EDTACAS# 60-00-4 |
- Bivalirudin Trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC1421
CAS No.:128270-60-0
- Dabigatran ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC1512
CAS No.:429658-95-7
- 5-R-Rivaroxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1313
CAS No.:865479-71-6
- Dabigatran etexilate mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1511
CAS No.:872728-81-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 60-00-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6049 | Appearance | Powder |
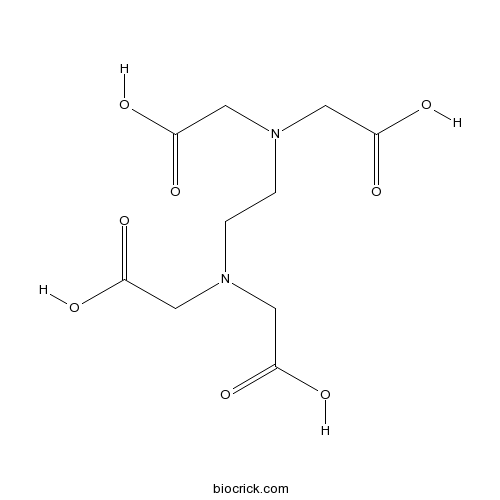
| Formula | C10H16N2O8 | M.Wt | 292.24 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[2-[bis(carboxymethyl)amino]ethyl-(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(CN(CC(=O)O)CC(=O)O)N(CC(=O)O)CC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H16N2O8/c13-7(14)3-11(4-8(15)16)1-2-12(5-9(17)18)6-10(19)20/h1-6H2,(H,13,14)(H,15,16)(H,17,18)(H,19,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Chelating agent; sequesters di- and trivalent metal ions. |

EDTA Dilution Calculator

EDTA Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4218 mL | 17.1092 mL | 34.2185 mL | 68.4369 mL | 85.5461 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6844 mL | 3.4218 mL | 6.8437 mL | 13.6874 mL | 17.1092 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3422 mL | 1.7109 mL | 3.4218 mL | 6.8437 mL | 8.5546 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0684 mL | 0.3422 mL | 0.6844 mL | 1.3687 mL | 1.7109 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0342 mL | 0.1711 mL | 0.3422 mL | 0.6844 mL | 0.8555 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tagitinin A
Catalog No.:BCN4102
CAS No.:59979-61-2
- Tagitinin F
Catalog No.:BCN4101
CAS No.:59979-57-6
- Carlinoside
Catalog No.:BCN2853
CAS No.:59952-97-5
- Malotilate
Catalog No.:BCC1196
CAS No.:59937-28-9
- 3',4'-dihydro-3'-hydroxy-Xanthyletin
Catalog No.:BCN3680
CAS No.:5993-18-0
- Vicriviroc maleate
Catalog No.:BCC2038
CAS No.:599179-03-0
- Vindesine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC8266
CAS No.:59917-39-4
- HPI 1
Catalog No.:BCC3938
CAS No.:599150-20-6
- Vicenin -3
Catalog No.:BCN3014
CAS No.:59914-91-9
- 3-Hydroxy-8,9-methylenedioxypterocarpene
Catalog No.:BCN1407
CAS No.:59901-98-3
- Sulfasalazine
Catalog No.:BCC2545
CAS No.:599-79-1
- 3,3'-Sulfonyldianiline
Catalog No.:BCC8595
CAS No.:599-61-1
- Guanethidine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC3789
CAS No.:60-02-6
- H-Tyr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3123
CAS No.:60-18-4
- Acetylcholine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2197
CAS No.:60-31-1
- (6-)ε-Aminocaproic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4888
CAS No.:60-32-2
- Linoleic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3821
CAS No.:60-33-3
- Acetamide
Catalog No.:BCN4114
CAS No.:60-35-5
- Acetyl-Strophanthidin
Catalog No.:BCC8113
CAS No.:60-38-8
- Tetracycline
Catalog No.:BCC9176
CAS No.:60-54-8
- Methimazole
Catalog No.:BCC3812
CAS No.:60-56-0
- Veratramine
Catalog No.:BCN2965
CAS No.:60-70-8
- Antipyrine
Catalog No.:BCC8834
CAS No.:60-80-0
- Phlorizin
Catalog No.:BCN4126
CAS No.:60-81-1
EDTA application on agricultural soils affects microelement uptake of plants.[Pubmed:28327292]
Sci Total Environ. 2017 Jan 15;577:166-173.
Chelates such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) enter soils via various sources but their effect on agricultural crops is mostly unknown. Sources of EDTA include industry, households, sewage water and agricultural practices. In a field experiment EDTA was applied in its free form at different rates (0, 150, 550, 1050kgha(-1)) to study its translocation in the soil profile and to evaluate its effect on yield and mineral composition of the cultivated crop, both in the year of application (oilseed rape) and in the following year (winter wheat). The results indicate that EDTA was translocated from the soil surface to deeper soil layers in the time-frame of the experiment. EDTA was still detectable in the rooting zone 19months after application, indicating its persistence in the soil. Only the highest EDTA rate (1050kgha(-1)) reduced vegetative growth of oilseed rape until stem elongation, but seed yield was not affected by EDTA application. EDTA application changed the mineral composition of plants. Higher phosphorus (P), sulphur (S), iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn) and lower cadmium (Cd) concentrations were determined in the seeds of oilseed rape. No yield effects of residual EDTA were observed for the following crop, winter wheat, but the Cd content in seeds was still lower in plots where EDTA had been applied in the previous year. Data show that EDTA application affects the mineral uptake of cultivated crops under field conditions.
Interactions between the Tetrasodium Salts of EDTA and 1-Hydroxyethane 1,1-Diphosphonic Acid with Sodium Hypochlorite Irrigants.[Pubmed:28342478]
J Endod. 2017 Apr;43(4):657-661.
INTRODUCTION: A clinically useful all-in-one endodontic irrigant with combined proteolytic and decalcifying properties is still elusive. In this study, the chemical effects of dissolving the tetrasodium salts of 1-hydroxyethane 1,1-diphosphonic acid (Na4HEDP) or Na4EDTA directly in sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) irrigants in polypropylene syringes were assessed during the course of 1 hour. METHODS: The solubility of the salts in water was determined. Their compatibility with 1% and 5% NaOCl was measured by iodometric titration and in a calcium complexation experiment by using a Ca(2+)-selective electrode. RESULTS: The salts dissolved within 1 minute. The dissolution maximum of Na4HEDP in water (wt/total wt) was 44.6% +/- 1.6%. The corresponding dissolution maximum of Na4EDTA was 38.2% +/- 0.8%. Na4HEDP at 18% in 5% NaOCl caused a mere loss of 16% of the initially available chlorine during 1 hour. In contrast, a corresponding mixture between NaOCl and the Na4EDTA salt caused 95% reduction in available chlorine after 1 minute. Mixtures of 3% Na4EDTA with 1% NaOCl were more stable, but only for 30 minutes. Na4HEDP lost 24% of its calcium complexation capacity after 60 minutes. The corresponding loss for Na4EDTA was 34%. CONCLUSIONS: The compatibility and solubility of particulate Na4HEDP with/in NaOCl solutions are such that these components can be mixed and used for up to 1 hour. In contrast, short-term compatibility of the Na4EDTA salt with NaOCl solutions was considerably lower, decreasing at higher concentrations of either compound. Especially for Na4HEDP but also for Na4EDTA, the NaOCl had little effect on calcium complexation.
Hypertension in dialysis patients: a consensus document by the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine (EURECA-m) working group of the European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) and the Hypertension and the Kidney working group of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH).[Pubmed:28340239]
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 Apr 1;32(4):620-640.
In patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) treated with haemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, hypertension is common and often poorly controlled. Blood pressure (BP) recordings obtained before or after haemodialysis display a J- or U-shaped association with cardiovascular events and survival, but this most likely reflects the low accuracy of these measurements and the peculiar haemodynamic setting related to dialysis treatment. Elevated BP detected by home or ambulatory BP monitoring is clearly associated with shorter survival. Sodium and volume excess is the prominent mechanism of hypertension in dialysis patients, but other pathways, such as arterial stiffness, activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone and sympathetic nervous systems, endothelial dysfunction, sleep apnoea and the use of erythropoietin-stimulating agents may also be involved. Non-pharmacologic interventions targeting sodium and volume excess are fundamental for hypertension control in this population. If BP remains elevated after appropriate treatment of sodium and volume excess, the use of antihypertensive agents is necessary. Drug treatment in the dialysis population should take into consideration the patient's comorbidities and specific characteristics of each agent, such as dialysability. This document is an overview of the diagnosis, epidemiology, pathogenesis and treatment of hypertension in patients on dialysis, aiming to offer the renal physician practical recommendations based on current knowledge and expert opinion and to highlight areas for future research.
Mortality risk disparities in children receiving chronic renal replacement therapy for the treatment of end-stage renal disease across Europe: an ESPN-ERA/EDTA registry analysis.[Pubmed:28336050]
Lancet. 2017 May 27;389(10084):2128-2137.
BACKGROUND: We explored the variation in country mortality rates in the paediatric population receiving renal replacement therapy across Europe, and estimated how much of this variation could be explained by patient-level and country-level factors. METHODS: In this registry analysis, we extracted patient data from the European Society for Paediatric Nephrology/European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ESPN/ERA-EDTA) Registry for 32 European countries. We included incident patients younger than 19 years receiving renal replacement therapy. Adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) and the explained variation were modelled for patient-level and country-level factors with multilevel Cox regression. The primary outcome studied was all-cause mortality while on renal replacement therapy. FINDINGS: Between Jan 1, 2000, and Dec 31, 2013, the overall 5 year renal replacement therapy mortality rate was 15.8 deaths per 1000 patient-years (IQR 6.4-16.4). France had a mortality rate (9.2) of more than 3 SDs better, and Russia (35.2), Poland (39.9), Romania (47.4), and Bulgaria (68.6) had mortality rates more than 3 SDs worse than the European average. Public health expenditure was inversely associated with mortality risk (per SD increase, aHR 0.69, 95% CI 0.52-0.91) and explained 67% of the variation in renal replacement therapy mortality rates between countries. Child mortality rates showed a significant association with renal replacement therapy mortality, albeit mediated by macroeconomics (eg, neonatal mortality reduced from 1.31 [95% CI 1.13-1.53], p=0.0005, to 1.21 [0.97-1.51], p=0.10). After accounting for country distributions of patient age, the variation in renal replacement therapy mortality rates between countries increased by 21%. INTERPRETATION: Substantial international variation exists in paediatric renal replacement therapy mortality rates across Europe, most of which was explained by disparities in public health expenditure, which seems to limit the availability and quality of paediatric renal care. Differences between countries in their ability to accept and treat the youngest patients, who are the most complex and costly to treat, form an important source of disparity within this population. Our findings can be used by policy makers and health-care providers to explore potential strategies to help reduce these health disparities. FUNDING: ERA-EDTA and ESPN.


