to discriminate the L-ligand from its optical isomer. THE PKa value for the ionization form of anhydrotrypsin responsible for the interaction with Bz-Arg-OH was estimated to be 7.60+/-0907


