Tagitinin ACAS# 59979-61-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 59979-61-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 181254 | Appearance | Cryst. |
| Formula | C19H28O7 | M.Wt | 368.4 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
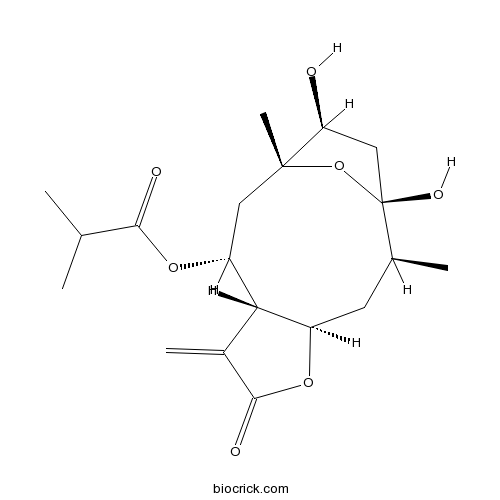
| SMILES | CC1CC2C(C(CC3(C(CC1(O3)O)O)C)OC(=O)C(C)C)C(=C)C(=O)O2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HREHFPZHVCNOMQ-XNNFIIJVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H28O7/c1-9(2)16(21)25-13-7-18(5)14(20)8-19(23,26-18)10(3)6-12-15(13)11(4)17(22)24-12/h9-10,12-15,20,23H,4,6-8H2,1-3,5H3/t10-,12+,13+,14-,15-,18+,19+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Tagitinin A is a plant insecticidal compound. 2. Tagitinin A has phytotoxic activity, it shows significant inhibition of wheat coleoptile growth, seed germination, and the growth of STS and weeds. 3. Tagitinin A is a PPARα/γ dual agonist , it exerts anti-diabetic effect through PPARγ pathway. |
| Targets | PPAR | Antifection |

Tagitinin A Dilution Calculator

Tagitinin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7144 mL | 13.5722 mL | 27.1444 mL | 54.2888 mL | 67.861 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5429 mL | 2.7144 mL | 5.4289 mL | 10.8578 mL | 13.5722 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2714 mL | 1.3572 mL | 2.7144 mL | 5.4289 mL | 6.7861 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0543 mL | 0.2714 mL | 0.5429 mL | 1.0858 mL | 1.3572 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0271 mL | 0.1357 mL | 0.2714 mL | 0.5429 mL | 0.6786 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tagitinin F
Catalog No.:BCN4101
CAS No.:59979-57-6
- Carlinoside
Catalog No.:BCN2853
CAS No.:59952-97-5
- Malotilate
Catalog No.:BCC1196
CAS No.:59937-28-9
- 3',4'-dihydro-3'-hydroxy-Xanthyletin
Catalog No.:BCN3680
CAS No.:5993-18-0
- Vicriviroc maleate
Catalog No.:BCC2038
CAS No.:599179-03-0
- Vindesine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC8266
CAS No.:59917-39-4
- HPI 1
Catalog No.:BCC3938
CAS No.:599150-20-6
- Vicenin -3
Catalog No.:BCN3014
CAS No.:59914-91-9
- 3-Hydroxy-8,9-methylenedioxypterocarpene
Catalog No.:BCN1407
CAS No.:59901-98-3
- Sulfasalazine
Catalog No.:BCC2545
CAS No.:599-79-1
- 3,3'-Sulfonyldianiline
Catalog No.:BCC8595
CAS No.:599-61-1
- Medicagenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3893
CAS No.:599-07-5
- EDTA
Catalog No.:BCC7493
CAS No.:60-00-4
- Guanethidine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC3789
CAS No.:60-02-6
- H-Tyr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3123
CAS No.:60-18-4
- Acetylcholine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2197
CAS No.:60-31-1
- (6-)ε-Aminocaproic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4888
CAS No.:60-32-2
- Linoleic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3821
CAS No.:60-33-3
- Acetamide
Catalog No.:BCN4114
CAS No.:60-35-5
- Acetyl-Strophanthidin
Catalog No.:BCC8113
CAS No.:60-38-8
- Tetracycline
Catalog No.:BCC9176
CAS No.:60-54-8
- Methimazole
Catalog No.:BCC3812
CAS No.:60-56-0
- Veratramine
Catalog No.:BCN2965
CAS No.:60-70-8
- Antipyrine
Catalog No.:BCC8834
CAS No.:60-80-0
Phytotoxins from Tithonia diversifolia.[Pubmed:25879678]
J Nat Prod. 2015 May 22;78(5):1083-92.
Tithonia diversifolia (Mexican sunflower) is a dominant plant of the Asteraceae family, which suggests it produces allelochemicals that interfere with the development of surrounding plants. The study described herein was conducted to identify the compounds that have phytotoxic activity in T. diversifolia extracts. Ethyl acetate extracts of the leaves, stems, and roots showed significant inhibition of wheat coleoptile growth, and the leaf extract had similar inhibitory effects to a commercial herbicide. Fourteen compounds, 12 of which were sesquiterpene lactones, have been isolated. Two sesquiterpene lactones are reported for the first time and were isolated as an inseparable mixture of 8beta-O-(2-methylbutyroyl)tirotundin (4) and 8beta-O-(isovaleroyl)tirotundin (5). Their structures were determined by spectroscopic analysis, including NMR techniques and mass spectrometry. The sesquiterpene lactones 1beta-methoxydiversifolin (6), Tagitinin A (7), and tagitinin C (8) were the major products identified. These compounds were active on etiolated wheat coleoptiles, seed germination, and the growth of STS and weeds. The phytotoxic activity shown by these sesquiterpene lactones indicates that they are the compounds responsible for the activity exhibited by the initial extracts.
Extracts from Field Margin Weeds Provide Economically Viable and Environmentally Benign Pest Control Compared to Synthetic Pesticides.[Pubmed:26599609]
PLoS One. 2015 Nov 23;10(11):e0143530.
Plants with pesticidal properties have been investigated for decades as alternatives to synthetics, but most progress has been shown in the laboratory. Consequently, research on pesticidal plants is failing to address gaps in our knowledge that constrain their uptake. Some of these gaps are their evaluation of their efficacy under field conditions, their economic viability and impact on beneficial organisms. Extracts made from four abundant weed species found in northern Tanzania, Tithonia diversifolia, Tephrosia vogelii, Vernonia amygdalina and Lippia javanica offered effective control of key pest species on common bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris) that was comparable to the pyrethroid synthetic, Karate. The plant pesticide treatments had significantly lower effects on natural enemies (lady beetles and spiders). Plant pesticide treatments were more cost effective to use than the synthetic pesticide where the marginal rate of return for the synthetic was no different from the untreated control, around 4USD/ha, compared to a rate of return of around 5.50USD/ha for plant pesticide treatments. Chemical analysis confirmed the presence of known insecticidal compounds in water extracts of T. vogelii (the rotenoid deguelin) and T. diversifolia (the sesquiterpene lactone Tagitinin A). Sesquiterpene lactones and the saponin vernonioside C were also identified in organic extracts of V. amygdalina but only the saponin was recorded in water extracts which are similar to those used in the field trial. Pesticidal plants were better able to facilitate ecosystem services whilst effectively managing pests. The labour costs of collecting and processing abundant plants near farm land were less than the cost of purchasing synthetic pesticides.
Sesquiterpene lactones from Tithonia diversifolia act as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists.[Pubmed:22424975]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012 Apr 15;22(8):2954-8.
Tithonia diversifolia is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine treating diabetes, hepatitis, and hepatocarcinoma but its molecular mechanism is not fully understood. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) alpha and gamma are members of nuclear receptor superfamily. Their agonists are prescribed as antihyperlipidemic and antihyperglycemic drugs now. In this study, sesquiterpene lactones, tirotundin and Tagitinin A, were isolated from T. diversifolia and evaluated for their activity against PPARs by the transient transfection reporter assay. Tirotundin and Tagitinin A transactivated PPARgamma dependent promoters including PPRE (PPARgamma response element), SHP, and ABCA1 gene promoters in dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, the fluorescence polarization competitive binding assay showed that tirotundin (IC(50)=27 muM) and Tagitinin A (IC(50)=55 muM) enhanced PPARgamma transactivation activity by directly binding to PPARgamma ligand binding domain. Additionally, they stimulated the transactivation of PPARalpha dependent SULT2A1 gene promoter by 2.3-fold of vehicle effect at 10 muM. These results highly indicated that tirotundin and Tagitinin A are the active components of T. diversifolia to exert anti-diabetic effect through PPARgamma pathway. Moreover, these sesquiterpene lactones behaved as PPARalpha/gamma dual agonists so they might be useful as the potential herbal treatment for diabetes.
Evaluation of extracts and oils of tick-repellent plants from Sweden.[Pubmed:16336298]
Med Vet Entomol. 2005 Dec;19(4):345-52.
Abstract. Leaves of Myrica gale Linnaeus (Myricaceae), Rhododendron tomentosum (Stokes) H. Harmaja (formerly Ledum palustre Linnaeus: Ericaceae) and Artemisia absinthium Linnaeus (Asteraceae) were extracted with organic solvents of different polarities and the essential oils of leaves were obtained by steam distillation. The extracts or oils were tested in the laboratory for repellency against host-seeking nymphs of Ixodes ricinus Linnaeus (Acari: Ixodidae). Rhododendron tomentosum oil, 10%, diluted in acetone, exhibited 95% repellency; R. tomentosum and A. absinthium extracts in ethyl acetate, > 70% repellency; A. absinthium extract in hexane, approximately 62% repellency; and M. gale oil, 10%, approximately 50% repellency on I. ricinus nymphs. Compounds in the leaf extracts or in the oils were collected by solid phase microextraction (SPME) and identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and/or MS. Characteristic volatiles detected from oil or extract of M. gale were the monoterpenes 1,8-cineole, alpha-terpineol, 4-terpineol and thujenol; and of R. tomentosum myrcene and palustrol. Characteristic volatiles from leaf extracts of A. absinthium were sabinene, oxygenated monoterpenes, e.g. thujenol and linalool, and geranyl acetate. Each plant species synthesized numerous volatiles known to exhibit acaricidal, insecticidal, 'pesticidal' and/or arthropod repellent properties. These plants may be useful sources of chemicals for the control of arthropods of medical, veterinary or agricultural importance.


